Effective Information
Effective Information (EI) is a core concept in the theory of Causal Emergence, used to measure the strength of causal effects in Markov dynamics. In this context, causal effect refers to the extent to which different input distributions lead to different output distributions when viewing the dynamics as a black box. The degree of this connection is the causal effect. EI can typically be decomposed into two components: Determinism and Degeneracy. Determinism indicates how well the next state of the system can be predicted from its previous state, while Degeneracy refers to how well one can infer the previous state from the next state. A system with higher Determinism or lower Degeneracy will have higher Effective Information. In this page, all [math]log[/math] represent logarithmic operations with a base of 2.
Historical Background
The concept of Effective Information (EI) was first introduced by Giulio Tononi in 2003 as a key measure in Integrated Information Theory[1]. A system is said to have a high degree of integration when there is a strong causal connection among its components, and EI is the metric used to quantify this degree of causal connection.
In 2013, Giulio Tononi's student, Erik Hoel, further refined the concept of EI to quantitatively characterize emergence, leading to the development of the theory of Causal Emergence[2]. In this theory, Hoel used Judea Pearl's "do" operator to modify the general mutual information metric, which made EI fundamentally different from mutual information. While mutual information measures correlation, EI—due to the use of the "do" operator—measures causality. The article also introduced a normalized version of EI, referred to as Eff.
Traditionally, EI was primarily applied to discrete-state Markov chains. To extend this to continuous domains, P. Chvykov and E. Hoel collaborated in 2020 to propose the theory of Causal Geometry, expanding EI's definition to function mappings with continuous state variables. By incorporating Information Geometry, they explored a perturbative form of EI and compared it with Fisher Information, proposing the concept of Causal Geometry. However, this method of calculating EI for continuous variables required the assumption of infinitesimal variance for normal distribution variables, which was an overly stringent condition.
In 2022, to address the calculation of EI in general feedforward neural networks, Zhang Jiang and Liu Kaiwei removed the variance constraint from the Causal Geometry approach and explored a more general form of EI. Nonetheless, a limitation remained: because the uniform distribution of variables in the real-number domain is strictly defined over an infinite space, the calculation of EI involved a parameter [math]L[/math], representing the range of the uniform distribution. To avoid this issue and enable comparisons of EI at different levels of granularity, the authors proposed the concept of dimension-averaged EI. They found that the measure of causal emergence defined by dimension-averaged EI was solely dependent on the determinant of the neural network's Jacobian matrix and the variance of the random variables in the two compared dimensions, independent of other parameters such as [math]L[/math]. Additionally, dimension-averaged EI could be viewed as a normalized EI, or Eff.
Essentially, EI is a quantity that depends only on the dynamics of a Markov system—specifically on the Markov state transition matrix—and is independent of the distribution of state variables. However, this point was not previously highlighted. In a 2024 review by Yuan Bing and others, the authors emphasized this fact and provided an explicit form of EI that depends only on the Markov state transition matrix. In their latest work on dynamical reversibility and causal emergence, Zhang Jiang and colleagues pointed out that EI is actually a characterization of the reversibility of the underlying Markov transition matrix, and they attempted to directly characterize the reversibility of Markov chain dynamics as a replacement for EI.
Overview
The EI metric is primarily used to measure the strength of causal effects in Markov dynamics. Unlike general causal inference theories, EI is used in cases where the dynamics (the Markov transition probability matrix) are known and no unknown variables (i.e., confounders) are present. Its core objective is to measure the strength of causal connections, rather than the existence of causal effects. This means EI is more suitable for scenarios where a causal relationship between variables X and Y is already established.
Formally, EI is a function of the causal mechanism (in a discrete-state Markov chain, this is the probability transition matrix of the Markov chain) and is independent of other factors. The formal definition of EI is:
[math]\displaystyle{ EI(P)\equiv I(Y;X|do(X\sim U)) }[/math]
where P represents the causal mechanism from X to Y, which is a probability transition matrix, [math]p_{ij}\equiv Pr(Y=j|X=i)[/math]; X is the cause variable, Y is the effect variable, and [math]do(X\sim U)[/math] denotes the intervention on X, changing its distribution to a uniform one. Under this intervention, and assuming the causal mechanism P remains unchanged, Y will be indirectly affected by the intervention on X. EI measures the mutual information between X and Y after this intervention.
The introduction of the "do" operator aims to eliminate the influence of X's distribution on EI, ensuring that the final EI metric is only a function of the causal mechanism f and is independent of X's distribution.
Below are three examples of Markov chains, with their respective EI values included:
| [math]\displaystyle{ P_1=\begin{pmatrix} &0 &0 &1 &0& \\ &1 &0 &0 &0& \\ &0 &0 &0 &1& \\ &0 &1 &0 &0& \\ \end{pmatrix} }[/math], | [math]\displaystyle{ P_2=\begin{pmatrix} &1/3 &1/3 &1/3 &0& \\ &1/3 &1/3 &1/3 &0& \\ &1/3 &1/3 &1/3 &0& \\ &0 &0 &0 &1& \\ \end{pmatrix} }[/math], | [math]\displaystyle{ P_3=\begin{pmatrix} &0 &0 &1 &0& \\ &1 &0 &0 &0& \\ &1 &0 &0 &0& \\ &1 &0 &0 &0& \\ \end{pmatrix} }[/math]. |
| [math]\begin{aligned}&EI(P_1)=2\ bits,\\&Det(P_1)=2\ bits,\\&Deg(P_1)=0\ bits\end{aligned}[/math] | [math]\begin{aligned}&EI(P_2)=0.81\ bits,\\&Det(P_2)=0.81\ bits,\\&Deg(P_2)=0\ bits\end{aligned}[/math] | [math]\begin{aligned}&EI(P_3)=0.81\ bits\\&Det(P_3)=2\ bits,\\&Deg(P_3)=1.19\ bits.\end{aligned}[/math] |
-
(example)
As we can see, the EI of the first matrix [math]P_1[/math] is higher than that of the second [math]P_2[/math] because this probability transition is fully deterministic: starting from a particular state, it transitions to another state with 100% probability. However, not all deterministic matrices correspond to high EI, such as matrix [math]P_3[/math]. Although its transition probabilities are also either 100% or 0, because all of the last three states transition to the first state, we cannot distinguish which state it was in the previous moment. Therefore, its EI is low, which we call degeneracy. Hence, if a transition matrix has high determinism and low degeneracy, its EI will be high. Additionally, EI can be decomposed as follows:
[math]\displaystyle{ EI=Det-Deg }[/math]
Where Det stands for Determinism, and Deg stands for Degeneracy. EI is the difference between the two. In the table, we also list the values of Det and Deg corresponding to the matrices.
The first transition probability matrix is a permutation matrix and is reversible; thus, it has the highest determinism, no degeneracy, and therefore the highest EI. The second matrix's first three states transition to each other with a 1/3 probability, resulting in the lowest determinism but also low degeneracy, yielding an EI of 0.81. The third matrix, despite having binary transitions, has high degeneracy because all three states transition to state 1, meaning we cannot infer their previous state. Thus, its EI equals that of the second matrix at 0.81.
