“鸟群算法”的版本间的差异
| 第1行: | 第1行: | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:Boids OpenGL example.webm|thumb|在[[[ OpenGL ]]中创建的 Boids 示例]] | |
| − | |||
| − | {{for| | + | '''鸟群算法 Boids'''是模拟鸟类群集行为的人工生命项目,由'''克雷格·雷诺兹 Craig Reynolds'''于1986年开发。该模型基于常用于计算机动画或计算机辅助设计的计算机三维几何。他关于这个主题的论文发表在1987年的 ACM SIGGRAPH(美国计算机协会计算机图形专业组组织的计算机图形学顶级年度会议)会议记录上。<ref>{{Cite book | last1=Reynolds| first1=Craig| title=Flocks, herds and schools: A distributed behavioral model.| year=1987 |journal=SIGGRAPH '87: Proceedings of the 14th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques| publisher=Association for Computing Machinery | pages=25–34| isbn=978-0-89791-227-3| doi=10.1145/37401.37406| citeseerx=10.1.1.103.7187}}</ref>“ boid”是“ bird-oid object”的缩写,指一个类鸟对象。<ref>{{Cite journal| last1=Banks| first1=Alec| last2=Vincent| first2=Jonathan| last3=Anyakoha| first3=Chukwudi | title=A review of particle swarm optimization. Part I: background and development|date=July 2007| journal=Natural Computing| volume=6| issue=4| pages=467–484| doi=10.1007/s11047-007-9049-5| citeseerx=10.1.1.605.5879}}</ref>恰巧,“boid”也是纽约都市方言中“bird”的发音。 |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{{multiple image|direction=vertical|image1=Rule separation.gif|caption1=Separation|image2=Rule alignment.gif|caption2=Alignment|image3=Rule cohesion.gif|caption3=Cohesion|header=Rules applied in simple Boids}} | {{multiple image|direction=vertical|image1=Rule separation.gif|caption1=Separation|image2=Rule alignment.gif|caption2=Alignment|image3=Rule cohesion.gif|caption3=Cohesion|header=Rules applied in simple Boids}} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | 与大多数人工生命模拟一样,Boids 是[[涌现 Emergent]]行为的一个例子; 也就是说,Boids 的复杂性来自于遵循一系列简单规则的个体代理(这里是 Boids)的相互作用。在最简单的Bolds 世界中适用的规则如下,其描述了鸟群中的个体如何根据周边同伴的位置和速度移动: | ||
* '''分离 Separation''': 移动以避开群体拥挤处 | * '''分离 Separation''': 移动以避开群体拥挤处 | ||
| 第218行: | 第16行: | ||
* '''靠近 Cohesion''': 朝群体的平均位置(质心)移动 | * '''靠近 Cohesion''': 朝群体的平均位置(质心)移动 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
每个 boid 个体都可以得知整体的几何参数,但群体要求其只对其周围某个小邻近范围作出反应。该邻近范围由一个距离(从该个体的中心算起)和一个角度(从其飞行方向算起)决定。此范围外的同伴不予考虑。该临近范围可以认为是一个有限知觉的模型(就像浑水中的鱼一样);但更恰当的想法可能是,其定义了鸟群影响了个体转向的区域范围。 | 每个 boid 个体都可以得知整体的几何参数,但群体要求其只对其周围某个小邻近范围作出反应。该邻近范围由一个距离(从该个体的中心算起)和一个角度(从其飞行方向算起)决定。此范围外的同伴不予考虑。该临近范围可以认为是一个有限知觉的模型(就像浑水中的鱼一样);但更恰当的想法可能是,其定义了鸟群影响了个体转向的区域范围。 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
可以添加更复杂的规则,如避障和寻找目标。 | 可以添加更复杂的规则,如避障和寻找目标。 | ||
| + | 该基本模型自雷诺兹提出以来,已用多种方法扩展。例如,Delgado-Mata <ref>{{cite journal|first1= Carlos | last1= Delgado-Mata|first2= Jesus Ibanez | last2= Martinez|first3= Simon | last3= Bee|first4= Rocio | last4= Ruiz-Rodarte|first5= Ruth | last5= Aylett|title= On the use of Virtual Animals with Artificial Fear in Virtual Environments | ||
