“联合熵”的版本间的差异
Thingamabob(讨论 | 贡献) |
|||
| 第1行: | 第1行: | ||
此词条Jie翻译。由CecileLi初步审校。文中部分公式内容未正常显示,有“模板”点击打开后却没有内容,还有未显示去掉格式后的英文,不清楚是程序错误还是未编辑完成orz······ | 此词条Jie翻译。由CecileLi初步审校。文中部分公式内容未正常显示,有“模板”点击打开后却没有内容,还有未显示去掉格式后的英文,不清楚是程序错误还是未编辑完成orz······ | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
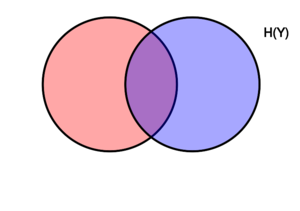
[[文件:Entropy-mutual-information-relative-entropy-relation-diagram.svg|缩略图|右|该图表示在变量X、Y相关联的各种信息量之间,进行加减关系的维恩图。两个圆重合的区域是联合熵H(X,Y)。左侧的圆(红色和紫色)是单个熵H(X),红色是条件熵H(X ǀ Y)。右侧的圆(蓝色和紫色)为H(Y),蓝色为H(Y ǀ X)。中间紫色的是相互信息i(X; Y)。]] | [[文件:Entropy-mutual-information-relative-entropy-relation-diagram.svg|缩略图|右|该图表示在变量X、Y相关联的各种信息量之间,进行加减关系的维恩图。两个圆重合的区域是联合熵H(X,Y)。左侧的圆(红色和紫色)是单个熵H(X),红色是条件熵H(X ǀ Y)。右侧的圆(蓝色和紫色)为H(Y),蓝色为H(Y ǀ X)。中间紫色的是相互信息i(X; Y)。]] | ||
| + | 在'''<font bold="#ff8000"> 信息论Information theory</font>'''中,'''<font color="#ff8000"> 联合熵Joint entropy</font>'''是用于对与一组变量相关的不确定性进行度量。<ref name=korn>{{cite book |author1=Theresa M. Korn |author2=Korn, Granino Arthur |title=Mathematical Handbook for Scientists and Engineers: Definitions, Theorems, and Formulas for Reference and Review |publisher=Dover Publications |location=New York |year= |isbn=0-486-41147-8 |oclc= |doi=}}</ref> | ||
| − | + | ==定义 == | |
| − | + | 联合熵Shannon entropy </font>'''的定义是:以比特为单位,对于具有<math>\mathcal X</math>和<math>\mathcal Y</math>的两个离散随机变量函数<math>X</math>和<math>Y</math>'''有<ref name=cover1991>{{cite book |author1=Thomas M. Cover |author2=Joy A. Thomas |title=Elements of Information Theory |publisher=Wiley |location=Hoboken, New Jersey |year= |isbn=0-471-24195-4}}</ref> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{{Equation box 1 | {{Equation box 1 | ||
| 第27行: | 第17行: | ||
|border colour = #0073CF | |border colour = #0073CF | ||
|background colour=#F5FFFA}} | |background colour=#F5FFFA}} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
其中<math>x</math>和<math>y</math>分别是<math>X</math>和<math>Y</math>的特定值,<math>P(x,y)</math>是这些值产生交集时的联合概率,如果<math>P(x,y)=0</math>那么<math>P(x,y) \log_2[P(x,y)]</math>定义为0。 | 其中<math>x</math>和<math>y</math>分别是<math>X</math>和<math>Y</math>的特定值,<math>P(x,y)</math>是这些值产生交集时的联合概率,如果<math>P(x,y)=0</math>那么<math>P(x,y) \log_2[P(x,y)]</math>定义为0。 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
对于两个以上的随机变量<math>X_1, ..., X_n</math>,它扩展为 | 对于两个以上的随机变量<math>X_1, ..., X_n</math>,它扩展为 | ||
| 第49行: | 第32行: | ||
|border colour = #0073CF | |border colour = #0073CF | ||
|background colour=#F5FFFA}} | |background colour=#F5FFFA}} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
其中<math>x_1,...,x_n</math>分别是<math>X_1,...,X_n</math>的特定值,<math>P(x_1, ..., x_n)</math>是这些值产生交集的概率,如果<math>P(x_1, ..., x_n)=0</math>那么<math>P(x_1, ..., x_n) \log_2[P(x_1, ..., x_n)]</math>定义为0。 | 其中<math>x_1,...,x_n</math>分别是<math>X_1,...,X_n</math>的特定值,<math>P(x_1, ..., x_n)</math>是这些值产生交集的概率,如果<math>P(x_1, ..., x_n)=0</math>那么<math>P(x_1, ..., x_n) \log_2[P(x_1, ..., x_n)]</math>定义为0。 | ||
| − | == | + | == 属性 == |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | ===非负性=== | ||
一组随机变量的联合熵是一个非负数。 | 一组随机变量的联合熵是一个非负数。 | ||
| − | |||
