“非线性系统”的版本间的差异
| 第1行: | 第1行: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
在数学及科学中,'''非线性系统 Nonlinear System'''是一种输出的变化与输入的变化不成比例的系统<ref>{{Cite news|url=https://news.mit.edu/2010/explained-linear-0226|title=Explained: Linear and nonlinear systems|work=MIT News|access-date=2018-06-30}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.birmingham.ac.uk/research/activity/mathematics/applied-maths/nonlinear-systems.aspx|title=Nonlinear systems, Applied Mathematics - University of Birmingham|website=www.birmingham.ac.uk|language=en-gb|access-date=2018-06-30}}</ref>。大多数系统在本质上是非线性的,因而非线性问题引起了工程师、,<ref>{{Citation|date=2007|pages=181–276|publisher=Springer Berlin Heidelberg|language=en|doi=10.1007/978-3-540-34153-6_7|isbn=9783540341529|title = The Nonlinear Universe|series = The Frontiers Collection|chapter = Nonlinear Biology}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|last=Korenberg|first=Michael J.|last2=Hunter|first2=Ian W.|date=March 1996|title=The identification of nonlinear biological systems: Volterra kernel approaches|journal=Annals of Biomedical Engineering|language=en|volume=24|issue=2|pages=250–268|doi=10.1007/bf02667354|issn=0090-6964}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|last=Mosconi|first=Francesco|last2=Julou|first2=Thomas|last3=Desprat|first3=Nicolas|last4=Sinha|first4=Deepak Kumar|last5=Allemand|first5=Jean-François|last6=Vincent Croquette|last7=Bensimon|first7=David|date=2008|title=Some nonlinear challenges in biology|url=http://stacks.iop.org/0951-7715/21/i=8/a=T03|journal=Nonlinearity|language=en|volume=21|issue=8|pages=T131|doi=10.1088/0951-7715/21/8/T03|issn=0951-7715|bibcode=2008Nonli..21..131M}}</ref>生物学家、物理学家<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Gintautas|first1=V.|title=Resonant forcing of nonlinear systems of differential equations|journal=Chaos|date=2008|volume=18|issue=3|pages=033118|doi=10.1063/1.2964200|pmid=19045456|arxiv=0803.2252|bibcode=2008Chaos..18c3118G}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|last1=Stephenson|first1=C.|last2=et.|first2=al.|title=Topological properties of a self-assembled electrical network via ab initio calculation|journal=Sci. Rep.|volume=7|pages=41621|date=2017|doi=10.1038/srep41621|pmid=28155863|pmc=5290745|bibcode=2017NatSR...741621S}}</ref>、数学家和许多其他科学家的兴趣。描述变量随时间变化的非线性动力系统与较之简单得多的线性系统相比,可能显得混沌、不可预测或违反直觉<ref>{{cite book|last1=de Canete|first1=Javier, Cipriano Galindo, and Inmaculada Garcia-Moral|title=System Engineering and Automation: An Interactive Educational Approach|date=2011|publisher=Springer|location=Berlin|isbn=978-3642202292|page=46|url=https://books.google.com/?id=h8rCQYXGGY8C&pg=PA46&lpg=PA46&dq=most+systems+are+inherently+nonlinear+in+nature#v=onepage&q=most%20systems%20are%20inherently%20nonlinear%20in%20nature&f=false|accessdate=20 January 2018}}</ref>。 | 在数学及科学中,'''非线性系统 Nonlinear System'''是一种输出的变化与输入的变化不成比例的系统<ref>{{Cite news|url=https://news.mit.edu/2010/explained-linear-0226|title=Explained: Linear and nonlinear systems|work=MIT News|access-date=2018-06-30}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.birmingham.ac.uk/research/activity/mathematics/applied-maths/nonlinear-systems.aspx|title=Nonlinear systems, Applied Mathematics - University of Birmingham|website=www.birmingham.ac.uk|language=en-gb|access-date=2018-06-30}}</ref>。大多数系统在本质上是非线性的,因而非线性问题引起了工程师、,<ref>{{Citation|date=2007|pages=181–276|publisher=Springer Berlin Heidelberg|language=en|doi=10.1007/978-3-540-34153-6_7|isbn=9783540341529|title = The Nonlinear Universe|series = The Frontiers Collection|chapter = Nonlinear Biology}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|last=Korenberg|first=Michael J.