| + | |journal= New Generation Computing|volume=25 |issue=2 |pages= 145–169|date=2007|doi= 10.1007/s00354-007-0009-5}}</ref>等人扩展基本模型以加入恐惧的影响。利过一种可用自由膨胀气体中的粒子模拟的信息素,动物间用嗅觉来传递情感。'''哈特曼 Hartman'''和'''贝内斯 Benes'''<ref>{{cite journal|first1= Christopher | last1= Hartman|first1= Christopher | last1= Hartman|first2= Bedr̆ich |last2= Benes̆|title= Autonomous boids|journal= Computer Animation and Virtual Worlds|volume=17 |issue=3–4 |pages= 199–206|date=July 2006|doi= 10.1002/cav.123}}</ref>为定位过程引入了一种补充力量,他们称之为领导权的更迭。这条决定了某只鸟成为领导者及试图逃跑的机会。 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Boids 的运动可以表现为混乱(分裂的群体和狂野的行为)或有序。意想不到的行为,比如群体分散和避开障碍后的团聚可以被认为是应急的。 | Boids 的运动可以表现为混乱(分裂的群体和狂野的行为)或有序。意想不到的行为,比如群体分散和避开障碍后的团聚可以被认为是应急的。 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Boids 框架通常用于计算机图形学,提供鸟群和其他生物(如鱼群)的逼真表现。例如,在1998年的电子游戏《'''半条命 Half-Life'''》中,游戏结束时Xen中出现的类似鸟类的飞行生物就使用了该框架(游戏文件中命名为“ boid”)。 | Boids 框架通常用于计算机图形学,提供鸟群和其他生物(如鱼群)的逼真表现。例如,在1998年的电子游戏《'''半条命 Half-Life'''》中,游戏结束时Xen中出现的类似鸟类的飞行生物就使用了该框架(游戏文件中命名为“ boid”)。 | ||
| + | Boids 模型可用于'''[[集群机器人]] Swarm Robotics'''中简单的无人地面车辆(UGV)<ref>{{cite conference |title= Design and analysis of Group Escape Behavior for distributed autonomous mobile robots |first1= Hongkyu |last1= Min |first2= Zhidong |last2= Wang |year= 2011 |conference= IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA)|doi= 10.1109/ICRA.2011.5980123 }}</ref> 或'''微型飞行器 Micro Aerial Vehicles'''(MAV)<ref>{{cite conference |title= Swarms of micro aerial vehicles stabilized under a visual relative localization |first1= Martin |last1= Saska |first2= Vakula |last2= Jan |first3= Preucil |last3= Libor |year= 2014 |conference= IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA)|doi= 10.1109/ICRA.2014.6907374 }}</ref>群体的直接控制和稳定。为了异质 UAV-UGV 群体的稳定性,Saska 等人将该模型用于板载相对定位。<ref>{{cite conference |title= Coordination and Navigation of Heterogeneous UAVs-UGVs Teams Localized by a Hawk-Eye Approach |first1= Martin |last1= Saska |first2= Vonasek |last2= Vojtech |first3= Krajnik |last3= Tomas |first4= Preucil |last4= Libor |year= 2012 |conference= IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS)|url=http://labe.felk.cvut.cz/~tkrajnik/ardrone/articles/formace.pdf}}</ref> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | | + | 在当时提出时,雷诺兹的方法相比于传统的计算机动画电影技术是一个巨大的进步。第一部利用了此模型的动画片是《'''史丹利和史黛拉: 破冰 Stanley and Stella in: Breaking The Ice'''》(1987),之后是'''蒂姆·伯顿 Tim Burton'''的故事片《'''蝙蝠侠归来 Batman Returns'''》(1992),电脑合成的蝙蝠群和成群的企鹅行进穿过'''哥谭市 Gotham City'''的街道。<ref>{{cite journal | url=http://lrss.fri.uni-lj.si/people/ilbajec/papers/ilb_ab09.pdf | last1=Lebar Bajec |first1= Iztok |first2= Frank H. |last2= Heppner | date=2009 | title=Organized flight in birds | journal=Animal Behaviour | volume = 78 | issue = 4 | pages = 777–789 | doi = 10.1016/j.anbehav.2009.07.007 }}</ref> |
| − | |||
