有序和无序
此词条暂由彩云小译翻译,未经人工整理和审校,带来阅读不便,请见谅。模板:Unreferenced
In physics, the terms order and disorder designate the presence or absence of some symmetry or correlation in a many-particle system.
In physics, the terms order and disorder designate the presence or absence of some symmetry or correlation in a many-particle system.
在物理学 Physics中,有序和无序指的是多粒子系统中某种对称性 Symmetry或相关性 Correlation的存在或不存在。
In condensed matter physics, systems typically are ordered at low temperatures; upon heating, they undergo one or several phase transitions into less ordered states.
In condensed matter physics, systems typically are ordered at low temperatures; upon heating, they undergo one or several phase transitions into less ordered states.
在凝聚态物理学 Condensed Matter Physics中,系统通常在低温下有序; 在加热时,它们经历一个或几个相变 Phase Transition进入无序状态。
Examples for such an order-disorder transition are:
Examples for such an order-disorder transition are:
这种有序-无序转变的例子有:
- the melting of ice: solid-liquid transition, loss of crystalline order;
冰的融化: 固-液转变,结晶秩序的丧失
- the demagnetization of iron by heating above the Curie temperature: ferromagnetic-paramagnetic transition, loss of magnetic order.
铁在居里点 Curie Temperature以上加热退磁: 铁磁-顺磁转变,磁有序的损失
The degree of freedom that is ordered or disordered can be translational (crystalline ordering), rotational (ferroelectric ordering), or a spin state (magnetic ordering).
The degree of freedom that is ordered or disordered can be translational (crystalline ordering), rotational (ferroelectric ordering), or a spin state (magnetic ordering).
有序或无序的自由度可以是平移(晶体 Crystal有序)、旋转(铁电性 ferroelectric有序)或自旋状态(磁性 Magnetic有序)。
The order can consist either in a full crystalline space group symmetry, or in a correlation. Depending on how the correlations decay with distance, one speaks of long range order or short range order.
The order can consist either in a full crystalline space group symmetry, or in a correlation. Depending on how the correlations decay with distance, one speaks of long range order or short range order.
这种顺序既可以是完全晶体空间群 Space Group的对称,也可以是相互关联的。根据相关系数随距离衰减的程度,我们可以说长程有序 Long Range Order或短程有序 Short Range Order。
If a disordered state is not in thermodynamic equilibrium, one speaks of quenched disorder. For instance, a glass is obtained by quenching (supercooling) a liquid. By extension, other quenched states are called spin glass, orientational glass. In some contexts, the opposite of quenched disorder is annealed disorder.
If a disordered state is not in thermodynamic equilibrium, one speaks of quenched disorder. For instance, a glass is obtained by quenching (supercooling) a liquid. By extension, other quenched states are called spin glass, orientational glass. In some contexts, the opposite of quenched disorder is annealed disorder.
如果一个无序的状态不存在于热力学平衡 Thermodynamic Equilibrium,那么就是淬致无序。例如,玻璃 Glass是通过淬火(过冷却 Supercooling)液体获得的。推而广之,其它淬火态称为自旋玻璃 Spin Glass、取向玻璃 Orientational Glass。在某些情况下,淬致无序的对立面是退火无序。
Characterizing order
Characterizing order
特征化秩序
Lattice periodicity and X-ray crystallinity
Lattice periodicity and X-ray crystallinity
晶格周期性与 x 射线结晶度
The strictest form of order in a solid is lattice periodicity: a certain pattern (the arrangement of atoms in a unit cell) is repeated again and again to form a translationally invariant tiling of space. This is the defining property of a crystal. Possible symmetries have been classified in 14 Bravais lattices and 230 space groups.
The strictest form of order in a solid is lattice periodicity: a certain pattern (the arrangement of atoms in a unit cell) is repeated again and again to form a translationally invariant tiling of space. This is the defining property of a crystal. Possible symmetries have been classified in 14 Bravais lattices and 230 space groups.
固体中秩序的最严格形式是晶格周期性: 某种模式( 单元格 Unit Cell 中原子的排列)一次又一次地重复,形成一个平移不变的空间平铺 Tiling。这就是晶体 Crystal的定义属性。可能的对称性已在14个布拉维斯晶格 Bravais Lattice和230个空间群 Space Group中分类。
Lattice periodicity implies long-range order: if only one unit cell is known, then by virtue of the translational symmetry it is possible to accurately predict all atomic positions at arbitrary distances. During much of the 20th century, the converse was also taken for granted – until the discovery of quasicrystals in 1982 showed that there are perfectly deterministic tilings that do not possess lattice periodicity.
Lattice periodicity implies long-range order: if only one unit cell is known, then by virtue of the translational symmetry it is possible to accurately predict all atomic positions at arbitrary distances. During much of the 20th century, the converse was also taken for granted – until the discovery of quasicrystals in 1982 showed that there are perfectly deterministic tilings that do not possess lattice periodicity.