Although EI was originally applied to discrete-state Markov chains, Zhang Jiang, Liu Kaiwei, and Yang Mingzhe extended the definition to more general continuous-variable cases. This extension builds on EI's original definition by intervening on the cause variable X as a uniform distribution over a sufficiently large bounded interval, [math][-\frac{L}{2}, \frac{L}{2}]^n[/math]. The causal mechanism is assumed to be a conditional probability that follows a Gaussian distribution with a mean function [math]f(x)[/math] and covariance matrix [math]\Sigma[/math]. Based on this, the EI between the causal variables is then measured. The causal mechanism here is determined by the mapping [math]f(x)[/math] and the covariance matrix, which together define the conditional probability [math]Pr(y|x)[/math].
More detailed explanations follow.
The Do-Operator and Its Explanation
The original definition of effective information (EI) was based on discrete Markov chains. However, to expand its applicability, we explore a more general form of EI here.
Formal Definition
Consider two random variables, [math]X[/math] and [math]Y[/math], representing the cause variable and the effect variable, respectively. Let their value ranges be [math]\mathcal{X}[/math] and [math]\mathcal{Y}[/math]. The effective information (EI) from [math]X[/math] to [math]Y[/math] is defined as:
[math]\displaystyle{ EI\equiv I(X:Y|do(X\sim U(\mathcal{X})))\equiv I(\tilde{X}:\tilde{Y}) }[/math]
Here, [math]do(X\sim U(\mathcal{X}))[/math] represents applying a do-intervention (or do-operator) on [math]X[/math], making it follow a uniform distribution [math]U(\mathcal{X})[/math] over [math]\mathcal{X}[/math], which corresponds to a maximum entropy distribution. [math]\tilde{X}[/math] and [math]\tilde{Y}[/math] represent the variables after the [math]do[/math]-intervention on [math]X[/math] and [math]Y[/math], respectively, where:
[math]\displaystyle{ Pr(\tilde{X}=x)=\frac{1}{\#(\mathcal{X})}, }[/math]
This means that the main difference between [math]\tilde{X}[/math] after the intervention and [math]X[/math] before the intervention is their distributions: [math]\tilde{X}[/math] follows a uniform distribution over [math]\mathcal{X}[/math], while [math]X[/math] may follow any arbitrary distribution. [math]\#(\mathcal{X})[/math] represents the cardinality of the set [math]\mathcal{X}[/math], or the number of elements in the set if it is finite.
According to Judea Pearl's theory, the do-operator cuts off all causal arrows pointing to variable [math]X[/math], while keeping other factors unchanged, particularly the causal mechanism from [math]X[/math] to [math]Y[/math]. The causal mechanism is defined as the conditional probability of [math]Y[/math] taking any value [math]\mathcal{Y}[/math] given [math]X[/math] takes a value [math]y\in \mathcal{Y}[/math]:
[math]\displaystyle{ f\equiv Pr(Y=y|X=x) }[/math]
In the intervention, this causal mechanism [math]f[/math] remains constant. When no other variables are influencing the system, this leads to a change in the distribution of [math]Y[/math], which is indirectly intervened upon and becomes:
[math]\displaystyle{ Pr(\tilde{Y}=y)=\sum_{x\in \mathcal{X}}Pr(X=x) Pr(Y=y|X=x)=\sum_{x\in \mathcal{X}} \frac{Pr(Y=y|X=x)}{\#(\mathcal{X})}. }[/math]
Among them, [math]\tilde{Y}[/math] represents the [math]Y[/math] variable indirectly changed by [math]X[/math]'s do-intervention while maintaining the causal mechanism [math]f[/math] unchanged, and this change is mainly reflected in the change of probability distribution.
Therefore, the effective information (EI) of a causal mechanism [math]f[/math] is the mutual information between the intervened cause variable [math]\tilde{X}[/math] and the intervened effect variable [math]\tilde{Y}[/math].
Why Use the Do-Operator?
While EI is essentially a measure of mutual information, it differs from traditional mutual information by including the do-operator, which applies an intervention to the input variable. Why is this intervention necessary?
According to Judea Pearl’s ladder of causality, causal inference can be divided into three levels: association, intervention, and counterfactuals. The higher the level, the stronger the causal features. Directly estimating mutual information from observational data measures the level of association. If we can intervene in the variables, i.e., set a variable to a specific value or make it follow a particular distribution, we move up to the intervention level. By introducing the do-operator in the definition of EI, we allow EI to capture causal features more effectively than mutual information alone.
From a practical perspective, incorporating the do-operator in EI’s calculation separates the data from the dynamics, eliminating the effect of the data distribution (i.e., the distribution of X) on the EI measurement. In causal graphs, the do-operator cuts off all causal arrows pointing to the intervened variable, preventing confounding factors from creating spurious associations. Similarly, in EI’s definition, the do-operator removes all causal arrows pointing to the cause variable X, including influences from other variables (both observable and unobservable). This ensures that EI captures the intrinsic characteristics of the dynamics itself.
The introduction of the do-operator makes EI distinct from other information metrics. The key difference is that EI is solely a function of the causal mechanism, which allows it to more precisely capture the essence of causality compared to other metrics like transfer entropy. However, this also means that EI requires knowledge of or access to the causal mechanism, which may be challenging if only observational data is available.
Why Intervene to Achieve a Uniform Distribution?
In Erik Hoel's original definition, the do operation intervenes on the dependent variable X, transforming it into a uniform distribution over its domain X (which is also the maximum entropy distribution). So, why should we intervene to achieve a uniform distribution? Can other distributions be used?
Firstly, according to the previous section, the essence of the do operation is to allow the Effective Information (EI) to better describe the nature of the causal mechanism f. Therefore, it is necessary to sever the connection between the dependent variable X and other variables and change its distribution so that the EI metric becomes independent of the distribution of X.
The reason for intervening to achieve a uniform distribution for the input variable is to more accurately characterize the properties of the causal mechanism.
This is because, when both X and Y are finite, countable sets, the causal mechanism f≡Pr(Y=y∣X=x) becomes a matrix with #(X) rows and #(Y) columns. We can expand the definition of EI:
-
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{aligned} EI &= I(X,Y|do(X)\sim U)= \sum_{x\in\mathcal{X}}\sum_{y\in\mathcal{Y}}Pr(X=x,Y=y)\log \frac{Pr(X=x,Y=y)}{Pr(X=x)Pr(Y=y)}\\ &= \sum_{x\in\mathcal{X}}\sum_{y\in\mathcal{Y}}Pr(X=x)Pr(Y=y|X=x)\log \frac{Pr(Y=y|X=x)}{Pr(Y=y)}\\ &= \sum_{x\in\mathcal{X}}\sum_{y\in\mathcal{Y}}Pr(X=x)Pr(Y=y|X=x)\log Pr(Y=y|X=x)- \sum_{x\in\mathcal{X}}\sum_{y\in\mathcal{Y}}Pr(X=x)Pr(Y=y|X=x)\log Pr(Y=y) \\ &=\frac{1}{\#(\mathcal{X})}\left(-\sum_{x\in\mathcal{X}}H(Pr(Y|X))\right) + H(Pr(Y)) \end{aligned} }[/math]
(1)
It is easy to see that the final equation tells us that EI is actually composed of two terms: the first term is the average of the negative entropy of each row of the causal mechanism matrix, and the second term is the entropy of the variable Y. In the first term, the probability distribution Pr(X=x) of X acts as the weight when averaging the entropy of each row. Only when we set this weight to be the same value (i.e., intervene to make X uniformly distributed) can we treat each row of the causal mechanism matrix equally.