| − | | date | + | Boids 模型已经被用于其他有趣应用。该系统已应用于互联网多频道广播电台的自动节目编排,.<ref>{{cite conference| title= DJ-boids: emergent collective behavior as multichannel radio station programming| first1 = Jesús | last1 = Ibáñez| first2 = Antonio F. | last2 = Gómez-Skarmeta| first3 = Josep | last3 = Blat| date = 2003| booktitle = Proceedings of the 8th international conference on Intelligent User Interfaces| pages = 248–250| doi= 10.1145/604045.604089}}</ref>以及可视化信息<ref>{{cite conference| title= Time-Varying Data Visualization Using Information Flocking Boids| last = Moere | first = A V| date= 2004| booktitle = Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Information Visualization| pages= 97–104| doi= 10.1109/INFVIS.2004.65}}</ref>和优化任务。<ref>{{cite journal|first1 = Zhihua | last1 = Cui|first2 = Zhongzhi | last2 = Shi|title= Boid particle swarm optimisation|journal= International Journal of Innovative Computing and Applications|volume=2 |issue=2 |pages= 77–85|date=2009|doi= 10.1504/IJICA.2009.031778}}</ref> |
| − | + | ==参见== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*[[Swarm intelligence]] 群体智能 | *[[Swarm intelligence]] 群体智能 | ||
| 第583行: | 第48行: | ||
| − | == | + | ==参考文献== |
{{Reflist}} | {{Reflist}} | ||
| 第589行: | 第54行: | ||
| − | == | + | ==外部链接== |
* [http://www.red3d.com/cwr/boids/ Craig Reynolds' Boids page] | * [http://www.red3d.com/cwr/boids/ Craig Reynolds' Boids page] | ||
| 第597行: | 第62行: | ||
* [https://gpolo.github.com/birdflocking JavaScript implementation] | * [https://gpolo.github.com/birdflocking JavaScript implementation] | ||
| − | *[https://lufemas.github.io/boid-ai-implementation/ JavaScript implementation with Phaser Framework] | + | * [https://lufemas.github.io/boid-ai-implementation/ JavaScript implementation with Phaser Framework] |
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20080205014305/http://www.navgen.com/3d_boids/ 3D Boids Simulation using OpenGL, used by the BBC's Natural History Unit] | * [https://web.archive.org/web/20080205014305/http://www.navgen.com/3d_boids/ 3D Boids Simulation using OpenGL, used by the BBC's Natural History Unit] | ||
| − | *[https://black-square.github.io/BirdFlock/ Live In-Browser 3D Simulation of Bird Flocking Behavior in Unity3D] – Open Source implementation for Windows, Linux and Mac | + | * [https://black-square.github.io/BirdFlock/ Live In-Browser 3D Simulation of Bird Flocking Behavior in Unity3D] – Open Source implementation for Windows, Linux and Mac |
* [https://github.com/piskvorky/PredatorPrey UNIX+Windows open source implementation in C++, using OpenGL and simulation controls] | * [https://github.com/piskvorky/PredatorPrey UNIX+Windows open source implementation in C++, using OpenGL and simulation controls] | ||
| 第607行: | 第72行: | ||
* [https://github.com/tofti/javafx-boids A java implementation using the javafx API] | * [https://github.com/tofti/javafx-boids A java implementation using the javafx API] | ||
| − | *GLSchool - part of [[XScreenSaver]] software | + | * GLSchool - part of [[XScreenSaver]] software |
| 第621行: | 第86行: | ||
本课程通过数个案例教会大家如何去动手搭建一个多主体仿真模型,以及如何利用NetLogo去实现。从生命游戏到人工鸟群,从模拟经济系统到病毒沿网络的传播,通过循序渐进的案例,该课程带你逐步走入NetLogo多主体建模的神奇世界。 | 本课程通过数个案例教会大家如何去动手搭建一个多主体仿真模型,以及如何利用NetLogo去实现。从生命游戏到人工鸟群,从模拟经济系统到病毒沿网络的传播,通过循序渐进的案例,该课程带你逐步走入NetLogo多主体建模的神奇世界。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