:<math>H(X,Y) \geq 0</math> | :<math>H(X,Y) \geq 0</math> | ||
| 第67行: | 第44行: | ||
:<math>H(X_1,\ldots, X_n) \geq 0</math> | :<math>H(X_1,\ldots, X_n) \geq 0</math> | ||
| − | + | ===高值性/最值性/大于或等于单个熵的最大值=== | |
| − | |||
| − | === | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
一组变量的联合熵大于或等于该组变量的所有单个熵的最大值。 | 一组变量的联合熵大于或等于该组变量的所有单个熵的最大值。 | ||
| 第81行: | 第54行: | ||
\Bigl\{H\bigl(X_i\bigr) \Bigr\}</math> | \Bigl\{H\bigl(X_i\bigr) \Bigr\}</math> | ||
| − | === | + | === 低值性/小于或等于单个熵的总和=== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
一组变量的联合熵小于或等于该组变量各个熵的总和,这是次可加性的一个运用实例。即当且仅当<math>X</math>和<math>Y</math>独立统计时,该不等式才是等式。<ref name=cover1991 />{{rp|30}} | 一组变量的联合熵小于或等于该组变量各个熵的总和,这是次可加性的一个运用实例。即当且仅当<math>X</math>和<math>Y</math>独立统计时,该不等式才是等式。<ref name=cover1991 />{{rp|30}} | ||
| 第92行: | 第62行: | ||
:<math>H(X_1,\ldots, X_n) \leq H(X_1) + \ldots + H(X_n)</math> | :<math>H(X_1,\ldots, X_n) \leq H(X_1) + \ldots + H(X_n)</math> | ||
| − | == | + | == 与其他熵测度的关系 == |
| − | |||
| − | |||
联合熵被用于定义'''<font color="#ff8000"> 条件熵Conditional entropy </font>''': | 联合熵被用于定义'''<font color="#ff8000"> 条件熵Conditional entropy </font>''': | ||
| 第103行: | 第71行: | ||
and <math display="block">H(X_1,\dots,X_n) = \sum_{k=1}^n H(X_k|X_{k-1},\dots, X_1)</math> | and <math display="block">H(X_1,\dots,X_n) = \sum_{k=1}^n H(X_k|X_{k-1},\dots, X_1)</math> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
它也被用于定义'''<font color="#ff8000"> 交互信息Mutual information</font>''': | 它也被用于定义'''<font color="#ff8000"> 交互信息Mutual information</font>''': | ||
| − | |||
:<math>\operatorname{I}(X;Y) = H(X) + H(Y) - H(X,Y)\,</math> | :<math>\operatorname{I}(X;Y) = H(X) + H(Y) - H(X,Y)\,</math> | ||
| − | |||
In [[quantum information theory]], the joint entropy is generalized into the [[joint quantum entropy]]. | In [[quantum information theory]], the joint entropy is generalized into the [[joint quantum entropy]]. | ||
| 第117行: | 第81行: | ||
| − | === | + | ===应用 === |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | 在这里我们提供了一个python软件包,可用于计算n个变量的数据集中的所有多元联合熵、交互信息、条件交互信息、总相关性以及信息距离。<ref>{{cite web|url=https://infotopo.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html|title=InfoTopo: Topological Information Data Analysis. Deep statistical unsupervised and supervised learning - File Exchange - Github|author=|date=|website=github.com/pierrebaudot/infotopopy/|accessdate=26 September 2020}}</ref> |
| − | |||
| − | + | == 联合微分熵 == | |
| + | ===定义 === | ||
上文中的定义是针对离散随机变量的,而其实对于连续随机变量,联合熵同样成立。离散联合熵的连续形式称为联合微分(或连续)熵。令<math>X</math>和<math>Y</math>分别为具有'''<font color="#ff8000"> 联合概率密度函数Joint probability density function</font>''' <math>f(x,y)</math>的连续随机变量,那么微分联合熵<math>h(X,Y)</math>定义为: | 上文中的定义是针对离散随机变量的,而其实对于连续随机变量,联合熵同样成立。离散联合熵的连续形式称为联合微分(或连续)熵。令<math>X</math>和<math>Y</math>分别为具有'''<font color="#ff8000"> 联合概率密度函数Joint probability density function</font>''' <math>f(x,y)</math>的连续随机变量,那么微分联合熵<math>h(X,Y)</math>定义为: | ||
| − | |||
{{Equation box 1 | {{Equation box 1 | ||
| 第139行: | 第98行: | ||
|border colour = #0073CF | |border colour = #0073CF | ||
|background colour=#F5FFFA}} | |background colour=#F5FFFA}} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