If the distribution is not uniform, some rows will be assigned a larger weight, while others will be given a smaller weight. This weight represents a certain "bias," which prevents the EI from reflecting the natural properties of the causal mechanism.
Effective Information of Markov Chains
Introduction to Markov Chains
In this section, all Markov transition probability matrices are denoted as P. N is the total number of states.
Erik Hoel and colleagues first proposed the measure of causality, Effective Information (EI), on the Markov dynamics with discrete states, also known as Markov chains. Therefore, this section introduces the specific form of EI on Markov chains.
A Markov chain refers to a type of stationary stochastic process with discrete states and discrete time. Its dynamics can generally be represented by a Transitional Probability Matrix (TPM), also known as a probability transition matrix or state transition matrix.
Specifically, a Markov chain consists of a set of random variables Xt, which take values in the state space X={1,2,⋯,N}, where t typically represents time. A transition probability matrix is a probability matrix, where the element in the i-th row and j-th column, pij, represents the probability of the system transitioning from state i at any time t to state j at time t+1. Each row satisfies the normalization condition: ∑j=1Npij=1.
[math]\displaystyle{ \sum_{j=1}^Np_{ij}=1, }[/math]
The state transition matrix can be viewed as the dynamics of the Markov chain because the probability distribution of the state at any time t+1, Pr(Xt), can be uniquely determined by the probability distribution of the state at the previous time t and the state transition matrix, satisfying the relationship: Pr(Xt+1=j)=∑i=1Npij⋅Pr(Xt=i), where i,j∈X are arbitrary states in X, and N=#(X), the total number of states in X.
[math]\displaystyle{ Pr(X_{t+1}=j)=\sum_{i=1}^N p_{ij}\cdot Pr(X_t=i), }[/math]
The following table presents three different transition probability matrices and their EI values:
| [math]\displaystyle{ P_1=\begin{pmatrix} &0 &0 &1 &0& \\ &1 &0 &0 &0& \\ &0 &0 &0 &1& \\ &0 &1 &0 &0& \\ \end{pmatrix} }[/math], | [math]\displaystyle{ P_2=\begin{pmatrix} &1/3 &1/3 &1/3 &0& \\ &1/3 &1/3 &1/3 &0& \\ &0 &0 &0 &1& \\ &0 &0 &0 &1& \\ \end{pmatrix} }[/math], | [math]\displaystyle{ P_3=\begin{pmatrix} &1/4 &1/4 &1/4 &1/4& \\ &1/4 &1/4 &1/4 &1/4& \\ &1/4 &1/4 &1/4 &1/4& \\ &1/4 &1/4 &1/4 &1/4& \\ \end{pmatrix} }[/math]. |
| [math]EI(P_1)=2[/math] bits | [math]EI(P_2)=1[/math] bits | [math]EI(P_3)=0[/math] bits |
For these three Markov chains, the state space is X={1,2,3,4}, so the size of their TPM is 4×4.
EI of Markov Chains
In a Markov chain, the state variable at any time Xt can be considered as the cause, and the state variable at the next time Xt+1 can be considered as the effect. Thus, the state transition matrix of a Markov chain is its causal mechanism. Therefore, we can apply the definition of Effective Information to Markov chains. [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{aligned} EI &= I(X_t,X_{t+1}|do(X_t)\sim U(\mathcal{X}))=I(\tilde{X}_t,\tilde{X}_{t+1}) \\ &= \sum^N_{i=1}\sum^N_{j=1}Pr(\tilde{X}_t=i,\tilde{X}_{t+1}=j)\log \frac{Pr(\tilde{X}_t=i,\tilde{X}_{t+1}=j)}{Pr(\tilde{X}_t=i)Pr(\tilde{X}_{t+1}=j)}\\ &= \sum^N_{i=1}Pr(\tilde{X}_t=i)\sum^N_{j=1}Pr(\tilde{X}_{t+1}=j|\tilde{X}_t=i)\log \frac{Pr(\tilde{X}_{t+1}=j|\tilde{X}_t=i)}{Pr(\tilde{X}_{t+1}=j)}\\ &= \frac{1}{N}\sum^N_{i=1}\sum^N_{j=1}p_{ij}\log\frac{N\cdot p_{ij}}{\sum_{k=1}^N p_{kj}} \end{aligned} }[/math]
Here, X~t,X~t+1 are the states at times t and t+1 after intervening to make Xt uniformly distributed, and pij is the probability of transitioning from state i to state j. From this equation, it is clear that EI is merely a function of the probability transition matrix P.
Vector Form of EI in Markov Chains
We can also represent the transition probability matrix P as a concatenation of N row vectors, i.e.:
[math]\displaystyle{ P=(P_1,P_2,\cdots,P_N)^T }[/math]
Where Pi is the i-th row vector of matrix P, and it satisfies the normalization condition for conditional probabilities: ∣∣Pi∣∣1=1, where ∣∣⋅∣∣1 denotes the L1-norm of a vector. Then, EI can be written as follows:
-
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{aligned} EI &= \frac{1}{N}\sum^N_{i=1}\sum^N_{j=1}p_{ij}\log\frac{N\cdot p_{ij}}{\sum_{k=1}^N p_{kj}}\\ &=\frac{1}{N}\cdot \sum_{i=1}^N\left(P_i\cdot \log P_i - P_i\cdot\log \bar{P}\right)\\ &=\frac{1}{N}\sum_{i=1}^N D_{KL}(P_i||\bar{P}) \end{aligned} }[/math]
(2)
By averaging the columns of the matrix, we obtain the average transition vector P=∑k=1NPk/N. DKL is the KL divergence between two distributions. Therefore, EI is the average KL divergence between each row transition vector Pi and the average transition vector P.
For the three state transition matrices listed above, their respective EI values are: 2 bits, 1 bit, and 0 bits. This shows that if more 0s or 1s appear in the transition probability matrix (i.e., if more of the row vectors are one-hot vectors, where one position is 1 and the others are 0), the EI value will be higher. In other words, the more deterministic the jump from one time to the next, the higher the EI value tends to be. However, this observation is not entirely precise, and more exact conclusions are provided in the following sections.
Normalization
Clearly, the magnitude of EI (Effective Information) is related to the size of the state space, which poses challenges when comparing Markov chains of different scales. To address this issue, we need a causal measure that is as independent of scale effects as possible. Therefore, we normalize EI to derive a metric that is independent of the system size.
According to the work of Erik Hoel and Tononi, the normalization process involves using the entropy under a uniform (i.e., maximum entropy) distribution as the denominator, which is [math]\log N[/math], where [math]N[/math] is the number of states in the state space [math]\mathcal{X}[/math][1]. Thus, the normalized EI becomes: Normalized EI=logNEI
[math]\displaystyle{ Eff=\frac{EI}{\log N} }[/math]
This normalized metric is also referred to as effectiveness.
However, when dealing with continuous state variables, normalizing EI by using the logarithm of the number of states in the state space may not be suitable, as the state number often depends on the dimensionality and the resolution of real numbers.