===[https://swarma.org/ 集智俱乐部]扩展阅读:[https://swarma.org/?p=16504 张江:乌合之众还是群智涌现?鸟群知道答案]=== | ===[https://swarma.org/ 集智俱乐部]扩展阅读:[https://swarma.org/?p=16504 张江:乌合之众还是群智涌现?鸟群知道答案]=== | ||
生命如何起源,智能如何涌现,因果如何反转,复杂谜题,引人深思。2019年7月13日,集智俱乐部创始人[[张江]]教授在混沌大学授课,详细解读了复杂系统中的混沌、涌现与进化,此文整理自课堂内容。 | 生命如何起源,智能如何涌现,因果如何反转,复杂谜题,引人深思。2019年7月13日,集智俱乐部创始人[[张江]]教授在混沌大学授课,详细解读了复杂系统中的混沌、涌现与进化,此文整理自课堂内容。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
===[https://v.qq.com/x/page/z13491sn7fy.html 动画片《Stanley and Stella in: Breaking the Ice (1987)》]=== | ===[https://v.qq.com/x/page/z13491sn7fy.html 动画片《Stanley and Stella in: Breaking the Ice (1987)》]=== | ||
| 第630行: | 第99行: | ||
Craig Reynolds 与 Symbolics Graphics 和 Whitney / Demos Production 的同事合作制作的利用 boids 模型的小短片,讲述了飞鸟与鱼相爱,鸟儿冲破冰面与鱼相见的故事。影片最早于87年在 SIGGRAPH 电子剧院展出。 | Craig Reynolds 与 Symbolics Graphics 和 Whitney / Demos Production 的同事合作制作的利用 boids 模型的小短片,讲述了飞鸟与鱼相爱,鸟儿冲破冰面与鱼相见的故事。影片最早于87年在 SIGGRAPH 电子剧院展出。 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:人工生命]] |
| + | [[Category:1986软件]] | ||
2020年8月3日 (一) 18:46的版本
鸟群算法 Boids是模拟鸟类群集行为的人工生命项目,由克雷格·雷诺兹 Craig Reynolds于1986年开发。该模型基于常用于计算机动画或计算机辅助设计的计算机三维几何。他关于这个主题的论文发表在1987年的 ACM SIGGRAPH(美国计算机协会计算机图形专业组组织的计算机图形学顶级年度会议)会议记录上。[1]“ boid”是“ bird-oid object”的缩写,指一个类鸟对象。[2]恰巧,“boid”也是纽约都市方言中“bird”的发音。
页面模板:Multiple image/styles.css没有内容。
与大多数人工生命模拟一样,Boids 是涌现 Emergent行为的一个例子; 也就是说,Boids 的复杂性来自于遵循一系列简单规则的个体代理(这里是 Boids)的相互作用。在最简单的Bolds 世界中适用的规则如下,其描述了鸟群中的个体如何根据周边同伴的位置和速度移动:
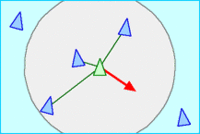
- 分离 Separation: 移动以避开群体拥挤处
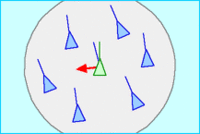
- 对齐 Alignment: 转向群体的平均航向
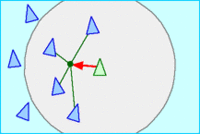
- 靠近 Cohesion: 朝群体的平均位置(质心)移动
每个 boid 个体都可以得知整体的几何参数,但群体要求其只对其周围某个小邻近范围作出反应。该邻近范围由一个距离(从该个体的中心算起)和一个角度(从其飞行方向算起)决定。此范围外的同伴不予考虑。该临近范围可以认为是一个有限知觉的模型(就像浑水中的鱼一样);但更恰当的想法可能是,其定义了鸟群影响了个体转向的区域范围。
可以添加更复杂的规则,如避障和寻找目标。
该基本模型自雷诺兹提出以来,已用多种方法扩展。例如,Delgado-Mata [3]等人扩展基本模型以加入恐惧的影响。利过一种可用自由膨胀气体中的粒子模拟的信息素,动物间用嗅觉来传递情感。哈特曼 Hartman和贝内斯 Benes[4]为定位过程引入了一种补充力量,他们称之为领导权的更迭。这条决定了某只鸟成为领导者及试图逃跑的机会。
Boids 的运动可以表现为混乱(分裂的群体和狂野的行为)或有序。意想不到的行为,比如群体分散和避开障碍后的团聚可以被认为是应急的。
Boids 框架通常用于计算机图形学,提供鸟群和其他生物(如鱼群)的逼真表现。例如,在1998年的电子游戏《半条命 Half-Life》中,游戏结束时Xen中出现的类似鸟类的飞行生物就使用了该框架(游戏文件中命名为“ boid”)。
Boids 模型可用于集群机器人 Swarm Robotics中简单的无人地面车辆(UGV)[5] 或微型飞行器 Micro Aerial Vehicles(MAV)[6]群体的直接控制和稳定。为了异质 UAV-UGV 群体的稳定性,Saska 等人将该模型用于板载相对定位。[7]
在当时提出时,雷诺兹的方法相比于传统的计算机动画电影技术是一个巨大的进步。第一部利用了此模型的动画片是《史丹利和史黛拉: 破冰 Stanley and Stella in: Breaking The Ice》(1987),之后是蒂姆·伯顿 Tim Burton的故事片《蝙蝠侠归来 Batman Returns》(1992),电脑合成的蝙蝠群和成群的企鹅行进穿过哥谭市 Gotham City的街道。[8]
Boids 模型已经被用于其他有趣应用。该系统已应用于互联网多频道广播电台的自动节目编排,.[9]以及可视化信息[10]和优化任务。[11]
参见
- Swarm intelligence 群体智能
- Collective cell migration 集体细胞迁移
参考文献
- ↑ Reynolds, Craig (1987). Flocks, herds and schools: A distributed behavioral model.. Association for Computing Machinery. pp. 25–34. doi:10.1145/37401.37406. ISBN 978-0-89791-227-3.