|last2=Hunter|first2=Ian W.|date=March 1996|title=The identification of nonlinear biological systems: Volterra kernel approaches|journal=Annals of Biomedical Engineering|language=en|volume=24|issue=2|pages=250–268|doi=10.1007/bf02667354|issn=0090-6964}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|last=Mosconi|first=Francesco|last2=Julou|first2=Thomas|last3=Desprat|first3=Nicolas|last4=Sinha|first4=Deepak Kumar|last5=Allemand|first5=Jean-François|last6=Vincent Croquette|last7=Bensimon|first7=David|date=2008|title=Some nonlinear challenges in biology|url=http://stacks.iop.org/0951-7715/21/i=8/a=T03|journal=Nonlinearity|language=en|volume=21|issue=8|pages=T131|doi=10.1088/0951-7715/21/8/T03|issn=0951-7715|bibcode=2008Nonli..21..131M}}</ref>生物学家、物理学家<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Gintautas|first1=V.|title=Resonant forcing of nonlinear systems of differential equations|journal=Chaos|date=2008|volume=18|issue=3|pages=033118|doi=10.1063/1.2964200|pmid=19045456|arxiv=0803.2252|bibcode=2008Chaos..18c3118G}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|last1=Stephenson|first1=C.|last2=et.|first2=al.|title=Topological properties of a self-assembled electrical network via ab initio calculation|journal=Sci. Rep.|volume=7|pages=41621|date=2017|doi=10.1038/srep41621|pmid=28155863|pmc=5290745|bibcode=2017NatSR...741621S}}</ref>、数学家和许多其他科学家的兴趣。描述变量随时间变化的非线性动力系统与较之简单得多的线性系统相比,可能显得混沌、不可预测或违反直觉<ref>{{cite book|last1=de Canete|first1=Javier, Cipriano Galindo, and Inmaculada Garcia-Moral|title=System Engineering and Automation: An Interactive Educational Approach|date=2011|publisher=Springer|location=Berlin|isbn=978-3642202292|page=46|url=https://books.google.com/?id=h8rCQYXGGY8C&pg=PA46&lpg=PA46&dq=most+systems+are+inherently+nonlinear+in+nature#v=onepage&q=most%20systems%20are%20inherently%20nonlinear%20in%20nature&f=false|accessdate=20 January 2018}}</ref>。 | ||
| 第22行: | 第13行: | ||
——'''斯塔尼斯拉夫·乌拉姆 Stanislaw Ulam''' | ——'''斯塔尼斯拉夫·乌拉姆 Stanislaw Ulam''' | ||
| − | == | + | ==定义== |
在数学中,[[线性映射]](或线性函数)<math>f(x)</math>满足以下两个性质: | 在数学中,[[线性映射]](或线性函数)<math>f(x)</math>满足以下两个性质: | ||
| 第100行: | 第91行: | ||
*'''[[摄动理论]] Perturbation Theory'''(也可应用于代数方程) | *'''[[摄动理论]] Perturbation Theory'''(也可应用于代数方程) | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===偏微分方程=== | ===偏微分方程=== | ||
| 第112行: | 第99行: | ||
其他方法包括检查特征线法及前面所述研究常微分方程的方法。 | 其他方法包括检查特征线法及前面所述研究常微分方程的方法。 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| 第123行: | 第107行: | ||
[[File:PendulumLinearizations.png|thumb|图二:单摆的线性化|right|200px]] | [[File:PendulumLinearizations.png|thumb|图二:单摆的线性化|right|200px]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
一个经典的被广泛研究的非线性问题是重力影响下的单摆的动力学。利用'''[[拉格朗日力学]] Lagrangian Mechanics''',可以证明单摆的运动<ref>[http://www.damtp.cam.ac.uk/user/tong/dynamics.html David Tong: Lectures on Classical Dynamics]</ref>可以用无量纲的非线性方程 | 一个经典的被广泛研究的非线性问题是重力影响下的单摆的动力学。利用'''[[拉格朗日力学]] Lagrangian Mechanics''',可以证明单摆的运动<ref>[http://www.damtp.cam.ac.uk/user/tong/dynamics.html David Tong: Lectures on Classical Dynamics]</ref>可以用无量纲的非线性方程 | ||
| 第154行: | 第133行: | ||
这相当于一个自由落体问题。把这样线性化的结果合在一起看,就能得到有关摆的运动的非常有用的图像,如右图所示。利用其他方法寻找(精确的)'''[[相图]] Phase Portrait'''和估计周期。 | 这相当于一个自由落体问题。把这样线性化的结果合在一起看,就能得到有关摆的运动的非常有用的图像,如右图所示。利用其他方法寻找(精确的)'''[[相图]] Phase Portrait'''和估计周期。 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==非线性动力学行为的类型== | ==非线性动力学行为的类型== | ||
| 第174行: | 第149行: | ||
==非线性方程的例子== | ==非线性方程的例子== | ||
| − | {{ | + | |
| + | {{Div col|colwidth=25em}} | ||
