条件熵
此词条暂由彩云小译翻译,未经人工整理和审校,带来阅读不便,请见谅。
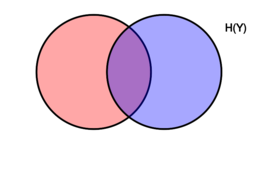
[[Venn diagram showing additive and subtractive relationships various information measures associated with correlated variables [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math]. The area contained by both circles is the joint entropy [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(X,Y) }[/math]. The circle on the left (red and violet) is the individual entropy [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(X) }[/math], with the red being the conditional entropy [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(X|Y) }[/math]. The circle on the right (blue and violet) is [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(Y) }[/math], with the blue being [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(Y|X) }[/math]. The violet is the mutual information [math]\displaystyle{ \operatorname{I}(X;Y) }[/math].]]
显示加减关系的文氏图各种信息测量与相关变量数学 x / 数学和 y / 数学相关。两个圆所包含的面积是联合熵 math Eta (x,y) / math。左边的圆圈(红色和紫色)是个体熵数学 Eta (x) / math,红色的是条件熵数学 Eta (x | y) / math。右边的圆(蓝色和紫色)是 math Eta (y) / math,蓝色的是 math Eta (y | x) / math。紫色是互信息 math operatorname { i }(x; y) / math. ]
In information theory, the conditional entropy (or equivocation) quantifies the amount of information needed to describe the outcome of a random variable [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] given that the value of another random variable [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] is known. Here, information is measured in shannons, nats, or hartleys. The entropy of [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] conditioned on [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] is written as [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(Y|X) }[/math].
In information theory, the conditional entropy (or equivocation) quantifies the amount of information needed to describe the outcome of a random variable [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] given that the value of another random variable [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] is known. Here, information is measured in shannons, nats, or hartleys. The entropy of [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] conditioned on [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] is written as [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(Y|X) }[/math].
在信息论中,假设另一个随机变量 math x / math 的值是已知的,信息条件熵量化描述随机变量 math y / math 的结果所需的信息量。在这里,信息是用夏农、纳特斯或哈特利来衡量的。数学 y / 数学的熵以数学 x / 数学为条件,表示为数学 Eta (y | x) / 数学。
Definition
Definition
定义
The conditional entropy of [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] given [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] is defined as
The conditional entropy of [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] given [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] is defined as
数学 y / 数学给定数学 x / 数学的条件熵定义为
{{Equation box 1
{{Equation box 1
{方程式方框1
|indent =
|indent =
不会有事的
|title=
|title=
标题
|equation =
[math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(Y|X)\ = -\sum_{x\in\mathcal X, y\in\mathcal Y}p(x,y)\log \frac {p(x,y)} {p(x)} }[/math]
|
|
(Eq.1) |
|equation = }}
会公式开始
|cellpadding= 6
|cellpadding= 6
6号手术室
|border
|border
边界
|border colour = #0073CF
|border colour = #0073CF
0073CF
|background colour=#F5FFFA}}
|background colour=#F5FFFA}}
5 / fffa }
where [math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal X }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal Y }[/math] denote the support sets of [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math].
where [math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal X }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal Y }[/math] denote the support sets of [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math].
