组合优化
组合优化是数学优化方法 Mathematical Optimization的一个子领域,与运筹学 Operations Research、算法理论 Algorithm Theory和计算复杂性理论 Computational Complexity有关。它在人工智能 Artificial Intelligence、机器学习 Machine Learning、拍卖理论 Auction Theory、软件工程 Software Engineering、应用数学 Applied Mathematics和理论计算机科学 Theoretical Computer Science等领域有着重要的应用。
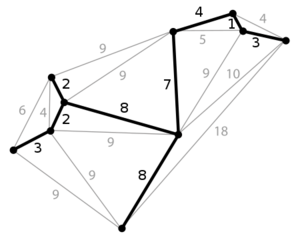
组合优化主要是从一个有限的对象集合中寻找一个最佳对象。在许多这样的问题中,穷举搜索 exhaustive search 是不易处理的。如果这些优化问题可行解集是离散的,或者可行解集可以化为离散的,那么可以在问题范围内进行运算,其目标是找到最优解。典型的问题是旅行商问题 Traveling Salesman Problem(“ TSP”)、最小生成树问题(“ MST”)和背包问题 Knapsack Problem。
一些研究文献[1]认为离散优化 Discrete Optimization 是由整数规划 Integer Programming和组合优化组成的(反过来由解决图结构的优化问题组成),尽管所有这些主题的研究文献都紧密地交织在一起。它通常涉及如何有效地分配用于寻找数学问题解决方案的资源的决策。
应用
组合优化的应用包括但不限于:
方法
对于某些特殊的离散优化问题,有大量的文献是关于多项式时间算法 Polynomial-Time Algorithm的,其中相当一部分是通过线性规划 Linear Programming理论统一起来的。属于这个框架的组合优化问题的一些例子包括最短路径 Shortest paths和最短路径树 Shortest-path Tree、流和循环 Flows And Circulations、生成树、匹配和拟阵 Matching And Matroid Problems问题。
对于NP完全 NP-Complete的离散优化问题,目前的研究文献包括以下主题:
- 多项式时间可精确解决的特殊问题(例如,固定参数可解)
- 在“随机”实例上表现良好的算法(例如,TSP)
- 近似算法 Approximation Algorithm在多项式时间内运行并找到一个“接近”最优值的解
- 解决现实世界中出现的实例,这些实例不一定表现出NP完全问题固有的最坏情况(例如,具有成千上万个节点的TSP实例)
组合优化问题可以看作是在一些离散项目中搜索最佳元素,因此,原则上,任何一种搜索算法或元启发式算法都可以用来解决它们。也许最普遍适用的方法是分支定界法 Branch-and-bound (一种可以在任何时间点停止来用作启发式的精确算法)、分支切割法 Branch-and-cut (使用线性最优化生成边界)、动态规划法 Dynamic Programming (一种有限搜索窗口的递归解构法)和禁忌搜索法 Tabu Search (一种贪婪交换算法)。然而,遗传搜索算法 Generic Search Algorithms 不能保证首先找到最优解,也不能保证快速运行(在多项式时间内)。由于一些离散优化问题是NP完全的,例如旅行商问题,除非P=NP,否则这是可以预期的。
形式化定义
从形式上来说,一个组合优化问题[math]\displaystyle{ A }[/math]是涉及四个变量[math]\displaystyle{ (I,f,m,g) }[/math]的问题 :
- [math]\displaystyle{ I }[/math]是实例中的数学集合;
- 给定[math]\displaystyle{ I }[/math]中的一个实例,[math]\displaystyle{ f(x) }[/math]是可行解的有限集合;
- 给定一个实例[math]\displaystyle{ x }[/math]和其对应的可行解[math]\displaystyle{ y }[/math],[math]\displaystyle{ m(x,y) }[/math]表示[math]\displaystyle{ y }[/math]的测度,其中,y通常是正实数。
- [math]\displaystyle{ g }[/math]是目标函数,可以是最小值也可以是最大值。
然后,我们的目标是找到实例[math]\displaystyle{ x }[/math]的一个最优解,也就是可行解[math]\displaystyle{ y }[/math]。
- [math]\displaystyle{ m(x, y) = g \{ m(x, y') \mid y' \in f(x) \} . }[/math]
对于每一个组合优化问题,都有一个相应的决策问题,它查找是否存在某一特定测度的可行解。例如,如果一个图形 [math]\displaystyle{ G }[/math] 包含顶点 [math]\displaystyle{ u }[/math] 和 [math]\displaystyle{ v }[/math] ,那么最优化问题可能是“找到一条从[math]\displaystyle{ u }[/math]到[math]\displaystyle{ v }[/math]使用最少边的路径”。这个问题的答案可能是,比方说,4。一个相应的决策问题是“是否存在一条从 [math]\displaystyle{ u }[/math] 到 [math]\displaystyle{ v }[/math] 使用10条或更少边的路径? ”这个问题可以用简单的“是”或“否”来回答。