*[[代数黎卡提方程]] Algebraic Riccati equation | *[[代数黎卡提方程]] Algebraic Riccati equation | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*[[球杆系统]] Ball and beam system | *[[球杆系统]] Ball and beam system | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*最佳策略的[[贝尔曼方程]] Bellman equation for optimal policy | *最佳策略的[[贝尔曼方程]] Bellman equation for optimal policy | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*[[玻尔兹曼方程 ]] Boltzmann equation | *[[玻尔兹曼方程 ]] Boltzmann equation | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*[[科尔布鲁克方程]] Colebrook equation | *[[科尔布鲁克方程]] Colebrook equation | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*[[广义相对论]] General relativity | *[[广义相对论]] General relativity | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*[[金兹堡-朗道方程]] Ginzburg–Landau theory | *[[金兹堡-朗道方程]] Ginzburg–Landau theory | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*[[石森方程]] Ishimori equation | *[[石森方程]] Ishimori equation | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*[[卡东穆塞夫-彼得韦亚斯维利方程]] Kadomtsev–Petviashvili equation | *[[卡东穆塞夫-彼得韦亚斯维利方程]] Kadomtsev–Petviashvili equation | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*[[KDV方程]] Korteweg–de Vries equation | *[[KDV方程]] Korteweg–de Vries equation | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*[[朗道-利夫希兹-吉尔伯特方程]] Landau–Lifshitz–Gilbert equation | *[[朗道-利夫希兹-吉尔伯特方程]] Landau–Lifshitz–Gilbert equation | ||
| − | |||
*[[林纳德方程]] Liénard equation | *[[林纳德方程]] Liénard equation | ||
| − | |||
*[[流体力学]] 的 [[纳维-斯托克斯]] 方程Navier–Stokes equations of fluid dynamics | *[[流体力学]] 的 [[纳维-斯托克斯]] 方程Navier–Stokes equations of fluid dynamics | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*[[非线性光学]] Nonlinear optics | *[[非线性光学]] Nonlinear optics | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*[[非线性薛定谔方程]] Nonlinear Schrödinger equation | *[[非线性薛定谔方程]] Nonlinear Schrödinger equation | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*[[功率流研究]] Power-flow study | *[[功率流研究]] Power-flow study | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*未饱和层水流的[[理查氏方程]]Richards equation for unsaturated water flow | *未饱和层水流的[[理查氏方程]]Richards equation for unsaturated water flow | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*[[自平衡独轮车]] Self-balancing unicycle | *[[自平衡独轮车]] Self-balancing unicycle | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*[[正弦-戈尔登方程]] Sine-Gordon equation | *[[正弦-戈尔登方程]] Sine-Gordon equation | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*[[范德波尔振荡器]] Van der Pol oscillator | *[[范德波尔振荡器]] Van der Pol oscillator | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*[[弗拉索夫方程]] Vlasov equation | *[[弗拉索夫方程]] Vlasov equation | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{{Div col end}} | {{Div col end}} | ||
==参见== | ==参见== | ||
| − | |||
*[[亚历山大·李亚普诺夫]] Aleksandr Mikhailovich Lyapunov | *[[亚历山大·李亚普诺夫]] Aleksandr Mikhailovich Lyapunov | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*[[动态系统]] Dynamical system | *[[动态系统]] Dynamical system | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*[[反馈]] Feedback | *[[反馈]] Feedback | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*[[初始条件]] Initial condition | *[[初始条件]] Initial condition | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*[[相互作用]] Interaction | *[[相互作用]] Interaction | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*[[线性系统]] Linear system | *[[线性系统]] Linear system | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*[[模式耦合]] Mode coupling | *[[模式耦合]] Mode coupling | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*[[矢量孤子]] Vector soliton | *[[矢量孤子]] Vector soliton | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*[[沃尔泰拉级数]] Volterra series | *[[沃尔泰拉级数]] Volterra series | ||
