Do演算
Do演算(Do-Calculus)是由三条推演规则构成的推演系统,这三条规则可以将包含干预变量和观测变量的概率分布表达式进行转化。
为何需要Do演算
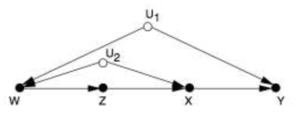
在处理一部分因果图时,可以使用后门调整和前门调整等技术进行统计调整,这样可以根据不涉及Do算子的数据来估算干预的效果。然而我们无法根据前门准则和后门准则事先确定一个给定的因果模型是否适用于这样的统计调整方式。后门调整和前门调整方法也无法处理所有可识别的模型,例如右侧的因果图是可识别的,但既无法使用后门调整也无法使用前门调整。
Do演算的规则集
在以下规则的表述中,使用符号[math]\displaystyle{ G_{\overline{X}} }[/math]表示删除有向图[math]\displaystyle{ G }[/math]中所有指向结点[math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math]的边后得到的子图,使用符号[math]\displaystyle{ G_{\overline{X}\underline{Z}} }[/math]表示删除有向图[math]\displaystyle{ G }[/math]中所有指向结点[math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math]的边和从结点[math]\displaystyle{ Z }[/math]指出的边后得到的子图。
规则一
增添或删除观察:
对于有向图[math]\displaystyle{ G }[/math],若满足[math]\displaystyle{ (Y \perp\!\!\!\perp Z \mid X, W)_{G_{\overline{X}}} }[/math](即在子图[math]\displaystyle{ G_{\overline{X}} }[/math]中,给定结点集[math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math]和[math]\displaystyle{ W }[/math]时,结点集[math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math]和[math]\displaystyle{ Z }[/math]满足d-分离条件),则
- [math]\displaystyle{ P(Y|do(X),Z,W)=P(Y|do(X),Z) }[/math]
规则二
交换干预和观察:
对于有向图[math]\displaystyle{ G }[/math],若满足[math]\displaystyle{ (Y \perp\!\!\!\perp Z \mid X, W)_{G_{\overline{X}\underline{Z}}} }[/math](即在子图[math]\displaystyle{ G_{\overline{X}\underline{Z}} }[/math]中,给定结点集[math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math]和[math]\displaystyle{ W }[/math]时,结点集[math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math]和[math]\displaystyle{ Z }[/math]满足d-分离条件),则
- [math]\displaystyle{ P(Y|do(X),do(Z),W)=P(Y|do(X),Z,W) }[/math]
规则三
增添或删除干预:
对于有向图[math]\displaystyle{ G }[/math],若满足[math]\displaystyle{ (Y \perp\!\!\!\perp Z \mid X, W)_{G_{\overline{X}\underline{Z(W)}}} }[/math](即在子图[math]\displaystyle{ G_{\overline{X}\underline{Z(W)}} }[/math]中,给定结点集[math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math]和[math]\displaystyle{ W }[/math]时,结点集[math]\displaystyle{ Y }[/math]和[math]\displaystyle{ Z }[/math]满足d-分离条件),则
- [math]\displaystyle{ P(Y|do(X),do(Z),W)=P(Y|do(X),W) }[/math]
其中符号[math]\displaystyle{ Z(W) }[/math] 表示 [math]\displaystyle{ Z / An(W)_{ G_{ \overline{X} } } }[/math] ,而符号[math]\displaystyle{ An(W)_{ G_{ \overline{X} } } }[/math] 表示在子图[math]\displaystyle{ G_{ \overline{X}} }[/math]中由结点集[math]\displaystyle{ W }[/math]及其祖先节点构成的点集。
Do演算的完备性(Completeness)
定理
[math]\displaystyle{ Q = P(y \mid do(x),z) }[/math] 是可识别的,当且仅当它可以被Do演算的三条规则转化为一个不包含Do算子的表达式。
证明
要证明上述定理的正确性,需要分别证明Do演算的可靠性(Soundness)和充分性(Sufficiency)。其中可靠性的证明由Judea Pearl于1995年给出[1],充分性的证明由Yimin Huang和Marco Valtorta于2006年给出[2]。
Do演算的应用
应用案例1
应用案例1
Do演算的相关算法
算法一
算法1
- ↑ Pearl, Judea (1995), "Causal diagrams for empirical research", Biometrika, 82 (4): 669–710, doi:10.1093/biomet/82.4.669.
- ↑ Huang, Yimin; Valtorta, Marco (2006). "Pearl's Calculus of Intervention is Complete". Proceedings of the Twenty-Second Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence: 217–224.