在 近似算法approximation algorithms领域,算法被设计来寻找困难问题的近似最优解。因此,通常的决策版本对问题的定义不够充分,因为它只指定了可接受的解决办法。尽管我们可以引入合适的决策问题,使这个问题更自然地被描述为一个最优化问题。[4]
NP优化问题
NP优化问题(NPO)是一个具有以下附加条件的组合优化问题。[5]注意,下面提到的多项式是相应函数输入大小的函数,而不是某些隐式输入实例集大小的函数。
- 每个可行解[math]\displaystyle{ y\in f(x) }[/math]的大小都是由给定实例[math]\displaystyle{ x }[/math]的大小多项式约束的,
- 语言[math]\displaystyle{ \{\,x\,\mid\, x \in I \,\} }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \{\,(x,y)\, \mid\, y \in f(x) \,\} }[/math]在多项式时间内可以可判定语言/识别,并且,
- [math]\displaystyle{ m }[/math]是可计算的多项式时间。
这意味着相应的决策问题在NP中。在计算机科学中,有趣的优化问题通常具有上述性质,因此是NPO问题。如果存在一种在多项式时间内找到最优解的算法,则该问题又称为P-优化(PO)问题 P-optimization problem 。通常,在处理NPO类问题时,人们对决策版本为NP完全的优化问题感兴趣。请注意,硬度关系总是与某些降低有关。由于近似算法和计算优化问题之间的联系,在某些方面保持近似性的缩减比一般的图灵和卡普规约 Turing and Karp Reductions 更为可取。这种规约的一个例子就是L-规约 L-reduction 。因此,具有NP完全决策版本的优化问题不一定称为NPO完全问题。[6]
NPO问题根据其近似性可分为以下子类: [5]
- NPO(I):等价于完全多项式时间近似方案 Fully Polynomial-time approximation scheme | PTAS 。包含背包问题。
- NPO(II):等价于多项式时间近似方案 Polynomial-time approximation scheme | PTAS 。包含分批调度问题。
- NPO(III):具有多项式时间算法的NPO问题类,其计算的解的成本最多为最优成本的“c”倍(对于最小化问题),或成本至少为最优成本的[math]\displaystyle{ 1/c }[/math](对于最大化问题)。在尤拉·赫罗姆科维奇 Juraj Hromkovic 的书中,除了P=NP之外,所有的NPO(II)问题都被排除在这个类之外。如果没有排除,则等于APX(approximable)。包含最大可满足性问题 MAX-SAT 和标准的旅行商问题| TSP。
- NPO(IV):多项式时间算法的一类NPO问题,以比率为输入大小的对数多项式来逼近最优解。在Hromkovic的书中,除非P=NP,否则所有的NPO(III)-问题都不属于此类。包含集合覆盖问题。
- NPO(V):多项式时间算法的一类NPO问题,以某个函数限定的比率来逼近最优解。在Hromkovic的书中,除非P=NP,否则所有NPO(IV)-问题都不属于这类问题。包含旅行商问题| TSP和团问题|最大团问题 Clique problem|Max Clique problems 。
如果对于每个实例[math]\displaystyle{ x }[/math]和[math]\displaystyle{ f(x) }[/math]中的每个解[math]\displaystyle{ y }[/math],其测度[math]\displaystyle{ m(x,y) , M(x,y) }[/math]被一个大小为[math]\displaystyle{ x }[/math]的多项式函数所限制,则该NPO问题称为多项式有界(PB)。NPOPB 类是一类多项式有界的 NPO 问题。
特定问题
- 指派问题 Assignment Problem
- 封闭性问题 Closure Problem
- 约束满足问题 Constraint Satisfaction Problem
- 切割问题 Cutting Stock Problem
- 控制集问题 Dominating Set
- 整数规划 Integer Programming
- 背包问题 Knapsack Problem
- 线性系统中的最小相关变量 Minimum Relevant Variables In Linear System
- 最小生成树 Minimum Spanning Tree
- 护士调度问题 Nurse Scheduling Problem
- 集合覆盖问题 Set Cover Problem
- 旅行商问题 Traveling Salesman Problem
- 车辆重新调度问题 Vehicle Rescheduling Problem
- 车辆线路优化问题 Vehicle Routing Problem
- 武器目标分配问题 Weapon Target Assignment Problem
参见
- 约束复合图
注解
- ↑ Discrete Optimization. Elsevier. http://www.elsevier.com/locate/disopt. Retrieved 2009-06-08.