| 第303行: | 第220行: | ||
==进一步阅读== | ==进一步阅读== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{{Refbegin|35em}} | {{Refbegin|35em}} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*{{cite book | *{{cite book | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| author= [[Diederich Hinrichsen]] and Anthony J. Pritchard | | author= [[Diederich Hinrichsen]] and Anthony J. Pritchard | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| year= 2005 | | year= 2005 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| title= Mathematical Systems Theory I - Modelling, State Space Analysis, Stability and Robustness | | title= Mathematical Systems Theory I - Modelling, State Space Analysis, Stability and Robustness | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| publisher= Springer Verlag | | publisher= Springer Verlag | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| isbn=9783540441250 | | isbn=9783540441250 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
}} | }} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*{{cite book | *{{cite book | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| last= Jordan | | last= Jordan | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| first= D. W. | | first= D. W. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| last2= Smith | | last2= Smith | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| first2= P. | | first2= P. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| year= 2007 | | year= 2007 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| edition= fourth | | edition= fourth | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| title= Nonlinear Ordinary Differential Equations | | title= Nonlinear Ordinary Differential Equations | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| publisher= Oxford University Press | | publisher= Oxford University Press | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| isbn= 978-0-19-920824-1 | | isbn= 978-0-19-920824-1 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
}} | }} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*{{cite book | *{{cite book | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| last= Khalil | | last= Khalil | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| first= Hassan K. | | first= Hassan K. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| year= 2001 | | year= 2001 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| title= Nonlinear Systems | | title= Nonlinear Systems | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| publisher= Prentice Hall | | publisher= Prentice Hall | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| isbn= 978-0-13-067389-3 | | isbn= 978-0-13-067389-3 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
}} | }} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*{{cite book | *{{cite book | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| last= Kreyszig | | last= Kreyszig | ||
| − | |||
| first= Erwin | | first= Erwin | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| authorlink= Erwin Kreyszig | | authorlink= Erwin Kreyszig | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| year= 1998 | | year= 1998 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| title= Advanced Engineering Mathematics | | title= Advanced Engineering Mathematics | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| url= https://archive.org/details/advancedengineer0008krey | | url= https://archive.org/details/advancedengineer0008krey | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| url-access= registration | | url-access= registration | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| publisher= Wiley | | publisher= Wiley | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| isbn= 978-0-471-15496-9 | | isbn= 978-0-471-15496-9 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