Determinism and Degeneracy
Decomposition of EI
From Equation (1), we see that EI can actually be decomposed into two terms:
EI=−⟨H(Pi)⟩+H(Pˉ)
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{aligned} EI&=\frac{1}{\#(\mathcal{X})} \left(-\sum_{x\in\mathcal{X}}H(Pr(Y|X))\right) + H\left(Pr(Y)\right)\\ \end{aligned} }[/math]
Similarly, in the context of Markov chains, EI can be decomposed as:
EI=−⟨H(Pi)⟩+H(Pˉ)
-
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{aligned} EI &= \frac{1}{N}\cdot \sum_{i=1}^N\left(P_i\cdot \log P_i - P_i\cdot\log \bar{P}\right)\\ &=\underbrace{-\langle H(P_i)\rangle}_{确定性项}+\underbrace{H(\bar{P})}_{非简并性项} \end{aligned} }[/math]
(tow_terms)
Where the first term, [math] -\langle H(P_i) \rangle = \frac{1}{N}\sum_{i=1}^N H(P_i) [/math], represents the negative average entropy of each row vector [math]P_i[/math], which measures the determinism of the Markov transition matrix.
The second term, [math] H(\bar{P}) [/math], is the entropy of the average row vector, where [math]\bar{P} = \frac{1}{N}\sum_{i=1}^N P_i [/math], and it measures the non-degeneracy of the Markov transition matrix.
Determinism and Degeneracy
In the above definition, the determinism and non-degeneracy terms are negative. To prevent this, we redefine the determinism of a Markov chain transition matrix [math]P[/math] as:
Determinism=−⟨H(Pi)⟩+logN
[math]\displaystyle{ Determinism \equiv \log N - \langle H(P_i)\rangle = \frac{1}{N}\sum_{i=1}^N \sum_{j=1}^N p_{ij}\log \left(N\cdot p_{ij}\right) }[/math]
This term is an average negative entropy, where the addition of [math]\log N[/math] prevents it from being negative. Determinism quantifies the certainty in predicting the system's next state given its current state. The reason lies in the fact that when a vector is closer to a uniform distribution, its entropy is larger, and when it is closer to a "one-hot" vector (where one element is 1 and others are 0), its entropy is smaller. The row vectors of the Markov transition matrix indicate the probabilities of transitioning from the current state to various future states. When the average negative entropy of the row vectors is high, it means that one element of the row vector has a probability of 1 while others are 0, indicating that the system will definitely transition to a specific state.
We also define the degeneracy of a Markov chain transition matrix [math]P[/math] as: Degeneracy=H(Pˉ)+logN
[math]\displaystyle{ Degeneracy \equiv \log N - H(\bar{P})=\log N + \sum_{j=1}^N \bar{P}_{\cdot j}\log \bar{P}_{\cdot j}=\sum_{j=1}^N \frac{\sum_{i=1}^Np_{ij}}{N}\log \left(\sum_{i=1}^Np_{ij}\right) }[/math]
This term measures degeneracy or non-degeneracy. The more difficult it is to infer the previous state from the current state, the higher the degeneracy of the Markov matrix. Degeneracy can be described using the negative entropy of the average row vector. If the row vectors of [math]P[/math] are linearly independent "one-hot" vectors, the average distribution will approximate a uniform distribution, resulting in maximum Shannon entropy, i.e., [math]\log N[/math]. In this case, the Markov transition matrix is reversible, indicating that we can deduce the previous state from the current state. Therefore, this Markov matrix is non-degenerate, and the computed degeneracy is zero.
Conversely, when all row vectors of [math]P[/math] are identical, the average vector is also a "one-hot" vector with minimum entropy. In this case, it is challenging to infer the previous state from the current state, leading to a degenerate (or non-reversible) Markov matrix, with a computed degeneracy equal to [math]\log N[/math].
In more general situations, if the row vectors of [math]P[/math] resemble a matrix formed by independent "one-hot" vectors, [math]P[/math] becomes less degenerate. On the other hand, if the row vectors are identical and close to a "one-hot" vector, [math]P[/math] becomes more degenerate.
Example
Below, we examine the determinism and degeneracy of three Markov chains.
| [math]\displaystyle{ P_1=\begin{pmatrix} &0 &0 &1 &0& \\ &1 &0 &0 &0& \\ &0 &0 &0 &1& \\ &0 &1 &0 &0& \\ \end{pmatrix} }[/math], | [math]\displaystyle{ P_2=\begin{pmatrix} &1/3 &1/3 &1/3 &0& \\ &1/3 &1/3 &1/3 &0& \\ &1/3 &1/3 &1/3 &0& \\ &0 &0 &0 &1& \\ \end{pmatrix} }[/math], | [math]\displaystyle{ P_3=\begin{pmatrix} &0 &0 &1 &0& \\ &1 &0 &0 &0& \\ &1 &0 &0 &0& \\ &1 &0 &0 &0& \\ \end{pmatrix} }[/math]. |
| [math]\begin{aligned}&Det(P_1)=2\ bits,\\&Deg(P_1)=0\ bits,\\&EI(P_1)=2\ bits\end{aligned}[/math] | [math]\begin{aligned}&Det(P_2)=0.81\ bits,\\&Deg(P_2)=0\ bits,\\&EI(P_2)=0.81\ bits\end{aligned}[/math] | [math]\begin{aligned}&Det(P_3)=2\ bits,\\&Deg(P_3)=1.19\ bits,\\&EI(P_3)=0.81\ bits\end{aligned}[/math] |
- The first transition probability matrix is a permutation matrix, which is invertible. It has the highest determinism and no degeneracy, leading to the maximum EI.
- The second matrix has the first three states transitioning to one another with equal probability (1/3), resulting in the lowest determinism but non-degeneracy, with EI being 0.81.
- The third matrix is deterministic but since three of the states transition to the first state, it's impossible to infer from state 1 which previous state led to it. Therefore, it has high degeneracy, and its EI is also 0.81, the same as the second.
Normalized Determinism and Degeneracy
In Erik Hoel's original paper, determinism and degeneracy are presented in a normalized form by dividing them by a scale-dependent quantity. To distinguish between the two, we refer to the normalized quantities as the determinism coefficient and the degeneracy coefficient.
Specifically, Eric Hall et al. decomposed the normalized valid information, i.e., Eve, corresponding to the determinism coefficient and the degeneracy coefficient.
[math]\displaystyle{ Eff = Determinism\ Coefficient - Degeneracy\ Coefficient }[/math]
The definitions of these two items are:
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{aligned} &Determinism\ Coefficient = \frac{1}{N\log N}\sum_{i,j}p_{ij}\log\left(N\cdot {p_{ij}}\right) \\ &Degeneracy\ Coefficient = \frac{1}{N\log N}\sum_{ij}p_{ij}\log{\left(\sum_k p_{k,j}\right)} \end{aligned} }[/math]
In summary, determinism refers to how much confidence we have in predicting future states based on the current state's probability distribution, while degeneracy refers to how much certainty we have in inferring previous states from the current state. Systems with high determinism and low degeneracy exhibit strong causal dynamics.
Properties of the EI Function
From Equation 2, we can see that in the transition probability matrix P, EI is a function of each element, representing the conditional probabilities of transitioning from one state to another. Thus, a natural question arises: What mathematical properties does this function have? Does it have extreme points, and if so, where are they? Is it convex? What are its maximum and minimum values?
Domain
In the case of Markov chains with discrete states and discrete time, the domain of EI is clearly the transition probability matrix P. P is a matrix composed of N×N elements, each representing a probability value pij∈[0,1]. Additionally, each row must satisfy the normalization condition, meaning for any ∀i∈[1,N], the sum of the row's probabilities equals:
-
[math]\displaystyle{ ||P_i||_1=\sum_{j=1}^N p_{ij}=1 }[/math]
(3)
Thus, the domain of EI, which is the possible space for P, is not the entire real space RN2. Due to the normalization condition, it is a subspace of the N×N-dimensional real space. How can we express this subspace?