- ↑ Sbihi, Abdelkader; Eglese, Richard W. (2007). "Combinatorial optimization and Green Logistics" (PDF). 4Or. 5 (2): 99–116. doi:10.1007/s10288-007-0047-3.
- ↑ Eskandarpour, Majid; Dejax, Pierre; Miemczyk, Joe; Péton, Olivier (2015). "Sustainable supply chain network design: An optimization-oriented review" (PDF). Omega. 54: 11–32. doi:10.1016/j.omega.2015.01.006.
- ↑ Ausiello, Giorgio; et al. (2003), Complexity and Approximation (Corrected ed.), Springer
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Hromkovic, Juraj (2002), Algorithmics for Hard Problems, Texts in Theoretical Computer Science (2nd ed.), Springer
- ↑ Kann, Viggo (1992), On the Approximability of NP-complete Optimization Problems, Royal Institute of Technology, Sweden
参考文献
- Beasley, J. E. "Integer programming" (lecture notes).
- Cook, William J.; Cunningham, William H.; Pulleyblank, William R.; Schrijver, Alexander (1997). Combinatorial Optimization. Wiley. ISBN 0-471-55894-X.
- Cook, William (2016). "Optimal TSP Tours". University of Waterloo. (Information on the largest TSP instances solved to date.)
- Crescenzi, Pierluigi; Kann, Viggo; Halldórsson, Magnús (eds.). "A Compendium of NP Optimization Problems". (This is a continuously updated catalog of approximability results for NP optimization problems.)
- Quantum Annealing and Related Optimization Methods. Lecture Notes in Physics. 679. Springer. 2005. Bibcode 2005qnro.book.....D.
- Das, Arnab; Chakrabarti, Bikas K (2008). "Colloquium: Quantum annealing and analog quantum computation". Rev. Mod. Phys. 80 (3): 1061. arXiv:0801.2193. Bibcode:2008RvMP...80.1061D. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.563.9990. doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.80.1061.
- Lawler, Eugene (2001). Combinatorial Optimization: Networks and Matroids. Dover. ISBN 0-486-41453-1.
- Lee, Jon (2004). A First Course in Combinatorial Optimization. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-01012-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=3pL1B7WVYnAC.
- Papadimitriou, Christos H.; Steiglitz, Kenneth (July 1998). Combinatorial Optimization : Algorithms and Complexity. Dover. ISBN 0-486-40258-4.
- Schrijver, Alexander (2003). Combinatorial Optimization: Polyhedra and Efficiency. Algorithms and Combinatorics. 24. Springer. ISBN 9783540443896. https://books.google.com/books?id=mqGeSQ6dJycC.
- Schrijver, Alexander (2005). "On the history of combinatorial optimization (till 1960)". Handbook of Discrete Optimization. Elsevier. pp. 1–68. http://homepages.cwi.nl/~lex/files/histco.pdf.
- Schrijver, Alexander (February 1, 2006). A Course in Combinatorial Optimization. http://homepages.cwi.nl/~lex/files/dict.pdf.
- Sierksma, Gerard; Ghosh, Diptesh (2010). Networks in Action; Text and Computer Exercises in Network Optimization. Springer. ISBN 978-1-4419-5512-8.
- Gerard Sierksma; Yori Zwols (2015). Linear and Integer Optimization: Theory and Practice. CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-498-71016-9.
- Pintea, C-M. (2014). Advances in Bio-inspired Computing for Combinatorial Optimization Problem. Intelligent Systems Reference Library. Springer. ISBN 978-3-642-40178-7. https://www.springer.com/la/book/9783642401787.
外部链接
- Java Combinatorial Optimization Platform (open source code)
编者推荐
本中文词条由信白初步编译,Flipped审校,糖糖编辑,如有问题,欢迎在讨论页面留言。
本词条内容源自wikipedia及公开资料,遵守 CC3.0协议。