}} | }} | ||
| − | |||
*{{cite book | *{{cite book | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| last= Sontag | | last= Sontag | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| first= Eduardo | | first= Eduardo | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| authorlink= Eduardo D. Sontag | | authorlink= Eduardo D. Sontag | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| year= 1998 | | year= 1998 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| title= Mathematical Control Theory: Deterministic Finite Dimensional Systems. Second Edition | | title= Mathematical Control Theory: Deterministic Finite Dimensional Systems. Second Edition | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| publisher= Springer | | publisher= Springer | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| isbn= 978-0-387-98489-6 | | isbn= 978-0-387-98489-6 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
}} | }} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{{Refend}} | {{Refend}} | ||
| − | + | ==外部链接== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*[http://www.dodccrp.org/ Command and Control Research Program (CCRP)] | *[http://www.dodccrp.org/ Command and Control Research Program (CCRP)] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*[http://necsi.edu/guide/concepts/linearnonlinear.html New England Complex Systems Institute: Concepts in Complex Systems] | *[http://necsi.edu/guide/concepts/linearnonlinear.html New England Complex Systems Institute: Concepts in Complex Systems] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*[http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/mathematics/18-353j-nonlinear-dynamics-i-chaos-fall-2012/ Nonlinear Dynamics I: Chaos] at [http://ocw.mit.edu/OcwWeb/index.htm MIT's OpenCourseWare] | *[http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/mathematics/18-353j-nonlinear-dynamics-i-chaos-fall-2012/ Nonlinear Dynamics I: Chaos] at [http://ocw.mit.edu/OcwWeb/index.htm MIT's OpenCourseWare] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*[http://www.hedengren.net/research/models.htm Nonlinear Model Library]{{snd}} (in [[MATLAB]]) a Database of Physical Systems | *[http://www.hedengren.net/research/models.htm Nonlinear Model Library]{{snd}} (in [[MATLAB]]) a Database of Physical Systems | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*[http://cnls.lanl.gov/ The Center for Nonlinear Studies at Los Alamos National Laboratory] | *[http://cnls.lanl.gov/ The Center for Nonlinear Studies at Los Alamos National Laboratory] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{{Systems science}} | {{Systems science}} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{{Differential equations topics}} | {{Differential equations topics}} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{{Authority control}} | {{Authority control}} | ||
2020年7月23日 (四) 19:53的版本
在数学及科学中,非线性系统 Nonlinear System是一种输出的变化与输入的变化不成比例的系统[1][2]。大多数系统在本质上是非线性的,因而非线性问题引起了工程师、,[3][4][5]生物学家、物理学家[6][7]、数学家和许多其他科学家的兴趣。描述变量随时间变化的非线性动力系统与较之简单得多的线性系统相比,可能显得混沌、不可预测或违反直觉[8]。
通常,非线性系统的行为在数学上被描述为一组非线性的联立方程组,其中未知数(或微分方程中的未知函数)作为一个高于一次的多项式变量出现,或者作为一个非一次多项式函数的参数出现。
换句话说,在非线性方程系统中,待解的方程不能被写成未知变量或函数的线性组合。无论方程中是否有已知的线性函数,系统都可以被定义为非线性。特别是当一个微分方程的未知函数及其导数是线性的,即使其他变量是非线性的,也称该方程是线性的。