其中 math mathcal x / math 和 math mathcal y / math 表示数学 x / math 和数学 y / math 的支持集。
Note: It is conventioned that the expressions [math]\displaystyle{ 0 \log 0 }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ 0 \log c/0 }[/math] for fixed [math]\displaystyle{ c \gt 0 }[/math] should be treated as being equal to zero. This is because [math]\displaystyle{ \lim_{\theta\to0^+} \theta\, \log \,c/\theta = 0 }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \lim_{\theta\to0^+} \theta\, \log \theta = 0 }[/math][1]
Note: It is conventioned that the expressions [math]\displaystyle{ 0 \log 0 }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ 0 \log c/0 }[/math] for fixed [math]\displaystyle{ c \gt 0 }[/math] should be treated as being equal to zero. This is because [math]\displaystyle{ \lim_{\theta\to0^+} \theta\, \log \,c/\theta = 0 }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \lim_{\theta\to0^+} \theta\, \log \theta = 0 }[/math]
注意: 对于固定数学 c 0 / math,表达式 math 0 log 0 / math 和 math 0 log c / 0 / math 应当被视为等于零。这是因为 math theta 0 ^ + theta log theta 0 / math 和 math theta 0 ^ + theta log theta 0 / math! -- 因为 p (x,y)仍然可以等于0,即使 p (x) ! 0和 p (y) ! 0.P (x,y) p (x)0怎么样?-->
Intuitive explanation of the definition :
Intuitive explanation of the definition :
对定义的直观解释:
According to the definition, [math]\displaystyle{ \displaystyle H( Y|X) =\mathbb{E}( \ f( X,Y) \ ) }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ \displaystyle f:( x,y) \ \rightarrow -\log_{2}( \ p( y|x) \ ) . }[/math] [math]\displaystyle{ \displaystyle f }[/math] associates to [math]\displaystyle{ \displaystyle ( x,y) }[/math] the information content of [math]\displaystyle{ \displaystyle ( Y=y) }[/math] given [math]\displaystyle{ \displaystyle (X=x) }[/math], which is the amount of information needed to describe the event [math]\displaystyle{ \displaystyle (Y=y) }[/math] given [math]\displaystyle{ (X=x) }[/math]. According to the law of large numbers, [math]\displaystyle{ \displaystyle H(Y|X) }[/math] is the arithmetic mean of a large number of independent realizations of [math]\displaystyle{ \displaystyle f(X,Y) }[/math].
According to the definition, [math]\displaystyle{ \displaystyle H( Y|X) =\mathbb{E}( \ f( X,Y) \ ) }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ \displaystyle f:( x,y) \ \rightarrow -\log_{2}( \ p( y|x) \ ) . }[/math] [math]\displaystyle{ \displaystyle f }[/math] associates to [math]\displaystyle{ \displaystyle ( x,y) }[/math] the information content of [math]\displaystyle{ \displaystyle ( Y=y) }[/math] given [math]\displaystyle{ \displaystyle (X=x) }[/math], which is the amount of information needed to describe the event [math]\displaystyle{ \displaystyle (Y=y) }[/math] given [math]\displaystyle{ (X=x) }[/math]. According to the law of large numbers, [math]\displaystyle{ \displaystyle H(Y|X) }[/math] is the arithmetic mean of a large number of independent realizations of [math]\displaystyle{ \displaystyle f(X,Y) }[/math].
根据定义,math displaystyle h (y | x) mathbb { e }( f (x,y)) / math displaystyle f: (x,y) righttarrow log {2}( p (y | x))。 / math displaystyle f / math 联想到 math displaystyle (x,y) / math 数学数学 displaystyle (y) / math 给定的 math displaystyle (x) / math,这是描述事件数学 displaystyle (y) / math 给定的 math (x) / math 所需的信息量。根据大数定律,math displaystyle h (y | x) / math 是 math displaystyle f (x,y) / math 的大量独立实现的算术平均数。
Motivation
Motivation
动机
Let [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(Y|X=x) }[/math] be the entropy of the discrete random variable [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] conditioned on the discrete random variable [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] taking a certain value [math]\displaystyle{ x }[/math]. Denote the support sets of [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] by [math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal X }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal Y }[/math]. Let [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] have probability mass function [math]\displaystyle{ p_Y{(y)} }[/math]. The unconditional entropy of [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] is calculated as [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(Y) := \mathbb{E}[\operatorname{I}(Y)] }[/math], i.e.
Let [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(Y|X=x) }[/math] be the entropy of the discrete random variable [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] conditioned on the discrete random variable [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] taking a certain value [math]\displaystyle{ x }[/math]. Denote the support sets of [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] by [math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal X }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal Y }[/math]. Let [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] have probability mass function [math]\displaystyle{ p_Y{(y)} }[/math]. The unconditional entropy of [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] is calculated as [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(Y) := \mathbb{E}[\operatorname{I}(Y)] }[/math], i.e.