For any row vector Pi, its value range is a hyper simplex in N-dimensional real space. For example, when N=2, this space is a line segment: pi,1+pi,2=1. When N=3, this space is a plane in three-dimensional space: pi,1+pi,2+pi,3=1. These two spaces are illustrated below:
In the general case, we define the value range space of the row vector Pi in N-dimensional space as Δ={pj∣∑j=1Npj=1,pj∈[0,1]}. The Cartesian product of N such spaces forms the domain of EI:
[math]\displaystyle{ Dom(EI)=\Delta\times \Delta\cdots\times\Delta=\Delta^N }[/math]
First Derivative and Extreme Points
Taking the first derivative of Equation 2 with respect to pij, and considering the normalization condition ∑j=1Npij=1, we get:
-
[math]\displaystyle{ \frac{\partial EI}{\partial p_{ij}}=\log\left(\frac{p_{ij}}{p_{iN}}\right)-\log\left(\frac{\bar{p}_{\cdot j}}{\bar{p}_{\cdot N}}\right), }[/math]
(3)
Here, pij denotes the conditional probability of transitioning from state i to state j in matrix P. Since each row of P is subject to the normalization constraint, the EI function has N(N−1) degrees of freedom. We can select 1≤i≤N and 1≤j≤N−1, with piN representing the conditional probability in the i-th row and N-th column. pˉ⋅j and pˉ⋅N represent the average conditional probabilities of the j-th and N-th columns, respectively.
It is easy to see that this derivative is defined only when, for the selected i,j∈[1,N], the probabilities pij,piN,pˉ⋅j,pˉ⋅N are all greater than 0. Otherwise, if any of these terms are 0, the derivative does not exist.
Setting Equation 3 to 0 yields the extreme points. For any 1≤i≤N,1≤j≤N−1, the following equation holds:
[math]\displaystyle{ p_{ij}=\bar{p}_{\cdot j}=\frac{1}{N}\sum_{k=1}^Np_{kj} }[/math]
It is straightforward to compute that in this case, EI=0, indicating that EI reaches an extreme point. From the second derivative of EI, we can easily determine that this is a minimum point. In other words, EI has many minimum points, as long as all the row vectors of the transition probability matrix are identical. Regardless of the specific distribution of these row vectors, EI will be zero.
Second Derivative and Convexity
To explore the convexity of the EI function, we can compute its second derivative[math]\displaystyle{ \frac{\partial^2 EI}{\partial p_{ij}\partial p_{st}} }[/math], where 1≤s≤N and 1≤t≤N−1. First, we introduce a function symbol δi,j,
[math]\displaystyle{ \delta_{i,j} = \begin{cases} 0 & \text{if } i\ne j,\\ 1 & \text{if } i = j. \end{cases} }[/math]
Then, proceed to derive the second derivative. When [math]\displaystyle{ i=s }[/math],
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{equation} \begin{aligned} \frac{\partial^2 EI}{\partial p_{ij}\partial p_{it}}&=\frac{\delta_{j,t}}{N}\left(\frac{1}{p_{ij}}-\frac{1}{N\cdot \bar{p}_{\cdot j}}\right)+\frac{1}{N\cdot p_{iN}}-\frac{1}{N^2\cdot \bar{p}_{\cdot N}}\\ &=\delta_{j,t}\frac{\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}p_{k j}-p_{ij}}{N^2\cdot p_{ij}\cdot \bar{p}_{\cdot j}}+\frac{\sum_{k=1}^{N-1}p_{k N}-p_{iN}}{N^2\cdot p_{iN}\cdot \bar{p}_{\cdot N}}\\ &=\delta_{j,t}\frac{\sum_{k\neq i}p_{kj}}{N^2\cdot p_{ij}\cdot \bar{p}_{\cdot j}}+\frac{\sum_{k\neq i}p_{k N}}{N^2\cdot p_{iN}\cdot \bar{p}_{\cdot N}}\gt 0, \end{aligned} \end{equation} }[/math]
When [math]\displaystyle{ i\ne s }[/math],
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{equation} \frac{\partial^2 EI}{\partial p_{ij}\partial p_{st}}=-\frac{\delta_{j,t}}{N^2\cdot \bar{p}_{\cdot j}}-\frac{1}{N^2\cdot \bar{p}_{\cdot N}}\lt 0. \end{equation} }[/math]
In summary, the second derivative of EI is:
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{equation} \frac{\partial^2 EI}{\partial p_{ij}\partial p_{st}}=\frac{1}{N}\cdot\left(\frac{\delta_{i,s}\delta_{j,t}}{p_{ij}}+\frac{\delta_{i,s}}{p_{iN}}-\frac{\delta_{j,t}}{N\cdot\bar{p}_{\cdot j}}-\frac{1}{N\cdot \bar{p}_{\cdot N}}\right). \end{equation} }[/math]
Moreover, the second derivative is positive when i=s and negative when i=s. Therefore, EI is neither convex nor concave.
Minimum Value
From the first derivative of EI, we discussed the extreme value problem, showing that EI reaches a minimum of 0 when all the row vectors of the transition matrix are identical. Is this minimum value the lowest possible?
We know that based on Equation 2, EI is essentially a form of KL divergence, which is always non-negative. Thus:
[math]\displaystyle{ EI\geq 0 }[/math]
The equality holds when pij=pˉ⋅j for all i,j. Hence, 0 is the minimum value of EI, with the minimum point being:
[math]\displaystyle{ EI_{min}=0. }[/math]
Maximum Value
From the previous discussion on determinism and degeneracy, we know that EI can be decomposed into two parts:
[math]\displaystyle{ EI = -\langle H(P_i)\rangle + H(\bar{P}), }[/math]
The definition of entropy is: [math]\displaystyle{ H(P_i)=-\sum_{j=1}^Np_{ij}\log p_{ij} }[/math]. Looking separately, the maximum value of the previous equation is 0, that is:
[math]\displaystyle{ - H(P_i)\leq 0, }[/math]
When [math]\displaystyle{ P_i }[/math] is a solitary heat vector without uncertainty, the equal sign of this equation holds. This occurs when Pi is a deterministic one-hot vector. Therefore, when all Pi are one-hot vectors, we have:
So, when [math]\displaystyle{ P_i }[/math] is the sole heating variable for all i, there is:
[math]\displaystyle{ -\langle H(P_i)\rangle=0 }[/math]
Established. On the other hand, there is also an inequality that holds for the entropy of the average vector of all row vectors in P,
[math]\displaystyle{ H(\bar{P})\leq \log N, }[/math]
The equal sign holds when the condition [math]\displaystyle{ \bar{P}=\frac{1}{N}\cdot \mathbb{1} }[/math] is satisfied.