由于非线性动力学方程难以求解,通常用线性方程来近似非线性系统(线性化 Linearization)。这种方法对于一定范围的输入和某些精度要求下的效果不错,但一些有趣的现象如孤子 Soliton、混沌 Chaos和奇异性 Singularity在线性化后被隐藏[9]。因此,非线性系统的动态行为在某些方面可能看起来违反直觉、不可预测、甚至混沌。尽管这种混沌行为可能感觉很像随机行为,但它实际上并不是随机的。例如,天气的某些方面被认为是混沌的,其系统某部分的微小扰动就会产生复杂的整体影响。这种非线性是目前技术无法进行精确长期预测的原因之一。
有些作者用非线性科学这一术语来研究非线性系统。这一术语引起了其他人的争议:
“使用‘非线性科学’这样的术语,就如同把动物学里大部分对象称作‘非大象动物’研究一样可笑。”[10] ——斯塔尼斯拉夫·乌拉姆 Stanislaw Ulam
定义
在数学中,线性映射(或线性函数)[math]\displaystyle{ f(x) }[/math]满足以下两个性质:
- 可加性 Additivity(叠加性 Superposition principle): [math]\displaystyle{ \textstyle f(x + y) = f(x) + f(y); }[/math]
- 齐次性 Homogeneity: [math]\displaystyle{ \textstyle f(\alpha x) = \alpha f(x). }[/math]
当α是有理数或实数,且[math]\displaystyle{ f(x) }[/math]是连续函数时,由可加性可以推出齐次性。但当α是复数时,可加性不能导出齐次性。例如,反线性映射是可加的,但不是齐次的。可加性和齐次性条件经常组合,称为叠加原理:
[math]\displaystyle{ f(\alpha x + \beta y) = \alpha f(x) + \beta f(y) }[/math]
对一个写成
[math]\displaystyle{ f(x) = C }[/math]
的方程,若 [math]\displaystyle{ f (x) }[/math] 是线性映射(如上定义) ,则称其为线性的 Linear,否则称为非线性的 Nonlinear。若[math]\displaystyle{ C = 0 }[/math],该方程称为是齐次的。
定义 [math]\displaystyle{ f(x) = C }[/math] 是非常具有一般性的,因为 [math]\displaystyle{ x }[/math] 可以是任意合理的数学对象(数字、向量、函数等),函数 [math]\displaystyle{ f(x) }[/math] 实际上可以是任意映射,包括有相关约束(如给定边界值)的积分或微分。若 [math]\displaystyle{ f(x) }[/math] 包含对 [math]\displaystyle{ x }[/math] 的微分运算,则该方程为微分方程。
相关概念辨析
线性Linear、非线性Nonlinear、亚线性 Sublinear、超线性 Superlinear:描述量与量之间的一种变化关系,例如[math]\displaystyle{ y=a+b*x^n }[/math],其中[math]\displaystyle{ n\gt 1 }[/math]。当[math]\displaystyle{ n=1 }[/math]时,表示为线性关系;[math]\displaystyle{ n\neq 1 }[/math]时,表示为非线性关系;当[math]\displaystyle{ 0\lt n\lt 1 }[/math]时,表示为亚线性关系;当[math]\displaystyle{ n\gt 1 }[/math]时,表示为超线性关系。
亚线性与超线性属于非线性变化关系范畴。当两个变量之间存在亚线性关系时,其典型特性是因变量的变化速率会随着自变量的增大而减小,即其一阶导数会随着自变量的增大而减小;两个变量之间存在超线性关系时,其典型特性是因变量的变化速率会随着自变量的增大而增大,即其一阶导数会随着自变量的增大而增大。
在线性系统中,整体等于部分和,描述线性系统的方程满足叠加原理,作用的总和正好等于每一部分作用相加的代数和,这意味着每一部分作用都是独立的、互不相关的;而在普遍存在的非线性系统中,作用的总和不等于每一部分作用相加的代数和,因为系统内部要素之间存在着复杂的非线性相互作用。
非线性代数方程
非线性代数方程 Algebraic Equation,又称多项式方程 Polynomial Equation,由某多项式(次数大于1)等于零定义。例如:
[math]\displaystyle{ x^2 + x - 1 = 0\,. }[/math]
对于一个单一的多项式方程,求根算法 Root-finding Algorithms可用于其求解(即找到满足该方程的变量的值集)。而代数方程组则相对复杂,其研究是现代数学的较难分支——代数几何 Algebraic Geometry领域的动力之一。甚至很难判断一个给定的代数系统是否有复数解(见希尔伯特零点定律 Hilbert's Nullstellensatz)。不过,对于具有有限个复数解的系统的多项式方程组,我们现在已经有了充分的理解,并且找到了有效的求解方法[11]。
非线性递推关系
非线性递归关系中,序列的连续项被定义为其前项的非线性函数。非线性递归关系的例子有 logistic 映射和定义各种霍夫斯塔特序列 Hofstadter Sequences 的关系。非线性离散模型代表了一类广泛的非线性递归关系,包括 NARMAX(外部输入非线性自回归移动平均)模型和相关的非线性系统辨识和分析程序[12]。这些方法可用于研究时域、频域和时空域的广泛复杂非线性行为。
非线性微分方程
若一个微分方程组不是线性系统,则称其为非线性的。涉及非线性微分方程的问题非常多样,对不同问题的解决或分析方法也不相同。非线性微分方程的例子有流体力学中的 纳维-斯托克斯方程 Navier-Stokes Equations和生物学中的洛特卡-沃尔泰拉方程 Lotka-Volterra Equations。
非线性问题最大的困难之一是通常不可能将已知的解组合成新的解。例如,在线性问题中,可以根据叠加原理以一族线性独立的解构造通解。一个很好的例子是带有狄利克雷边界条件 Dirichlet Boundary Conditions的一维热传导问题,其解可以写成(随时间变化)不同频率的正弦波的线性组合,这使得解非常灵活。而对非线性方程,通常可以找到几个非常特殊的解,但是此时叠加原理不适用,故无法构造新的解。
常微分方程
一阶常微分方程,尤其是自治(自主)方程,通常可以用分离变量法 Separation of Variables来精确求解。例如,非线性方程
[math]\displaystyle{ \frac{d u}{d x} = -u^2 }[/math]
将 [math]\displaystyle{ u=\frac{1}{x+C} }[/math] 作为一般解(也有特解 u = 0,对应于 C 趋于无穷时的一般解的极限)。该方程是非线性的,因为它可以改写成
[math]\displaystyle{ \frac{du}{d x} + u^2=0 }[/math]
方程的左边不是 u 及其导数的线性函数。注意,若将 u2 项替换为u,该问题将变为线性的(指数衰减 Exponential Decay问题)。
二阶和高阶常微分方程(更一般地说,非线性方程组)很少能产生封闭解,而隐式解和非初等函数积分形式的解较为常见。
非线性常微分方程定性分析的常用方法包括:
- 检查是否有任意守恒量 Conserved Quantities(特别是在哈密顿系统 Hamiltonian System中)
- 检查是否有类似守恒量的耗散量(见李亚普诺夫函数 Lyapunov Function)
- 基于[[泰勒展开] Taylor Expansion的线性化
- 将变量进行代换以便更好的进行研究
- 分岔理论 Bifurcation Theory
- 摄动理论 Perturbation Theory(也可应用于代数方程)
偏微分方程
研究非线性偏微分方程最常用的基本方法是变量代换(或转换问题),使变换后的问题更简单(甚至可能变为线性的)。有时可以将此类方程转化成一或多个常微分方程(如同分离变量法所示),此时不论得到的常微分方程是否可解,但是对研究问题总是有用的。
另一个流体力学和热力学中常见的策略(虽然不是数学上的)是利用尺度分析 Scale Analysis将一特定边界条件下简化一般自然方程。例如,在描述圆管内一维层流的瞬态时,非线性的纳维-斯托克斯方程 Navier-Stokes 可以简化为一个线性的偏微分方程; 尺度分析提供了层流和一维流动的条件,也产生了简化的方程。