- ↑ Banks, Alec; Vincent, Jonathan; Anyakoha, Chukwudi (July 2007). "A review of particle swarm optimization. Part I: background and development". Natural Computing. 6 (4): 467–484. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.605.5879. doi:10.1007/s11047-007-9049-5.
- ↑ Delgado-Mata, Carlos; Martinez, Jesus Ibanez; Bee, Simon; Ruiz-Rodarte, Rocio; Aylett, Ruth (2007). "On the use of Virtual Animals with Artificial Fear in Virtual Environments". New Generation Computing. 25 (2): 145–169. doi:10.1007/s00354-007-0009-5.
- ↑ Hartman, Christopher; Benes̆, Bedr̆ich (July 2006). "Autonomous boids". Computer Animation and Virtual Worlds. 17 (3–4): 199–206. doi:10.1002/cav.123.
- ↑ Min, Hongkyu; Wang, Zhidong (2011). Design and analysis of Group Escape Behavior for distributed autonomous mobile robots. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). doi:10.1109/ICRA.2011.5980123.
- ↑ Saska, Martin; Jan, Vakula; Libor, Preucil (2014). Swarms of micro aerial vehicles stabilized under a visual relative localization. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). doi:10.1109/ICRA.2014.6907374.
- ↑ Saska, Martin; Vojtech, Vonasek; Tomas, Krajnik; Libor, Preucil (2012). Coordination and Navigation of Heterogeneous UAVs-UGVs Teams Localized by a Hawk-Eye Approach (PDF). IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS).
- ↑ Lebar Bajec, Iztok; Heppner, Frank H. (2009). "Organized flight in birds" (PDF). Animal Behaviour. 78 (4): 777–789. doi:10.1016/j.anbehav.2009.07.007.
- ↑ Ibáñez, Jesús; Gómez-Skarmeta, Antonio F.; Blat, Josep (2003). DJ-boids: emergent collective behavior as multichannel radio station programming. pp. 248–250. doi:10.1145/604045.604089.
{{cite conference}}: Unknown parameter|booktitle=ignored (help) - ↑ Moere, A V (2004). Time-Varying Data Visualization Using Information Flocking Boids. pp. 97–104. doi:10.1109/INFVIS.2004.65.
{{cite conference}}: Unknown parameter|booktitle=ignored (help) - ↑ Cui, Zhihua; Shi, Zhongzhi (2009). "Boid particle swarm optimisation". International Journal of Innovative Computing and Applications. 2 (2): 77–85. doi:10.1504/IJICA.2009.031778.
外部链接
- Live In-Browser 3D Simulation of Bird Flocking Behavior in Unity3D – Open Source implementation for Windows, Linux and Mac
- GLSchool - part of XScreenSaver software
模板:Collective animal behaviour
编者推荐
集智学园课程:透过人工鸟群Boid模型学习List的使用
讲师:张江(北师大系统科学学院教授、博士生导师,集智俱乐部、集智学园创始人。)
本课程通过数个案例教会大家如何去动手搭建一个多主体仿真模型,以及如何利用NetLogo去实现。从生命游戏到人工鸟群,从模拟经济系统到病毒沿网络的传播,通过循序渐进的案例,该课程带你逐步走入NetLogo多主体建模的神奇世界。
集智俱乐部扩展阅读:张江:乌合之众还是群智涌现?鸟群知道答案
生命如何起源,智能如何涌现,因果如何反转,复杂谜题,引人深思。2019年7月13日,集智俱乐部创始人张江教授在混沌大学授课,详细解读了复杂系统中的混沌、涌现与进化,此文整理自课堂内容。
动画片《Stanley and Stella in: Breaking the Ice (1987)》
Craig Reynolds 与 Symbolics Graphics 和 Whitney / Demos Production 的同事合作制作的利用 boids 模型的小短片,讲述了飞鸟与鱼相爱,鸟儿冲破冰面与鱼相见的故事。影片最早于87年在 SIGGRAPH 电子剧院展出。