设数学是离散型随机变量数学 y / math 的熵,条件是离散型随机变量数学 x / math 取一定值数学 x / math。用 math mathcal x / math 和 math mathcal y / math 表示数学 x / math 和数学 y / math 的支持集。让数学 y / 数学有概率质量函数 / 数学 p {(y)} / 数学。数学 y / math 的无条件熵计算为 math Eta (y) : mathbb { e }[ operatorname { i }(y)] / math,即。
- [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(Y) = \sum_{y\in\mathcal Y} {\mathrm{Pr}(Y=y)\,\mathrm{I}(y)} \lt math\gt \Eta(Y) = \sum_{y\in\mathcal Y} {\mathrm{Pr}(Y=y)\,\mathrm{I}(y)} 数学中的 Eta (y)(y)(y)(y)(y)(y)(y) = -\sum_{y\in\mathcal Y} {p_Y(y) \log_2{p_Y(y)}}, }[/math]
= -\sum_{y\in\mathcal Y} {p_Y(y) \log_2{p_Y(y)}},</math>
- 和数学 y }{ py (y) log 2{ py (y)} ,/ math
where [math]\displaystyle{ \operatorname{I}(y_i) }[/math] is the information content of the outcome of [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] taking the value [math]\displaystyle{ y_i }[/math]. The entropy of [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] conditioned on [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] taking the value [math]\displaystyle{ x }[/math] is defined analogously by conditional expectation:
where [math]\displaystyle{ \operatorname{I}(y_i) }[/math] is the information content of the outcome of [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] taking the value [math]\displaystyle{ y_i }[/math]. The entropy of [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] conditioned on [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] taking the value [math]\displaystyle{ x }[/math] is defined analogously by conditional expectation:
其中 math operatorname { i }(yi) / math 是取值 math y / math 的数学 y / math 结果的信息内容。数学 y / 数学的熵取决于数学 x / 数学的取值,数学 x / 数学的定义类似于条件期望的定义:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(Y|X=x) \lt math\gt \Eta(Y|X=x) (y | x) = -\sum_{y\in\mathcal Y} {\Pr(Y = y|X=x) \log_2{\Pr(Y = y|X=x)}}. }[/math]
= -\sum_{y\in\mathcal Y} {\Pr(Y = y|X=x) \log_2{\Pr(Y = y|X=x)}}. </math>
- 和数学 y }{ Pr (y | x) log 2{ Pr (y | x)}。数学
[math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(Y|X) }[/math] is the result of averaging [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(Y|X=x) }[/math] over all possible values [math]\displaystyle{ x }[/math] that [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] may take.
[math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(Y|X) }[/math] is the result of averaging [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(Y|X=x) }[/math] over all possible values [math]\displaystyle{ x }[/math] that [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] may take.
数学是对所有可能的数值求平均值的结果,数学 x / 数学可能需要。
Given discrete random variables [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] with image [math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal X }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] with image [math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal Y }[/math], the conditional entropy of [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] given [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] is defined as the weighted sum of [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(Y|X=x) }[/math] for each possible value of [math]\displaystyle{ x }[/math], using [math]\displaystyle{ p(x) }[/math] as the weights:[2]:15
Given discrete random variables [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] with image [math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal X }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] with image [math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal Y }[/math], the conditional entropy of [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] given [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] is defined as the weighted sum of [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(Y|X=x) }[/math] for each possible value of [math]\displaystyle{ x }[/math], using [math]\displaystyle{ p(x) }[/math] as the weights:
给定离散随机变量数学 x / 数学 x / 数学 x / 数学 y / 数学 y / 数学,数学 y / 数学 x / 数学的条件熵定义为数学 x / 数学每个可能值的加权和,用数学 p (x) / 数学作为权重:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \lt math\gt 数学 \begin{align} \begin{align} Begin { align } \Eta(Y|X)\ &\equiv \sum_{x\in\mathcal X}\,p(x)\,\Eta(Y|X=x)\\ \Eta(Y|X)\ &\equiv \sum_{x\in\mathcal X}\,p(x)\,\Eta(Y|X=x)\\ 数学 x 中的 Eta (y | x) ,p (x) ,Eta (y | x) & =-\sum_{x\in\mathcal X} p(x)\sum_{y\in\mathcal Y}\,p(y|x)\,\log\, p(y|x)\\ & =-\sum_{x\in\mathcal X} p(x)\sum_{y\in\mathcal Y}\,p(y|x)\,\log\, p(y|x)\\ 数学 x } p (x) sum y } ,p (y | x) ,log,p (y | x) & =-\sum_{x\in\mathcal X}\sum_{y\in\mathcal Y}\,p(x,y)\,\log\,p(y|x)\\ & =-\sum_{x\in\mathcal X}\sum_{y\in\mathcal Y}\,p(x,y)\,\log\,p(y|x)\\ 数学中的 x 和 y,p (x,y) ,log,p (y | x) & =-\sum_{x\in\mathcal X, y\in\mathcal Y}p(x,y)\log\,p(y|x)\\ & =-\sum_{x\in\mathcal X, y\in\mathcal Y}p(x,y)\log\,p(y|x)\\ 数学 x,y = p (x,y) log,p (y | x) & =-\sum_{x\in\mathcal X, y\in\mathcal Y}p(x,y)\log \frac {p(x,y)} {p(x)}. \\ & =-\sum_{x\in\mathcal X, y\in\mathcal Y}p(x,y)\log \frac {p(x,y)} {p(x)}. \\ (x,y) log-frac { p (x,y)}{ p (x,y)}.\\ & = \sum_{x\in\mathcal X, y\in\mathcal Y}p(x,y)\log \frac {p(x)} {p(x,y)}. \\ & = \sum_{x\in\mathcal X, y\in\mathcal Y}p(x,y)\log \frac {p(x)} {p(x,y)}. \\ (x,y) log frac { p (x)}{ p (x,y)}.\\ \end{align} \end{align} End { align } }[/math]
</math>
数学
<! -- 本段不正确; 最后一行不是任何两个分布之间的 KL 散度,因为 p (x)[一般]不是 x 和 y 域上的有效分布。上面的最后一个公式是 Kullback-Leibler 的背离,也被称为相对熵。相对熵总是正的,只有当且仅当数学 p (x,y) p (x) / math 时才消失。这是当我们知道数学 x / 数学告诉我们关于数学 y / 数学的一切。补充: 这个评论是否过时了,因为 KL 的分歧没有在上面提到?2014年11月--
Properties
Properties
属性
Conditional entropy equals zero
Conditional entropy equals zero
条件熵等于零
[math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(Y|X)=0 }[/math] if and only if the value of [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] is completely determined by the value of [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math].
[math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(Y|X)=0 }[/math] if and only if the value of [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] is completely determined by the value of [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math].
Math Eta (y | x)0 / math 当且仅当 math y / math 的值完全由 math x / math 的值决定。
Conditional entropy of independent random variables
Conditional entropy of independent random variables
独立随机变量的条件熵
Conversely, [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(Y|X) = \Eta(Y) }[/math] if and only if [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] are independent random variables.
Conversely, [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(Y|X) = \Eta(Y) }[/math] if and only if [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] are independent random variables.
相反,math Eta (y | x) Eta (y) / math 当且仅当 math y / math 和 math x / math 是独立随机变量。
Chain rule
Chain rule
链式规则
Assume that the combined system determined by two random variables [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] has joint entropy [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(X,Y) }[/math], that is, we need [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(X,Y) }[/math] bits of information on average to describe its exact state. Now if we first learn the value of [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math], we have gained [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(X) }[/math] bits of information. Once [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] is known, we only need [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(X,Y)-\Eta(X) }[/math] bits to describe the state of the whole system. This quantity is exactly [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(Y|X) }[/math], which gives the chain rule of conditional entropy:
Assume that the combined system determined by two random variables [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] has joint entropy [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(X,Y) }[/math], that is, we need [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(X,Y) }[/math] bits of information on average to describe its exact state. Now if we first learn the value of [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math], we have gained [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(X) }[/math] bits of information. Once [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] is known, we only need [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(X,Y)-\Eta(X) }[/math] bits to describe the state of the whole system. This quantity is exactly [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(Y|X) }[/math], which gives the chain rule of conditional entropy:
假设由两个随机变量数学 x / math 和数学 y / math 组成的组合系统具有联合熵数学 Eta (x,y) / math,也就是说,我们平均需要 math Eta (x,y) / math 位信息来描述它的精确状态。现在,如果我们首先学习数学 x / math 的值,我们就得到了数学 Eta (x) / 数学信息位。一旦知道了数学 x / math,我们只需要 math Eta (x,y)- Eta (x) / math 位来描述整个系统的状态。这个量正是 math Eta (y | x) / math,它给出了条件熵的链式法则:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(Y|X)\, = \, \Eta(X,Y)- \Eta(X). }[/math][2]:17
[math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(Y|X)\, = \, \Eta(X,Y)- \Eta(X). }[/math]
Math Eta (y | x) , Eta (x,y)- Eta (x) . / math
The chain rule follows from the above definition of conditional entropy:
The chain rule follows from the above definition of conditional entropy:
链式规则遵循以上条件熵的定义:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} \lt math\gt \begin{align} 数学 begin { align } \Eta(Y|X) &= \sum_{x\in\mathcal X, y\in\mathcal Y}p(x,y)\log \left(\frac{p(x)}{p(x,y)} \right) \\[4pt] \Eta(Y|X) &= \sum_{x\in\mathcal X, y\in\mathcal Y}p(x,y)\log \left(\frac{p(x)}{p(x,y)} \right) \\[4pt] Eta (y | x) & sum (x,y) p (x,y) log 左(frac (x)} p (x,y)右)[4 pt ] &= -\sum_{x\in\mathcal X, y\in\mathcal Y}p(x,y)\log (p(x,y)) + \sum_{x\in\mathcal X, y\in\mathcal Y}{p(x,y)\log(p(x))} \\[4pt] &= -\sum_{x\in\mathcal X, y\in\mathcal Y}p(x,y)\log (p(x,y)) + \sum_{x\in\mathcal X, y\in\mathcal Y}{p(x,y)\log(p(x))} \\[4pt] 数学 x,y 中数学 y } p (x,y) log (p (x,y)) + 数学 x,y 中数学 y } p (x,y) log (p (x))[4 pt ] & = \Eta(X,Y) + \sum_{x \in \mathcal X} p(x)\log (p(x) ) \\[4pt] & = \Eta(X,Y) + \sum_{x \in \mathcal X} p(x)\log (p(x) ) \\[4pt] & Eta (x,y) + sum { x } p (x) log (p (x))[4 pt ] & = \Eta(X,Y) - \Eta(X). & = \Eta(X,Y) - \Eta(X). & Eta (x,y)- Eta (x). \end{align} }[/math]
\end{align}</math>
End { align } / math
In general, a chain rule for multiple random variables holds:
In general, a chain rule for multiple random variables holds:
一般来说,多个随机变量的链式规则适用于:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(X_1,X_2,\ldots,X_n) = \lt math\gt \Eta(X_1,X_2,\ldots,X_n) = Math Eta (x1,x2, ldots,xn) \sum_{i=1}^n \Eta(X_i | X_1, \ldots, X_{i-1}) }[/math][2]:22
\sum_{i=1}^n \Eta(X_i | X_1, \ldots, X_{i-1}) </math>
{ i } ^ n Eta (xi | x1,ldots,x { i-1}) / math
It has a similar form to chain rule in probability theory, except that addition instead of multiplication is used.
It has a similar form to chain rule in probability theory, except that addition instead of multiplication is used.
它有一个类似的形式链规则在概率论,除了加法代替乘法是使用。
Bayes' rule
Bayes' rule
贝叶斯规则
Bayes' rule for conditional entropy states
Bayes' rule for conditional entropy states
条件熵的贝叶斯规则
- [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(Y|X) \,=\, \Eta(X|Y) - \Eta(X) + \Eta(Y). }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(Y|X) \,=\, \Eta(X|Y) - \Eta(X) + \Eta(Y). }[/math]
Math Eta (y | x) , Eta (x | y)- Eta (x) + Eta (y) . / math
Proof. [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(Y|X) = \Eta(X,Y) - \Eta(X) }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(X|Y) = \Eta(Y,X) - \Eta(Y) }[/math]. Symmetry entails [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(X,Y) = \Eta(Y,X) }[/math]. Subtracting the two equations implies Bayes' rule.
Proof. [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(Y|X) = \Eta(X,Y) - \Eta(X) }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(X|Y) = \Eta(Y,X) - \Eta(Y) }[/math]. Symmetry entails [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(X,Y) = \Eta(Y,X) }[/math]. Subtracting the two equations implies Bayes' rule.