其他方法包括检查特征线法及前面所述研究常微分方程的方法。
单摆
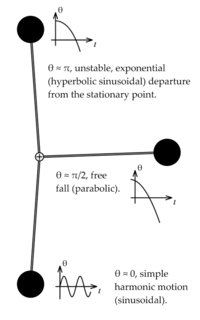
一个经典的被广泛研究的非线性问题是重力影响下的单摆的动力学。利用拉格朗日力学 Lagrangian Mechanics,可以证明单摆的运动[13]可以用无量纲的非线性方程
- [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{d^2 \theta}{d t^2} + \sin(\theta) = 0 }[/math]
描述,其中重力指向“下”,[math]\displaystyle{ \theta }[/math] 是摆与其静止位置形成的角度,如右图所示。“解”这个方程的方法之一是用 [math]\displaystyle{ d\theta/dt }[/math] 作为积分因子 Integrating Factor,最终得
[math]\displaystyle{ \int{\frac{d \theta}{\sqrt{C_0 + 2 \cos(\theta)}}} = t + C_1 }[/math]
这是一个含椭圆积分 Elliptic Integral的隐式解。这个“解”通常没什么用,因为这个解的大部分性质都隐藏在非初等函数积分中(除非[math]\displaystyle{ C_0 = 2 }[/math],否则是非初等的)。
另一种解决这个问题的方法是利用泰勒展开将任意非线性项(此时为正弦函数项)在某些点进行线性化。例如,在[math]\displaystyle{ \theta = 0 }[/math] 的点附近线性化(称为小角度近似)为
- [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{d^2 \theta}{d t^2} + \theta = 0 }[/math]
因为 [math]\displaystyle{ \theta \approx 0 }[/math] 时,有 [math]\displaystyle{ \sin(\theta) \approx \theta }[/math]。这是一个简谐振子 Simple Harmonic Oscillator ,对应于摆在其路径底部附近的摆动。另一种线性化方法是在 [math]\displaystyle{ \theta = \pi }[/math]附近线性化,对应于运动到最高点的摆:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{d^2 \theta}{d t^2} + \pi - \theta = 0 }[/math]
因为 [math]\displaystyle{ \theta \approx \pi }[/math] 时,有 [math]\displaystyle{ \sin(\theta) \approx \pi - \theta }[/math]。这个问题的解含双曲正弦曲线;注意到不同于小角度近似,它是不稳定的,这意味着 [math]\displaystyle{ |\theta| }[/math] 通常会无限增长(但解也有可能是有界的)。这就解释了摆在最高点达到平衡的困难,此时实际上是一种不稳定的状态。
一个更有趣的线性化可能是在 [math]\displaystyle{ \theta = \pi/2 }[/math]附近,此时 [math]\displaystyle{ \sin(\theta) \approx 1 }[/math]:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{d^2 \theta}{d t^2} + 1 = 0. }[/math]
这相当于一个自由落体问题。把这样线性化的结果合在一起看,就能得到有关摆的运动的非常有用的图像,如右图所示。利用其他方法寻找(精确的)相图 Phase Portrait和估计周期。
非线性动力学行为的类型
- 振幅死亡 Amplitude Death——系统内的某振荡因系统的自回馈或与其他系统的某种相互作用而停止的现象
- 混沌 Chaos——系统内的值无法无限期地预测到遥远的未来;波动是非周期性的
- 多稳态 Multistability——两或多个稳态的存在
- 孤波 Solitons——自增强的孤立波
- 极限环 Limit Cycles——吸引不稳定不动点的渐近周期轨道
- 自激振荡 Self-oscillations——开放耗散物理系统中的反馈振荡
非线性方程的例子
- 代数黎卡提方程 Algebraic Riccati equation
- 球杆系统 Ball and beam system
- 最佳策略的贝尔曼方程 Bellman equation for optimal policy
- 玻尔兹曼方程 Boltzmann equation
- 科尔布鲁克方程 Colebrook equation
- 广义相对论 General relativity
- 金兹堡-朗道方程 Ginzburg–Landau theory
- 石森方程 Ishimori equation
- 卡东穆塞夫-彼得韦亚斯维利方程 Kadomtsev–Petviashvili equation
- KDV方程 Korteweg–de Vries equation
- 朗道-利夫希兹-吉尔伯特方程 Landau–Lifshitz–Gilbert equation
- 林纳德方程 Liénard equation
- 非线性光学 Nonlinear optics
- 非线性薛定谔方程 Nonlinear Schrödinger equation
- 功率流研究 Power-flow study
- 未饱和层水流的理查氏方程Richards equation for unsaturated water flow
- 自平衡独轮车 Self-balancing unicycle
- 正弦-戈尔登方程 Sine-Gordon equation
- 范德波尔振荡器 Van der Pol oscillator
- 弗拉索夫方程 Vlasov equation
参见
- 亚历山大·李亚普诺夫 Aleksandr Mikhailovich Lyapunov
- 动态系统 Dynamical system
- 反馈 Feedback
- 初始条件 Initial condition
- 相互作用 Interaction
- 线性系统 Linear system
- 模式耦合 Mode coupling
- 矢量孤子 Vector soliton
- 沃尔泰拉级数 Volterra series
References 参考资料
- ↑ "Explained: Linear and nonlinear systems". MIT News. Retrieved 2018-06-30.
- ↑ "Nonlinear systems, Applied Mathematics - University of Birmingham". www.birmingham.ac.uk (in British English). Retrieved 2018-06-30.
- ↑ "Nonlinear Biology", The Nonlinear Universe, The Frontiers Collection (in English), Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2007, pp. 181–276, doi:10.1007/978-3-540-34153-6_7, ISBN 9783540341529
- ↑ Korenberg, Michael J.; Hunter, Ian W. (March 1996). "The identification of nonlinear biological systems: Volterra kernel approaches". Annals of Biomedical Engineering (in English). 24 (2): 250–268. doi:10.1007/bf02667354. ISSN 0090-6964.
