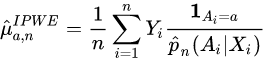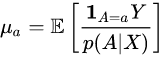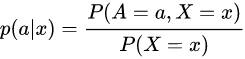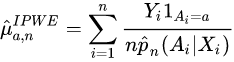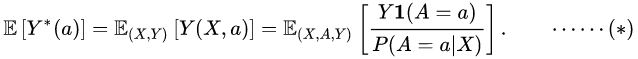双稳健
Inverse probability weighting is a statistical technique for calculating statistics standardized to a pseudo-population different from that in which the data was collected. Study designs with a disparate sampling population and population of target inference (target population) are common in application. There may be prohibitive factors barring researchers from directly sampling from the target population such as cost, time, or ethical concerns. A solution to this problem is to use an alternate design strategy, e.g. stratified sampling. Weighting, when correctly applied, can potentially improve the efficiency and reduce the bias of unweighted estimators.
One very early weighted estimator is the Horvitz–Thompson estimator of the mean. When the sampling probability is known, from which the sampling population is drawn from the target population, then the inverse of this probability is used to weight the observations. This approach has been generalized to many aspects of statistics under various frameworks. In particular, there are weighted likelihoods, weighted estimating equations, and weighted probability densities from which a majority of statistics are derived. These applications codified the theory of other statistics and estimators such as marginal structural models, the standardized mortality ratio, and the EM algorithm for coarsened or aggregate data.
Inverse probability weighting is also used to account for missing data when subjects with missing data cannot be included in the primary analysis. With an estimate of the sampling probability, or the probability that the factor would be measured in another measurement, inverse probability weighting can be used to inflate the weight for subjects who are under-represented due to a large degree of missing data.
Inverse Probability Weighted Estimator (IPWE)
The inverse probability weighting estimator can be used to demonstrate causality when the researcher cannot conduct a controlled experiment but has observed data to model. Because it is assumed that the treatment is not randomly assigned, the goal is to estimate the counterfactual or potential outcome if all subjects in population were assigned either treatment.
Suppose observed data are ![]() drawn i.i.d (independent and identically distributed) from unknown distribution P, where
drawn i.i.d (independent and identically distributed) from unknown distribution P, where
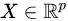 covariates
covariates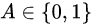 are the two possible treatments.
are the two possible treatments.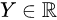 response
response- We do not assume treatment is randomly assigned.
The goal is to estimate the potential outcome,![]() , that would be observed if the subject were assigned treatment . Then compare the mean outcome if all patients in the population were assigned either treatment:
, that would be observed if the subject were assigned treatment . Then compare the mean outcome if all patients in the population were assigned either treatment:![]() . We want to estimate using observed data
. We want to estimate using observed data ![]() .
.
Estimator Formula[edit]
Constructing the IPWE[edit]
With the mean of each treatment group computed, a statistical t-test or ANOVA test can be used to judge difference between group means and determine statistical significance of treatment effect.
Assumptions[edit]
Recall the joint probability model (X,A,Y)~P for the covariate X , action A, and response Y. If X and A are known as x and a, respectively, then the response Y(X=x,A=a)=Y(x=a)has the distribution
We make the following assumptions.
- (A1) Consistency: Y=Y*(A)
- (A2) No unmeasured confounders:
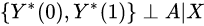 . More formally, for each bounded and measurable functions and ,
. More formally, for each bounded and measurable functions and , 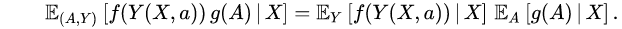 This means that treatment assignment is based solely on covariate data and independent of potential outcomes.
This means that treatment assignment is based solely on covariate data and independent of potential outcomes. - (A3) Positivity:
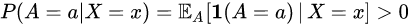 for all a and x.
for all a and x.
Formal derivation[edit]
Under the assumptions (A1)-(A3), we will derive the following identities
The first equality follows from the definition and (A1). For the second equality, first use the iterated expectation to write
![]() By (A3),
By (A3), ![]() almost surely. Then using (A2), note that
almost surely. Then using (A2), note that
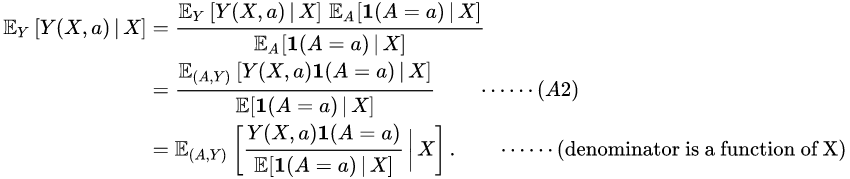 Hence integrating out the last expression with respect to and noting that
Hence integrating out the last expression with respect to and noting that ![]() almost surely, the second equality in follows.
almost surely, the second equality in follows.
Limitations[edit]
The Inverse Probability Weighted Estimator (IPWE) can be unstable if estimated propensities are small. If the probability of either treatment assignment is small, then the logistic regression model can become unstable around the tails causing the IPWE to also be less stable.
Augmented Inverse Probability Weighted Estimator (AIPWE)
An alternative estimator is the augmented inverse probability weighted estimator (AIPWE) combines both the properties of the regression based estimator and the inverse probability weighted estimator. It is therefore a 'doubly robust' method in that it only requires either the propensity or outcome model to be correctly specified but not both. This method augments the IPWE to reduce variability and improve estimate efficiency. This model holds the same assumptions as the Inverse Probability Weighted Estimator (IPWE).
Estimator Formula
With the following notations:
- is an indicator function if subject i is part of treatment group a (or not).
- Construct regression estimator to predict outcome based on covariates and treatment , for some subject i. For example, using ordinary least squares regression.
- Construct propensity (probability) estimate . For example, using logistic regression.
- Combine in AIPWE to obtain
Interpretation and "double robustness"
The later rearrangement of the formula helps reveal the underlying idea: our estimator is based on the average predicted outcome using the model (i.e.: ). However, if the model is biased, then the residuals of the model will not be (in the full treatment group a) around 0. We can correct this potential bias by adding the extra term of the average residuals of the model (Q) from the true value of the outcome (Y) (i.e.: ). Because we have missing values of Y, we give weights to inflate the relative importance of each residual (these weights are based on the inverse propensity, a.k.a. probability, of seeing each subject observations) (see page 10 in ).
The "doubly robust" benefit of such an estimator comes from the fact that it's sufficient for one of the two models to be correctly specified, for the estimator to be unbiased (either or , or both). This is because if the outcome model is well specified then its residuals will be around 0 (regardless of the weights each residual will get). While if the model is biased, but the weighting model is well specified, then the bias will be well estimated (And corrected for) by the weighted average residuals.
The bias of the doubly robust estimators is called a second-order bias, and it depends on the product of the difference and the difference . This property allows us, when having a "large enough" sample size, to lower the overall bias of doubly robust estimators by using machine learning estimators (instead of parametric models).