[math]\displaystyle{ EI\leq 0+\log N=\log N }[/math]
When the equal sign of these two equations holds simultaneously, that is, when [math]\displaystyle{ P_i }[/math] is a solitary heat vector and [math]\displaystyle{ \bar{P} }[/math] is uniformly distributed (at this time, it is necessary to require [math]P_i[/math] to be perpendicular to each other, that is, P is a permutation matrix) — EI reaches its maximum value of:
[math]\displaystyle{ EI_{max}=\log N }[/math]
Analytical Solution of the Simplest Markov Chain
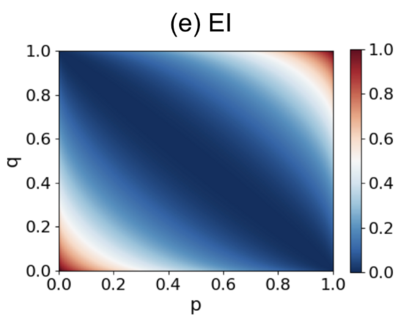
We consider the simplest 2x2 Markov chain matrix:
[math]\displaystyle{ P=\begin{pmatrix}p & 1-p \\1-q & q\end{pmatrix}, }[/math]
Here, [math]p[/math] and [math]q[/math] are parameters that take values in the range [math][0,1][/math].
The EI (Effective Information) of this transition probability matrix, which depends on p and q, can be calculated using the following analytical solution:
[math]\displaystyle{ EI=\frac{1}{2}\left[p\log_2\frac{2p}{1+p-q}+(1-p)\log_2\frac{2(1-p)}{1-p+q}\right. + \left.(1-q)\log_2\frac{2(1-q)}{1+p-q}+q\log_2\frac{2q}{1-p+q}\right] }[/math]
The diagram below shows how EI changes with different values of [math]p[/math] and [math]q[/math].
It is clear from the graph that when p+q=1, meaning that all the row vectors are identical, EI reaches its minimum value of 0. Otherwise, as p and q increase along the direction perpendicular to p+q=1, EI increases, with the maximum value being 1.
Causal Emergence
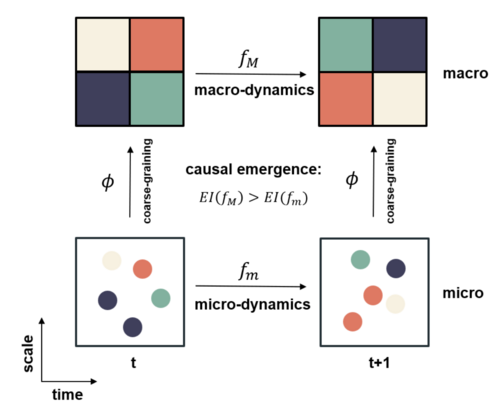
With the metric of Effective Information (EI) in place, we can now discuss causal emergence in Markov chains. For a Markov chain, an observer can adopt a multi-scale perspective to distinguish between micro and macro levels. First, the original Markov transition matrix P defines the micro-level dynamics. Second, after a coarse-graining process that maps microstates into macrostates (typically by grouping microstates together), the observer can obtain a macro-level transition matrix P′, which describes the transition probabilities between macrostates. We can compute EI for both dynamics. If the macro-level EI is greater than the micro-level EI, we say that the system exhibits causal emergence.
A new metric can be defined to directly measure the degree of causal emergence:
[math]\displaystyle{ CE = EI(P') - EI(P) }[/math]
Here, P is the microstate Markov transition matrix with dimensions N×N, where N is the number of microstates. P′ is the macro-state transition matrix obtained after coarse-graining, with dimensions M×M, where M<N represents the number of macrostates.
The process of coarse-graining a Markov transition matrix typically involves two steps: 1) grouping N microstates into M macrostates, and 2) reducing the Markov transition matrix accordingly. For more details on the specific methods for coarse-graining a Markov chain, refer to the topic of Markov chain coarse-graining.
If the computed CE>0, the system is said to exhibit causal emergence; otherwise, it does not.
Below, we demonstrate a specific example of causal emergence:
| [math]\displaystyle{ P_m=\begin{pmatrix} &1/3 &1/3 &1/3 &0& \\ &1/3 &1/3 &1/3 &0& \\ &1/3 &1/3 &1/3 &0& \\ &0 &1 &0 &1& \\ \end{pmatrix} }[/math], | [math]\displaystyle{ P_M=\begin{pmatrix} &1 &0 & \\ &0 &1 & \\ \end{pmatrix} }[/math]. |
| [math]\begin{aligned}&Det(P_m)=0.81\ bits,\\&Deg(P_m)=0\ bits,\\&EI(P_m)=0.81\ bits\end{aligned}[/math] | [math]\begin{aligned}&Det(P_M)=1\ bits,\\&Deg(P_M)=0\ bits,\\&EI(P_M)=1\ bits\end{aligned}[/math] |
In this example, the microstate transition matrix is a 4x4 matrix, where the first three states transition to each other with a probability of 1/3. This leads to a transition matrix with relatively low determinism, and thus, the EI is not very high, with a value of 0.81. However, when we coarse-grain this matrix—merging the first three states into one macrostate a, and the last state becomes another macrostate b—all transitions between the original three microstates now become internal transitions within macrostate a. Thus, the transition probability matrix becomes PM, with an EI of 1. In this case, the causal emergence can be measured as:
[math]\displaystyle{ CE=EI(P_M)-EI(P_m)=1-0.81=0.19\ bits }[/math]
That is, there is 0.19 bits of causal emergence.
Sometimes, causal emergence is calculated using the normalized EI, defined as:
[math]\displaystyle{ ce=Eff(P_M)-Eff(P_m)=1-0.405=0.595 }[/math]
Since normalized EI eliminates the effect of system size, the measure of causal emergence becomes larger.
Python Source Code for Calculating EI
Below is the Python source code for calculating EI for a Markov transition matrix. The input tpm is a Markov transition matrix that satisfies the row normalization condition. The returned values are ei_all, which is the EI, and other parameters such as effectiveness (eff), determinism (det), degeneracy (deg), determinism coefficient (det_c), and degeneracy coefficient (deg_c).
python:
def tpm_ei(tpm, log_base = 2):
'''
tpm: 输入的概率转移矩阵,可以是非方阵
log_base:对数的底
ei_all:EI的值
det:EI中确定性的部分
deg:EI中简并性的部分
eff:有效性
det_c:确定性系数
deg_c:简并性系数
'''
# marginal distribution of y given x ~ Unifrom Dist
puy = tpm.mean(axis=0)
m,n = tpm.shape
if m > n:
q = n
else:
q = m
# replace 0 to a positive number to avoid log error
eps = 0.5
tpm_e = np.where(tpm==0, eps, tpm)
puy_e = np.where(puy==0, eps, puy)
# calculate EI of specific x
ei_x = (np.log2(tpm_e / puy_e) / np.log2(log_base) * tpm).sum(axis=1)
# calculate det and deg
det = np.log2(n) + (tpm * np.log2(tpm_e)).sum(axis=1).mean(axis=0)
deg = np.log2(n) + (puy * np.log2(puy_e)).sum()
det = det / np.log2(log_base)
deg = deg / np.log2(log_base)
det_c = det / np.log2(q) * np.log2(log_base)
deg_c = deg / np.log2(q) * np.log2(log_base)
# calculate total EI
ei_all = ei_x.mean()
eff = ei_all / np.log2(q) * np.log2(log_base)
return ei_all,det,deg,eff,det_c,deg_c
tpm_ei(mi_states)
EI for Continuous Variables
In reality, most systems need to be considered in continuous spaces, so it is necessary to extend the concept of EI to continuous systems.
The core idea of this extension is to simplify the causal mechanism in continuous space into a deterministic function mapping f(X), combined with a noise variable ξ. In the cases listed below, ξ∼N(0,Σ), meaning it follows a Gaussian distribution, allowing us to obtain an analytical expression for EI. For more general cases, there is no literature available for discussion yet.