格点周期性意味着长程有序: 如果只知道一个单位单元,那么借助于平移对称性,就有可能在任意距离上精确地预测所有原子的位置。在20世纪的大部分时间里,相反的情况也被认为是合理的——直到1982年准晶体 Quasicrystal的发现表明,完全确定性的倾斜并不具有晶格周期性。
Besides structural order, one may consider charge ordering, spin ordering, magnetic ordering, and compositional ordering. Magnetic ordering is observable in neutron diffraction.
Besides structural order, one may consider charge ordering, spin ordering, magnetic ordering, and compositional ordering. Magnetic ordering is observable in neutron diffraction.
除了结构有序外,还可以考虑电荷有序 Charge Ordering、自旋 Spin有序、磁有序 Magnetic Ordering和成分有序。磁有序可以在中子衍射 Neutron Diffraction中观察到。
It is a thermodynamic entropy concept often displayed by a second-order phase transition. Generally speaking, high thermal energy is associated with disorder and low thermal energy with ordering, although there have been violations of this. Ordering peaks become apparent in diffraction experiments at low energy.
It is a thermodynamic entropy concept often displayed by a second-order phase transition. Generally speaking, high thermal energy is associated with disorder and low thermal energy with ordering, although there have been violations of this. Ordering peaks become apparent in diffraction experiments at low energy.
这是一个熵 Thermodynamics Entropy的概念,通常表现为一个二阶相变 Phase Transition。一般来说,高热能与无序有关,低热能与有序有关,但有违背这一规律的现象存在。在低能衍射实验中,有序峰变得明显。
Long-range order
Long-range order
长程有序
Long-range order characterizes physical systems in which remote portions of the same sample exhibit correlated behavior.
Long-range order characterizes physical systems in which remote portions of the same sample exhibit correlated behavior.
长程有序描述了同一样本的远程部分表现出相关 correlated行为的物理系统 System。
This can be expressed as a correlation function, namely the spin-spin correlation function:
This can be expressed as a correlation function, namely the spin-spin correlation function:
这可以用相关函数 Correlated Function(量子场论)来表示,即旋转相关函数 Spin-spin Correlation Function(量子场论) :
- [math]\displaystyle{ G(x,x') = \langle s(x),s(x') \rangle. \, }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ G(x,x') = \langle s(x),s(x') \rangle. \, }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ G(x,x') = \langle s(x),s(x') \rangle. \, }[/math]
where s is the spin quantum number and x is the distance function within the particular system.
where s is the spin quantum number and x is the distance function within the particular system.
其中 s 是自旋量子数,x 是特定系统中的距离函数。
This function is equal to unity when [math]\displaystyle{ x=x' }[/math] and decreases as the distance [math]\displaystyle{ |x-x'| }[/math] increases. Typically, it decays exponentially to zero at large distances, and the system is considered to be disordered. But if the correlation function decays to a constant value at large [math]\displaystyle{ |x-x'| }[/math] then the system is said to possess long-range order. If it decays to zero as a power of the distance then it is called quasi-long-range order (for details see Chapter 11 in the textbook cited below. See also Berezinskii–Kosterlitz–Thouless transition). Note that what constitutes a large value of [math]\displaystyle{ |x-x'| }[/math] is understood in the sense of asymptotics.
This function is equal to unity when [math]\displaystyle{ x=x' }[/math] and decreases as the distance [math]\displaystyle{ |x-x'| }[/math] increases. Typically, it decays exponentially to zero at large distances, and the system is considered to be disordered. But if the correlation function decays to a constant value at large [math]\displaystyle{ |x-x'| }[/math] then the system is said to possess long-range order. If it decays to zero as a power of the distance then it is called quasi-long-range order (for details see Chapter 11 in the textbook cited below. See also Berezinskii–Kosterlitz–Thouless transition). Note that what constitutes a large value of [math]\displaystyle{ |x-x'| }[/math] is understood in the sense of asymptotics.
当[math]\displaystyle{ x=x' }[/math]时,这个函数等于单位数,当距离[math]\displaystyle{ |x-x'| }[/math]增加时,这个函数减少。通常情况下,它在很大距离上呈指数衰减 Decays Exponentially为零,系统被认为是无序的。但是如果相关函数(量子场论)衰变为一个常数值,那么这个系统就被认为具有长程序。如果它衰变为零作为距离的幂,那么它被称为准长程序(详见下面引用的教科书第11章)。参见Berezinskii–Kosterlitz–Thouless过渡 Berezinskii–Kosterlitz–Thouless Transition)。请注意,构成较大的[math]\displaystyle{ |x-x'| }[/math]的值可以理解为渐近性。
Quenched disorder
Quenched disorder
淬致无序
In statistical physics, a system is said to present quenched disorder when some parameters defining its behavior are random variables which do not evolve with time, i.e. they are quenched or frozen. Spin glasses are a typical example. It is opposite to annealed disorder, where the random variables are allowed to evolve themselves.