对于两个以上的连续随机变量<math>X_1, ..., X_n</math>,其定义可概括为: | 对于两个以上的连续随机变量<math>X_1, ..., X_n</math>,其定义可概括为: | ||
| 第153行: | 第110行: | ||
|border colour = #0073CF | |border colour = #0073CF | ||
|background colour=#F5FFFA}} | |background colour=#F5FFFA}} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
这里可以用积分处理表达<math>f</math>。当然,如果微分熵没有定义,那么积分也可能不存在。 | 这里可以用积分处理表达<math>f</math>。当然,如果微分熵没有定义,那么积分也可能不存在。 | ||
| − | === | + | ===属性 === |
| − | |||
| − | |||
与离散条件下的联合熵相似,联合微分熵也具有同样的属性,即:一组随机变量的联合微分熵小于或等于各个随机变量的熵之和: | 与离散条件下的联合熵相似,联合微分熵也具有同样的属性,即:一组随机变量的联合微分熵小于或等于各个随机变量的熵之和: | ||
| − | |||
:<math>h(X_1,X_2, \ldots,X_n) \le \sum_{i=1}^n h(X_i)</math><ref name=cover1991 />{{rp|253}} | :<math>h(X_1,X_2, \ldots,X_n) \le \sum_{i=1}^n h(X_i)</math><ref name=cover1991 />{{rp|253}} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
以下链式法则适用于两个随机变量: | 以下链式法则适用于两个随机变量: | ||
| − | |||
:<math>h(X,Y) = h(X|Y) + h(Y)</math> | :<math>h(X,Y) = h(X|Y) + h(Y)</math> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
对于两个以上的随机变量,一般可归纳为: | 对于两个以上的随机变量,一般可归纳为: | ||
| − | |||
:<math>h(X_1,X_2, \ldots,X_n) = \sum_{i=1}^n h(X_i|X_1,X_2, \ldots,X_{i-1})</math> | :<math>h(X_1,X_2, \ldots,X_n) = \sum_{i=1}^n h(X_i|X_1,X_2, \ldots,X_{i-1})</math> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
联合微分熵也用于定义连续随机变量之间的交互信息: | 联合微分熵也用于定义连续随机变量之间的交互信息: | ||
| − | |||
:<math>\operatorname{I}(X,Y)=h(X)+h(Y)-h(X,Y)</math> | :<math>\operatorname{I}(X,Y)=h(X)+h(Y)-h(X,Y)</math> | ||
| − | == | + | ==参考文献 == |
{{Reflist}} | {{Reflist}} | ||
2021年8月15日 (日) 19:02的版本
此词条Jie翻译。由CecileLi初步审校。文中部分公式内容未正常显示,有“模板”点击打开后却没有内容,还有未显示去掉格式后的英文,不清楚是程序错误还是未编辑完成orz······
在 信息论Information theory中, 联合熵Joint entropy是用于对与一组变量相关的不确定性进行度量。[1]
定义
联合熵Shannon entropy 的定义是:以比特为单位,对于具有[math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal X }[/math]和[math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal Y }[/math]的两个离散随机变量函数[math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math]和[math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math]有[2]
[math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(X,Y) = -\sum_{x\in\mathcal X} \sum_{y\in\mathcal Y} P(x,y) \log_2[P(x,y)] }[/math]
|
|
(Eq.1) |
其中[math]\displaystyle{ x }[/math]和[math]\displaystyle{ y }[/math]分别是[math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math]和[math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math]的特定值,[math]\displaystyle{ P(x,y) }[/math]是这些值产生交集时的联合概率,如果[math]\displaystyle{ P(x,y)=0 }[/math]那么[math]\displaystyle{ P(x,y) \log_2[P(x,y)] }[/math]定义为0。
对于两个以上的随机变量[math]\displaystyle{ X_1, ..., X_n }[/math],它扩展为
[math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(X_1, ..., X_n) =
-\sum_{x_1 \in\mathcal X_1} ... \sum_{x_n \in\mathcal X_n} P(x_1, ..., x_n) \log_2[P(x_1, ..., x_n)] }[/math]
|
|
(Eq.2) |
其中[math]\displaystyle{ x_1,...,x_n }[/math]分别是[math]\displaystyle{ X_1,...,X_n }[/math]的特定值,[math]\displaystyle{ P(x_1, ..., x_n) }[/math]是这些值产生交集的概率,如果[math]\displaystyle{ P(x_1, ..., x_n)=0 }[/math]那么[math]\displaystyle{ P(x_1, ..., x_n) \log_2[P(x_1, ..., x_n)] }[/math]定义为0。
属性