Random Function Mapping
Initially, Erik Hoel considered this and proposed the framework of causal geometry. This framework not only discusses the calculation of EI for random function mappings but also introduces the concepts of intervention noise and causal geometry. It defines the local form of EI and draws analogies and comparisons with information geometry. Below, we will discuss one-dimensional and multi-dimensional function mappings and the local form of EI.
One-Dimensional Function Mapping
First, let's consider the simplest case:
[math]\displaystyle{ y=f(x)+\varepsilon, \varepsilon\sim\mathcal{N}(0,\sigma^2) }[/math]
Here, [math]x,y\in \mathcal{R}[/math] are both one-dimensional real variables. According to the definition of Effective Information (EI), we need to intervene on variable x so that it follows a uniform distribution over its domain. If the domain of x is a fixed interval, such as [a,b], where a and b are real numbers, the probability density function of x is [math]1/(b-a)[/math]. However, if the domain of x extends over the entire real line, the interval becomes infinite, making the probability density function of x infinitesimally small.
To address this issue, we assume that the domain of x is not the entire real line but rather a sufficiently large region: [math][-L/2,L/2][/math], where L represents the size of the interval. In this case, the uniform distribution's density function over this region is [math]1/L[/math]. We hope that as [math]L\rightarrow +\infty[/math], the EI will converge to a finite value. However, EI is actually a quantity dependent on the size of the domain of x, so EI is a function of the parameter L, which can be seen from the definition of EI:
-
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{aligned} EI&=I(y;x|do(x\sim U[-L/2,L/2]))\\ &=\int_{-\frac{L}{2}}^{\frac{L}{2}}\int_{f([-\frac{L}{2},\frac{L}{2}])}p(x)p(y|x)\ln\frac{p(y|x)}{p(y)}dydx\\ &=\int_{-\frac{L}{2}}^{\frac{L}{2}}\int_{f([-\frac{L}{2},\frac{L}{2}])}p(x)p(y|x)\ln p(y|x)dydx -\int_{-\frac{L}{2}}^{\frac{L}{2}}\int_{f([-\frac{L}{2},\frac{L}{2}])}p(x)p(y|x)\ln p(y)dydx \end{aligned} }[/math]
(4)
Here, [math]p(y|x)=\frac{1}{\sigma\sqrt{2\pi}}\exp\left(-\frac{(y-f(x))^2}{\sigma^2}\right)[/math] is the conditional probability density of y given x. Since [math]\varepsilon[/math] follows a normal distribution with mean 0 and variance [math]\sigma^2[/math], [math]y=f(x)+\varepsilon[/math] follows a normal distribution with mean [math]f(x)[/math] and variance [math]\sigma^2[/math].
The integration range of y is [math]f([-\frac{L}{L},\frac{L}{2}])[/math], i.e., the range of y is formed by mapping the domain [math][-\frac{L}{2},\frac{L}{2}][/math] of x through the function f.
[math]\displaystyle{ p(y)=\int_{-\frac{L}{2}}^{\frac{L}{2}}p(x_0)p(y|x_0)dx_0=\int_{-\frac{L}{2}}^{\frac{L}{2}}\frac{1}{L}\frac{1}{\sigma\sqrt{2\pi}}\exp\left(-\frac{(y-f(x_0))^2}{\sigma^2}\right)dx_0 }[/math]
The marginal probability density function of y, p(y), can be obtained by integrating the joint probability density function [math]p(x,y)=p(x)p(y|x)[/math] over x. To facilitate the subsequent discussion, we rename x as [math]x_0[/math] to distinguish it from other x variables in equation 4.
Since L is large, the interval [math][-\frac{L}{2},\frac{L}{2}][/math] is large, and hence, we assume that the interval [math]f([-\frac{L}{L},\frac{L}{2}])[/math] is also large. This allows us to approximate the integration limits as infinite, which gives the first term in equation 4:
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{aligned} \int_{-\frac{L}{2}}^{\frac{L}{2}}\int_{f([-\frac{L}{2},\frac{L}{2}])}p(x)p(y|x)\ln p(y|x)dydx&\approx \int_{-\infty}^{\infty}\int_{-\infty}^{\infty}p(x)p(y|x)\ln p(y|x)dydx\\ &=\int_{-\infty}^{\infty}\int_{-\infty}^{\infty}\frac{1}{L}\frac{1}{\sigma\sqrt{2\pi}}\exp\left(-\frac{(y-f(x))^2}{\sigma^2}\right)\ln\left[\frac{1}{\sigma\sqrt{2\pi}}\exp\left(-\frac{(y-f(x))^2}{\sigma^2}\right)\right]dydx\\ &=\ln(\frac{1}{\sigma\cdot\sqrt{2\pi e}}) \end{aligned} }[/math]
Here, e is the base of the natural logarithm, and the last equality is derived using the Shannon entropy formula for a Gaussian distribution.
However, calculating the second term remains challenging, even with the assumption of infinite integration limits. Therefore, we perform a first-order Taylor expansion on the function [math]f(x_0)[/math]:
[math]\displaystyle{ f(x_0)\approx f(x)+f'(x)(x_0-x) }[/math]
Here, [math]x\in[-\frac{L}{2},\frac{L}{2}][/math] is any point within the domain of x.
Thus, p(y) can be approximated:
[math]\displaystyle{ p(y)=\int_{-\frac{L}{2}}^{\frac{L}{2}}\frac{1}{L}\frac{1}{\sigma\sqrt{2\pi}}\exp\left(-\frac{(y-f(x_0))^2}{\sigma^2}\right)dx_0\approx \int_{-\infty}^{\infty}\frac{1}{L}\frac{1}{\sigma\sqrt{2\pi}}\exp\left(-\frac{(y-f(x)-f'(x)(x_0-x))^2}{\sigma^2}\right)dx_0\approx \frac{1}{L}\cdot\frac{1}{f'(x)} }[/math]
It is important to note that in this step, we not only approximate [math]f(x_0)[/math]as a linear function but also introduce an assumption that the result of p(y) is independent of y and depends on [math]x[/math]. Since the second term of the EI calculation includes an integration over x, this approximation implies that p(y) is approximately different at different values of x.
Thus, the second term in equation 4 can be approximated as:
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{aligned} \int_{-\frac{L}{2}}^{\frac{L}{2}}\int_{f([-\frac{L}{2},\frac{L}{2}])}p(x)p(y|x)\ln p(y)dydx\approx -\ln L - \frac{1}{L}\int_{-\frac{L}{2}}^{\frac{L}{2}}\ln f'(x)dx \end{aligned} }[/math]
The final EI can be approximately computed using the following equation:
[math]\displaystyle{ EI\approx \ln(\frac{L}{\sqrt{2\pi e}})+\frac{1}{2L}\int_{-\frac{L}{2}}^{\frac{L}{2}}\ln \left(\frac{f'(x)}{\sigma}\right)^2dx }[/math]This kind of derivation was first seen in Hoel's 2013 paper [1] and was further discussed in detail in the "Neural Information Squeezer" paper [2].