- ↑ Mosconi, Francesco; Julou, Thomas; Desprat, Nicolas; Sinha, Deepak Kumar; Allemand, Jean-François; Vincent Croquette; Bensimon, David (2008). "Some nonlinear challenges in biology". Nonlinearity (in English). 21 (8): T131. Bibcode:2008Nonli..21..131M. doi:10.1088/0951-7715/21/8/T03. ISSN 0951-7715.
- ↑ Gintautas, V. (2008). "Resonant forcing of nonlinear systems of differential equations". Chaos. 18 (3): 033118. arXiv:0803.2252. Bibcode:2008Chaos..18c3118G. doi:10.1063/1.2964200. PMID 19045456.
- ↑ Stephenson, C.; et., al. (2017). "Topological properties of a self-assembled electrical network via ab initio calculation". Sci. Rep. 7: 41621. Bibcode:2017NatSR...741621S. doi:10.1038/srep41621. PMC 5290745. PMID 28155863.
- ↑ de Canete, Javier, Cipriano Galindo, and Inmaculada Garcia-Moral (2011). System Engineering and Automation: An Interactive Educational Approach. Berlin: Springer. p. 46. ISBN 978-3642202292. https://books.google.com/?id=h8rCQYXGGY8C&pg=PA46&lpg=PA46&dq=most+systems+are+inherently+nonlinear+in+nature#v=onepage&q=most%20systems%20are%20inherently%20nonlinear%20in%20nature&f=false. Retrieved 20 January 2018.
- ↑ Nonlinear Dynamics I: Chaos -{zh-cn:互联网档案馆; zh-tw:網際網路檔案館; zh-hk:互聯網檔案館;}-的存檔,存档日期2008-02-12. at MIT's OpenCourseWare
- ↑ Campbell, David K. (25 November 2004). "Nonlinear physics: Fresh breather". Nature (in English). 432 (7016): 455–456. Bibcode:2004Natur.432..455C. doi:10.1038/432455a. ISSN 0028-0836. PMID 15565139.
- ↑ Lazard, D. (2009). "Thirty years of Polynomial System Solving, and now?". Journal of Symbolic Computation. 44 (3): 222–231. doi:10.1016/j.jsc.2008.03.004.
- ↑ Billings S.A. "Nonlinear System Identification: NARMAX Methods in the Time, Frequency, and Spatio-Temporal Domains". Wiley, 2013
- ↑ David Tong: Lectures on Classical Dynamics
进一步阅读
- Diederich Hinrichsen and Anthony J. Pritchard (2005). Mathematical Systems Theory I - Modelling, State Space Analysis, Stability and Robustness. Springer Verlag. ISBN 9783540441250.
- Jordan, D. W.; Smith, P. (2007). Nonlinear Ordinary Differential Equations (fourth ed.). Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-920824-1.
- Khalil, Hassan K. (2001). Nonlinear Systems. Prentice Hall. ISBN 978-0-13-067389-3.
- Kreyszig, Erwin (1998). Advanced Engineering Mathematics. Wiley. ISBN 978-0-471-15496-9. https://archive.org/details/advancedengineer0008krey.
- Sontag, Eduardo (1998). Mathematical Control Theory: Deterministic Finite Dimensional Systems. Second Edition. Springer. ISBN 978-0-387-98489-6.
外部链接
- Command and Control Research Program (CCRP)
- New England Complex Systems Institute: Concepts in Complex Systems
- Nonlinear Dynamics I: Chaos at MIT's OpenCourseWare
- Nonlinear Model Library模板:Snd (in MATLAB) a Database of Physical Systems
- The Center for Nonlinear Studies at Los Alamos National Laboratory
模板:Systems science 模板:Differential equations topics
编者推荐
非线性动力学和混沌理论是系统发展的,从一阶微分方程及其分岔开始,然后是相平面分析,极限环和它们的分岔,最终得到Lorenz方程,混沌,迭代映射,周期倍增,重整化,分形和奇怪吸引。
此系列课程由斯蒂文·斯特罗加茨 Steven H. Strogatz主持,内容包括机械振动,激光,生物节律,超导电路,昆虫爆发,化学振荡器,遗传控制系统,混沌水轮,甚至是使用混乱发送秘密信息的技术。在每种情况下,科学背景都在初级阶段进行解释,并与数学理论紧密结合。
Category:Dynamical systems
类别: 动力系统
Category:Concepts in physics
分类: 物理概念
This page was moved from wikipedia:en:Nonlinear system. Its edit history can be viewed at 非线性系统/edithistory