In statistical physics, a system is said to present quenched disorder when some parameters defining its behavior are random variables which do not evolve with time, i.e. they are quenched or frozen. Spin glasses are a typical example. It is opposite to annealed disorder, where the random variables are allowed to evolve themselves.
在统计物理学中,当定义系统行为的某些参数是不随时间演化的随机变量时,系统称为淬灭无序。它们被淬火或者冷冻。旋转眼镜就是一个典型的例子。与退火无序相反,随机变量允许自身进化。
In mathematical terms, quenched disorder is harder to analyze than its annealed counterpart, since the thermal and the noise averaging play very different roles. In fact, the problem is so hard that few techniques to approach each are known, most of them relying on approximations. The most used are
In mathematical terms, quenched disorder is harder to analyze than its annealed counterpart, since the thermal and the noise averaging play very different roles. In fact, the problem is so hard that few techniques to approach each are known, most of them relying on approximations. The most used are
在数学术语中,淬火无序比退火无序更难分析,因为热平均和噪声平均起着非常不同的作用。事实上,这个问题是如此的困难,以至于很少有技术可以处理每一个问题,大多数都依赖于近似值。最常用的是
- a technique based on a mathematical analytical continuation known as the replica trick
a technique based on a mathematical analytical continuation known as the replica trick
一种基于数学解析延拓的技术,被称为复制技巧
- the Cavity method; although these give results in accord with experiments in a large range of problems, they are not generally proven to be a rigorous mathematical procedure.
the Cavity method; although these give results in accord with experiments in a large range of problems, they are not generally proven to be a rigorous mathematical procedure.
虽然这些方法给出的结果与许多问题的实验结果相一致,但它们通常不被证明是一个严格的数学过程。
More recently it has been shown by rigorous methods, however, that at least in the archetypal spin-glass model (the so-called Sherrington–Kirkpatrick model) the replica based solution is indeed exact.
More recently it has been shown by rigorous methods, however, that at least in the archetypal spin-glass model (the so-called Sherrington–Kirkpatrick model) the replica based solution is indeed exact.
然而,最近通过严格的方法表明,至少在典型的自旋玻璃模型(所谓的 sherlington-Kirkpatrick 模型)中,基于复制的解确实是精确的。
The second most used technique in this field is generating functional analysis. This method is based on path integrals, and is in principle fully exact, although generally more difficult to apply than the replica procedure.
The second most used technique in this field is generating functional analysis. This method is based on path integrals, and is in principle fully exact, although generally more difficult to apply than the replica procedure.
该领域第二常用的技术是生成函数分析。这种方法是基于路径积分的,原则上是完全精确的,虽然通常比复制过程更难应用。
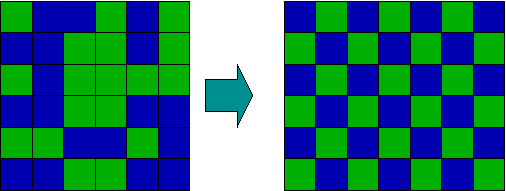
Transition from disordered (left) to ordered (right) states
从无序(左)状态过渡到有序(右)状态
Annealed disorder
Annealed disorder
退火无序
A system is said to present annealed disorder when some parameters entering its definition are random variables, but whose evolution is related to that of the degrees of freedom defining the system. It is defined in opposition to quenched disorder, where the random variables may not change their values.
A system is said to present annealed disorder when some parameters entering its definition are random variables, but whose evolution is related to that of the degrees of freedom defining the system. It is defined in opposition to quenched disorder, where the random variables may not change their values.
当一个系统的某些参数进入其定义为随机变量时,称系统呈现退火无序,但其演化与定义系统的自由度有关。它的定义与淬灭无序相反,在淬灭无序中,随机变量可能不会改变其值。
Systems with annealed disorder are usually considered to be easier to deal with mathematically, since the average on the disorder and the thermal average may be treated on the same footing.
Systems with annealed disorder are usually considered to be easier to deal with mathematically, since the average on the disorder and the thermal average may be treated on the same footing.
退火无序系统通常被认为更容易在数学上处理,因为无序系统的平均值和热平均值可以在同一基础上处理。
See also
See also
参见
- In high energy physics, the formation of the chiral condensate in quantum chromodynamics is an ordering transition; it is discussed in terms of superselection.
Further reading
Further reading
进一步阅读
- H Kleinert: Gauge Fields in Condensed Matter (, 2 volumes) Singapore: World Scientific (1989).
Category:Statistical mechanics
类别: 统计力学
Category:Crystallography
类别: 结晶学
This page was moved from wikipedia:en:Order and disorder. Its edit history can be viewed at 有序和无序/edithistory