证据。Math Eta (y | x) Eta (x,y)- Eta (x) / math Eta (x | y) Eta (y,x)- Eta (y) / math.对称性需要数学 Eta (x,y) Eta (y,x) / 数学。减去这两个方程就得到了贝叶斯定律。
If [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] is conditionally independent of [math]\displaystyle{ Z }[/math] given [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] we have:
If [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] is conditionally independent of [math]\displaystyle{ Z }[/math] given [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] we have:
如果数学 y / 数学是条件独立于数学 z / 数学给定的数学 x / 数学,我们有:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(Y|X,Z) \,=\, \Eta(Y|X). }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(Y|X,Z) \,=\, \Eta(Y|X). }[/math]
Math Eta (y | x,z) , Eta (y | x) . / math
Other properties
Other properties
其他物业
For any [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math]:
For any [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math]:
对于任何数学 x / 数学 y / 数学:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} \lt math display="block"\gt \begin{align} 数学显示“ block” begin { align } \Eta(Y|X) &\le \Eta(Y) \, \\ \Eta(Y|X) &\le \Eta(Y) \, \\ 三、 Eta (y | x)和 le Eta (y) , \Eta(X,Y) &= \Eta(X|Y) + \Eta(Y|X) + \operatorname{I}(X;Y),\qquad \\ \Eta(X,Y) &= \Eta(X|Y) + \Eta(Y|X) + \operatorname{I}(X;Y),\qquad \\ (x,y) & Eta (x | y) + Eta (y | x) + operatorname { i }(x; y) , \Eta(X,Y) &= \Eta(X) + \Eta(Y) - \operatorname{I}(X;Y),\, \\ \Eta(X,Y) &= \Eta(X) + \Eta(Y) - \operatorname{I}(X;Y),\, \\ Eta (x,y) & Eta (x) + Eta (y)-操作者名称{ i }(x; y) , , \operatorname{I}(X;Y) &\le \Eta(X),\, \operatorname{I}(X;Y) &\le \Eta(X),\, { i }(x; y) & le Eta (x) , , \end{align} }[/math]
\end{align}</math>
End { align } / math
where [math]\displaystyle{ \operatorname{I}(X;Y) }[/math] is the mutual information between [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math].
where [math]\displaystyle{ \operatorname{I}(X;Y) }[/math] is the mutual information between [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math].
其中 math operatorname { i }(x; y) / math 是 math x / math 和 math y / math 之间的相互信息。
For independent [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math]:
For independent [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math]:
对于独立数学 x / 数学 y / 数学:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(Y|X) = \Eta(Y) }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(X|Y) = \Eta(X) \, }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(Y|X) = \Eta(Y) }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(X|Y) = \Eta(X) \, }[/math]
Math Eta (y | x) Eta (y) / math Eta (x | y) Eta (x) ,/ math
Although the specific-conditional entropy [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(X|Y=y) }[/math] can be either less or greater than [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(X) }[/math] for a given random variate [math]\displaystyle{ y }[/math] of [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(X|Y) }[/math] can never exceed [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(X) }[/math].
Although the specific-conditional entropy [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(X|Y=y) }[/math] can be either less or greater than [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(X) }[/math] for a given random variate [math]\displaystyle{ y }[/math] of [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(X|Y) }[/math] can never exceed [math]\displaystyle{ \Eta(X) }[/math].
虽然对于给定的随机变量 y / 数学 y / 数学,特定条件熵数学 Eta (x | y) / 数学可以比 math Eta (x) / 数学更小或更大,math Eta (x | y) / 数学永远不能超过 math Eta (x) / 数学。
Conditional differential entropy
Conditional differential entropy
条件微分熵
Definition
Definition
定义
The above definition is for discrete random variables. The continuous version of discrete conditional entropy is called conditional differential (or continuous) entropy. Let [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] be a continuous random variables with a joint probability density function [math]\displaystyle{ f(x,y) }[/math]. The differential conditional entropy [math]\displaystyle{ h(X|Y) }[/math] is defined as[2]:249
The above definition is for discrete random variables. The continuous version of discrete conditional entropy is called conditional differential (or continuous) entropy. Let [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] be a continuous random variables with a joint probability density function [math]\displaystyle{ f(x,y) }[/math]. The differential conditional entropy [math]\displaystyle{ h(X|Y) }[/math] is defined as
上述定义适用于离散型随机变量。离散条件熵的连续形式称为条件微分(或连续)熵。让数学 x / math 和数学 y / math 是一个连续的随机变量和一个概率密度函数 / 数学 f (x,y) / math。微分 / 条件熵数学 h (x | y) / math 定义为
{{Equation box 1
{{Equation box 1
{方程式方框1
|indent =
|indent =
不会有事的
|title=
|title=
标题
|equation =
[math]\displaystyle{ h(X|Y) = -\int_{\mathcal X, \mathcal Y} f(x,y)\log f(x|y)\,dx dy }[/math]
|
|
(Eq.2) |
|equation = }}
会公式开始
|cellpadding= 6
|cellpadding= 6
6号手术室
|border
|border
边界
|border colour = #0073CF
|border colour = #0073CF
0073CF
|background colour=#F5FFFA}}
|background colour=#F5FFFA}}
5 / fffa }
Properties
Properties
属性
In contrast to the conditional entropy for discrete random variables, the conditional differential entropy may be negative.
