“多稳态”的版本间的差异
| 第4行: | 第4行: | ||
In a [[dynamical system]], '''multistability''' is the property of having multiple [[Stability theory|stable equilibrium points]] in the [[vector space]] spanned by the states in the system. By mathematical necessity, there must also be unstable equilibrium points between the stable points. Points that are stable in some dimensions and unstable in others are termed unstable, as is the case with the first three [[Lagrangian points]]. | In a [[dynamical system]], '''multistability''' is the property of having multiple [[Stability theory|stable equilibrium points]] in the [[vector space]] spanned by the states in the system. By mathematical necessity, there must also be unstable equilibrium points between the stable points. Points that are stable in some dimensions and unstable in others are termed unstable, as is the case with the first three [[Lagrangian points]]. | ||
| − | + | 在[[动力系统]]中,多稳态是系统中的一种状态属性,即由该系统的状态所形成的向量空间中,存在多个稳定平衡点。根据数学上的必然性,在稳定点之间也一定存在不稳定的平衡点。 | |
| − | + | 与''L''<sub>1、''L''<sub>2</sub></sub>、''L''<sub>3</sub>前拉格朗日点一样,在某些维度上稳定而在其他维度上不稳定的点被称为不稳定点。 | |
| − | + | == 双稳态 == | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
双稳态是具有两个稳定平衡点的特殊情形。这是多重稳定性的最简单形式,可以发生在只有一个状态变量的系统中,因为它只需要一个一维空间来分隔两个点。 | 双稳态是具有两个稳定平衡点的特殊情形。这是多重稳定性的最简单形式,可以发生在只有一个状态变量的系统中,因为它只需要一个一维空间来分隔两个点。 | ||
| 第16行: | 第14行: | ||
| − | == | + | ==初始不稳定性== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | 在不稳定平衡点附近,任何系统对噪声、初始条件和系统参数都很敏感,这肯能会导致它向多个不同的方向发展。 | |
In economics and social sciences, path dependence gives rise to divergent directions of development. | In economics and social sciences, path dependence gives rise to divergent directions of development. | ||
| − | + | 在经济学和社会科学中,[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Path_dependence 路径依赖]导致了发展方向上的分歧。一些路径的依赖过程可以通过多稳态来充分描述:在到达稳态之前,对输入的初始状态很敏感,比如最初市场份额不稳定,随后可能会演变成多个可能的供应商之一的稳定垄断。 | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | == 多稳态知觉 == | |
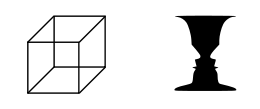
| − | + | [[Image:Multistability.svg.png|right|thumb|260px|模棱两可的图像]] | |
| − | |||
| − | + | 多稳态知觉是一种较少见的视知觉现象。多稳态知觉常被描述为在观看一图形时,会主观性的观察到图形无法预期的自发性改变,并且这改变会接续不断发生。 | |
| + | In vision science, [[multistable perception]] characterizes the wavering percepts that can be brought about by certain | ||
| + | visually ambiguous pattern such as the [[Necker cube]], [[monocular rivalry]] or [[binocular rivalry]]. | ||
| + | 当一个图形对人类的视觉系统来说,是具有歧义性时,就会引发多稳态知觉的现象。如一些知名的例子如奈克方块Necker cube、运动中探知结构(structure from motion)、单眼竞争(monocular rivalry)和双眼竞争binocular rivalry。但更为人所知的是暧昧图形(ambiguous image)。因为这些图形通常会在两种知觉状态之间相互交换,所以又称为双稳态知觉。通过横向抑制,其中一个图像在受到刺激时会抑制邻近图像的活动。<ref>{{cite journal | url = http://neuro.bcm.edu/eagleman/papers/Eagleman.NatureRevNeuro.Illusions.pdf | title = Visual Illusions and Neurobiology | last = Eagleman | first = David | journal = Nature Reviews Neuroscience | date = 2001 | volume = 2 | issue = 12 | pages = 920-926 | doi = 10.1038/35104092 | deadurl = yes | archiveurl = https://web.archive.org/web/20070927212714/http://neuro.bcm.edu/eagleman/papers/Eagleman.NatureRevNeuro.Illusions.pdf | archivedate = 2007-09-27 }}</ref> | ||
| − | == | + | ==外部链接== |
*[https://web.archive.org/web/20070928121528/http://www.icbm.de/komplsyst/9905.html Def of multistability from icbm.de] | *[https://web.archive.org/web/20070928121528/http://www.icbm.de/komplsyst/9905.html Def of multistability from icbm.de] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
2021年1月22日 (五) 16:47的版本
此词条暂由彩云小译翻译,翻译字数共232,未经人工整理和审校,带来阅读不便,请见谅。 此词条由舒寒初步翻译。
In a dynamical system, multistability is the property of having multiple stable equilibrium points in the vector space spanned by the states in the system. By mathematical necessity, there must also be unstable equilibrium points between the stable points. Points that are stable in some dimensions and unstable in others are termed unstable, as is the case with the first three Lagrangian points.
在动力系统中,多稳态是系统中的一种状态属性,即由该系统的状态所形成的向量空间中,存在多个稳定平衡点。根据数学上的必然性,在稳定点之间也一定存在不稳定的平衡点。
与L1、L2、L3前拉格朗日点一样,在某些维度上稳定而在其他维度上不稳定的点被称为不稳定点。
双稳态
双稳态是具有两个稳定平衡点的特殊情形。这是多重稳定性的最简单形式,可以发生在只有一个状态变量的系统中,因为它只需要一个一维空间来分隔两个点。
初始不稳定性
在不稳定平衡点附近,任何系统对噪声、初始条件和系统参数都很敏感,这肯能会导致它向多个不同的方向发展。
In economics and social sciences, path dependence gives rise to divergent directions of development.
在经济学和社会科学中,路径依赖导致了发展方向上的分歧。一些路径的依赖过程可以通过多稳态来充分描述:在到达稳态之前,对输入的初始状态很敏感,比如最初市场份额不稳定,随后可能会演变成多个可能的供应商之一的稳定垄断。
多稳态知觉
多稳态知觉是一种较少见的视知觉现象。多稳态知觉常被描述为在观看一图形时,会主观性的观察到图形无法预期的自发性改变,并且这改变会接续不断发生。
In vision science, multistable perception characterizes the wavering percepts that can be brought about by certain
visually ambiguous pattern such as the Necker cube, monocular rivalry or binocular rivalry.
当一个图形对人类的视觉系统来说,是具有歧义性时,就会引发多稳态知觉的现象。如一些知名的例子如奈克方块Necker cube、运动中探知结构(structure from motion)、单眼竞争(monocular rivalry)和双眼竞争binocular rivalry。但更为人所知的是暧昧图形(ambiguous image)。因为这些图形通常会在两种知觉状态之间相互交换,所以又称为双稳态知觉。通过横向抑制,其中一个图像在受到刺激时会抑制邻近图像的活动。[1]
外部链接
- ↑ Eagleman, David (2001). "Visual Illusions and Neurobiology" (PDF). Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 2 (12): 920–926. doi:10.1038/35104092. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-09-27.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (help)