非负性
一组随机变量的联合熵是一个非负数。
- [math]\displaystyle{ H(X,Y) \geq 0 }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ H(X_1,\ldots, X_n) \geq 0 }[/math]
高值性/最值性/大于或等于单个熵的最大值
一组变量的联合熵大于或等于该组变量的所有单个熵的最大值。
- [math]\displaystyle{ H(X,Y) \geq \max \left[H(X),H(Y) \right] }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ H \bigl(X_1,\ldots, X_n \bigr) \geq \max_{1 \le i \le n} \Bigl\{H\bigl(X_i\bigr) \Bigr\} }[/math]
低值性/小于或等于单个熵的总和
一组变量的联合熵小于或等于该组变量各个熵的总和,这是次可加性的一个运用实例。即当且仅当[math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math]和[math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math]独立统计时,该不等式才是等式。[2]:30
- [math]\displaystyle{ H(X,Y) \leq H(X) + H(Y) }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ H(X_1,\ldots, X_n) \leq H(X_1) + \ldots + H(X_n) }[/math]
与其他熵测度的关系
联合熵被用于定义 条件熵Conditional entropy :
- [math]\displaystyle{ H(X|Y) = H(X,Y) - H(Y)\, }[/math],
and [math]\displaystyle{ H(X_1,\dots,X_n) = \sum_{k=1}^n H(X_k|X_{k-1},\dots, X_1) }[/math]
它也被用于定义 交互信息Mutual information:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \operatorname{I}(X;Y) = H(X) + H(Y) - H(X,Y)\, }[/math]
In quantum information theory, the joint entropy is generalized into the joint quantum entropy.
在 量子信息论Quantum information theory中,使用的是广义化的联合熵,即 联合量子熵Joint quantum entropy。
应用
在这里我们提供了一个python软件包,可用于计算n个变量的数据集中的所有多元联合熵、交互信息、条件交互信息、总相关性以及信息距离。[3]
联合微分熵
定义
上文中的定义是针对离散随机变量的,而其实对于连续随机变量,联合熵同样成立。离散联合熵的连续形式称为联合微分(或连续)熵。令[math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math]和[math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math]分别为具有 联合概率密度函数Joint probability density function [math]\displaystyle{ f(x,y) }[/math]的连续随机变量,那么微分联合熵[math]\displaystyle{ h(X,Y) }[/math]定义为:
[math]\displaystyle{ h(X,Y) = -\int_{\mathcal X , \mathcal Y} f(x,y)\log f(x,y)\,dx dy }[/math]
|
|
(Eq.3) |
对于两个以上的连续随机变量[math]\displaystyle{ X_1, ..., X_n }[/math],其定义可概括为:
[math]\displaystyle{ h(X_1, \ldots,X_n) = -\int f(x_1, \ldots,x_n)\log f(x_1, \ldots,x_n)\,dx_1 \ldots dx_n }[/math]
|
|
(Eq.4) |
这里可以用积分处理表达[math]\displaystyle{ f }[/math]。当然,如果微分熵没有定义,那么积分也可能不存在。
属性
与离散条件下的联合熵相似,联合微分熵也具有同样的属性,即:一组随机变量的联合微分熵小于或等于各个随机变量的熵之和:
- [math]\displaystyle{ h(X_1,X_2, \ldots,X_n) \le \sum_{i=1}^n h(X_i) }[/math][2]:253
以下链式法则适用于两个随机变量:
- [math]\displaystyle{ h(X,Y) = h(X|Y) + h(Y) }[/math]
对于两个以上的随机变量,一般可归纳为:
- [math]\displaystyle{ h(X_1,X_2, \ldots,X_n) = \sum_{i=1}^n h(X_i|X_1,X_2, \ldots,X_{i-1}) }[/math]
联合微分熵也用于定义连续随机变量之间的交互信息:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \operatorname{I}(X,Y)=h(X)+h(Y)-h(X,Y) }[/math]
参考文献
- ↑ Theresa M. Korn; Korn, Granino Arthur. Mathematical Handbook for Scientists and Engineers: Definitions, Theorems, and Formulas for Reference and Review. New York: Dover Publications. ISBN 0-486-41147-8.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Thomas M. Cover; Joy A. Thomas. Elements of Information Theory. Hoboken, New Jersey: Wiley. ISBN 0-471-24195-4.
- ↑ "InfoTopo: Topological Information Data Analysis. Deep statistical unsupervised and supervised learning - File Exchange - Github". github.com/pierrebaudot/infotopopy/. Retrieved 26 September 2020.