In contrast to the conditional entropy for discrete random variables, the conditional differential entropy may be negative.
与离散随机变量的条件熵相反,条件微分熵可能是负的。
As in the discrete case there is a chain rule for differential entropy:
As in the discrete case there is a chain rule for differential entropy:
在离散情况下,微分熵有一个链式规则:
- [math]\displaystyle{ h(Y|X)\,=\,h(X,Y)-h(X) }[/math][2]:253
[math]\displaystyle{ h(Y|X)\,=\,h(X,Y)-h(X) }[/math]
数学 h (y | x) ,h (x,y)-h (x) / math
Notice however that this rule may not be true if the involved differential entropies do not exist or are infinite.
Notice however that this rule may not be true if the involved differential entropies do not exist or are infinite.
然而,请注意,如果所涉及的微分熵不存在或者是无限的,那么这个规则可能不成立。
Joint differential entropy is also used in the definition of the mutual information between continuous random variables:
Joint differential entropy is also used in the definition of the mutual information between continuous random variables:
联合微分熵也用于连续随机变量之间互信息的定义:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \operatorname{I}(X,Y)=h(X)-h(X|Y)=h(Y)-h(Y|X) }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ \operatorname{I}(X,Y)=h(X)-h(X|Y)=h(Y)-h(Y|X) }[/math]
{ i }(x,y) h (x)-h (x | y) h (y)-h (y | x) / math
[math]\displaystyle{ h(X|Y) \le h(X) }[/math] with equality if and only if [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] are independent.[2]:253
[math]\displaystyle{ h(X|Y) \le h(X) }[/math] with equality if and only if [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] are independent.
数学 h (x | y) le h (x) / math with equality 当且仅当数学 x / math 和数学 y / math 是独立的。
Relation to estimator error
Relation to estimator error
与估计误差的关系
The conditional differential entropy yields a lower bound on the expected squared error of an estimator. For any random variable [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math], observation [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] and estimator [math]\displaystyle{ \widehat{X} }[/math] the following holds:[2]:255
The conditional differential entropy yields a lower bound on the expected squared error of an estimator. For any random variable [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math], observation [math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math] and estimator [math]\displaystyle{ \widehat{X} }[/math] the following holds:
条件微分熵对估计量的期望平方误差产生一个下限。对于任何随机变量的数学 x / math,观察数学 y / math 和估计数学 x / math,下面的观点成立:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbb{E}\left[\bigl(X - \widehat{X}{(Y)}\bigr)^2\right] \lt math display="block"\gt \mathbb{E}\left[\bigl(X - \widehat{X}{(Y)}\bigr)^2\right] 数学显示块“左”[ bigl (x-widehat {(y)} bigr) ^ 2] \ge \frac{1}{2\pi e}e^{2h(X|Y)} }[/math]
\ge \frac{1}{2\pi e}e^{2h(X|Y)}</math>
(x | y)} / math
This is related to the uncertainty principle from quantum mechanics.
This is related to the uncertainty principle from quantum mechanics.
这与量子力学的不确定性原理有关。
Generalization to quantum theory
Generalization to quantum theory
对量子理论的推广
In quantum information theory, the conditional entropy is generalized to the conditional quantum entropy. The latter can take negative values, unlike its classical counterpart.
In quantum information theory, the conditional entropy is generalized to the conditional quantum entropy. The latter can take negative values, unlike its classical counterpart.
在量子信息论中,条件熵被推广为条件量子熵。后者可以采取负值,不像它的古典对应物。
See also
See also
参见
References
References
参考资料
- ↑ "David MacKay: Information Theory, Pattern Recognition and Neural Networks: The Book". www.inference.org.uk. Retrieved 2019-10-25.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 T. Cover; J. Thomas (1991). Elements of Information Theory. ISBN 0-471-06259-6. https://archive.org/details/elementsofinform0000cove.
Category:Entropy and information
类别: 熵和信息
Category:Information theory
范畴: 信息论
This page was moved from wikipedia:en:Conditional entropy. Its edit history can be viewed at 条件熵/edithistory