High-Dimensional Case
We can extend the EI (Effective Information) calculation for one-dimensional variables to a more general n-dimensional scenario. Specifically:
-
[math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{y}=f(\mathbf{x})+\xi, }[/math]
(5)
Let [math]\xi\sim \mathcal{N}(0,\Sigma)[/math], where [math]\displaystyle{ \Sigma }[/math] is the covariance matrix of the Gaussian noise [math]\displaystyle{ \xi }[/math]. First, we intervene on [math]\mathbf{x}[/math] such that it follows a uniform distribution over [math]\displaystyle{ [-L/2,L/2]^n\subset\mathcal{R}^n }[/math], where [math]\displaystyle{ [-L/2,L/2]^n }[/math] represents a hypercube in n-dimensional space. We assume [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{y}\in\mathcal{R}^m }[/math], where [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ m }[/math] are positive integers. In the presence of observational noise only, the EI can be generalized as follows:
-
[math]\displaystyle{ EI\approx \ln\left(\frac{L^n}{(2\pi e)^{m/2}}\right)+\frac{1}{L^n}\int_{-[\frac{L}{2},\frac{L}{2}]^n}\ln\left|\det\left(\frac{\partial_\mathbf{x} f(\mathbf{x})}{\Sigma^{1/2}}\right)\right| d\mathbf{x}, }[/math]
(6)
Where [math]\displaystyle{ |\cdot| }[/math] denotes the absolute value, and [math]\displaystyle{ \det }[/math] refers to the determinant.
Dimension-Averaged EI
In discrete-state systems, when comparing systems of different scales, we can compute either the direct EI difference or the normalized EI difference. Normalized EI is divided by [math]\log N[/math], where [math]N=#(\mathcal{X})[/math] represents the number of elements in the discrete state space [math]\mathcal{X}[/math].
However, for continuous variables, if the original EI is used, an unreasonable result may occur. Firstly, as shown in equation (6), the EI formula contains a term [math]\ln L^n[/math]. Since L is a large positive number, the EI result will be significantly affected by L. Secondly, when calculating normalized EI (Eff), the issue arises that for continuous variables, the number of elements in the state space is infinite. A potential solution is to treat the volume of the space as the number N, and thus normalize it by [math]n \ln L[/math], meaning it is proportional to n and ln L:
[math]\displaystyle{ Eff=\frac{EI}{\ln L^n}\approx 1-\frac{m\ln\left(2\pi e\right)}{2n \ln L}+\frac{1}{n\ln L}\int_{[-\frac{L}{2},\frac{L}{2}]^n}\frac{1}{L^n}\cdot \ln\left|\det\left(\frac{\partial_\mathbf{x} f(\mathbf{x})}{\Sigma^{1/2}}\right)\right| d\mathbf{x}, }[/math]
However, this still contains the L term, affecting Eff significantly. Moreover, when comparing microscopic (n-dimensional) and macroscopic (m-dimensional, where m < n) Eff, the L term cannot be eliminated. This suggests that the normalization issue in continuous variable systems cannot simply be transferred from the discrete case.
When the Neural Information Squeezer (NIS) framework was proposed, the authors invented another way to normalize EI for continuous variables using state space dimensions. This approach solves the EI comparison problem for continuous state variables, introducing the Dimension-Averaged Effective Information (dEI):
[math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal{J}\equiv\frac{EI}{n} }[/math]
Where n is the dimension of the state space. It can be proven that in the discrete state space, dimension-averaged EI and Eff are actually equivalent. The EI for continuous variables will be further discussed below.
For n-dimensional iterative dynamical systems, [math]\mathbf{y}[/math] and [math]\mathbf{x}[/math] are variables of the same dimension, meaning [math]m=n[/math]. Substituting equation (6) into the dimension-averaged EI gives:
[math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal{J}=\frac{EI}{n}\approx \ln L - \frac{1}{2}\ln (2\pi e)+\frac{1}{n}\int_{[-\frac{L}{2},\frac{L}{2}]^n}\frac{1}{L^n}\cdot \ln\left|\det\left(\frac{\partial_\mathbf{x} f(\mathbf{x})}{\Sigma^{1/2}}\right)\right| d\mathbf{x} }[/math]
Although L has not disappeared, when calculating the dimension-averaged causal emergence—where the n-dimensional state variable [math]\mathbf{x}_t[/math] is projected onto an N-dimensional macroscopic state variable [math]\mathbf{X}_t[/math]—and the corresponding macrodynamics F and noise covariance [math]\Sigma'[/math], the difference between the macrodynamics and microdynamics' dimension-averaged EI is:
[math]\displaystyle{ \Delta \mathcal{J}\equiv \mathcal{J_F}-\mathcal{J_f}=\frac{EI_F}{N}-\frac{EI_f}{n}\approx \frac{1}{N}\int_{-[\frac{L}{2},\frac{L}{2}]^N}\frac{1}{L^N}\cdot \ln \left|\det\left(\frac{\partial_\mathbf{X} F(\mathbf{X})}{\Sigma'^{1/2}}\right)\right| dX - \frac{1}{n}\int_{[-\frac{L}{2},\frac{L}{2}]^n}\frac{1}{L^n}\cdot \ln\left|\det\left(\frac{\partial_\mathbf{x} f(\mathbf{x})}{\Sigma^{1/2}}\right)\right| d\mathbf{x} }[/math]
Note that the integral in the above equation can be written as the expectation under a uniform distribution, i.e. [math]\int_{[-\frac{L}{2},\frac{L}{2}]}\frac{1}{L^n}\cdot=\mathbb{E}_{\mathbf{x}\sim \mathcal{U}[-\frac{L}{2},\frac{L}{2}]^n}\cdot[/math], then the above equation is transformed into:[math]\displaystyle{ \Delta \mathcal{J}\approx \frac{1}{N}\mathbb{E}_{X\sim\mathcal{U}[-\frac{L}{2},\frac{L}{2}]^N}\ln \left|\det\left(\frac{\partial_\mathbf{X} F(\mathbf{X})}{\Sigma'^{1/2}}\right)\right| - \frac{1}{n}\mathbb{E}_{\mathbf{x}\sim\mathcal{U}[-\frac{L}{2},\frac{L}{2}]^n}\ln\left|\det\left(\frac{\partial_\mathbf{x} f(\mathbf{x})}{\Sigma^{1/2}}\right)\right| }[/math]
Here [math]\mathcal{U}([-\frac{L}{2},\frac{L}{2}]^n)[/math] represents the uniform distribution on the cube [math][-\frac{L}{2},\frac{L}{2}]^n[/math]. From this, it can be seen that although L is still implicitly included in the expectation, all terms in the equation that explicitly contain L are eliminated. In actual numerical calculations, the expected calculation can be manifested as taking the average of multiple samples on [math][-\frac{L}{2},\frac{L}{2}]^n[/math], and therefore is also independent of the size of L. This demonstrates the rationality of introducing dimension averaged EI.
Random Iterative Systems
We can extend the above results to linear iterative dynamical systems. For an iterative system of the form:
[math]\displaystyle{ x_{t+1}=Ax_t+\varepsilon_t, }[/math]
Where [math]A\in\mathcal{R}^{n\times n}[/math] is a full-rank n*n matrix representing the dynamics of the linear iterative system, and [math]\varepsilon_t\sim\mathcal{N}(0,\Sigma)[/math] is n-dimensional Gaussian noise with mean zero and covariance matrix [math]\Sigma[/math]. Among them, the covariance matrix [math]\Sigma[/math] is also full rank.
可以看出这一迭代系统可以看做是公式5的特例,其中[math]y[/math]对应这里的[math]x_{t+1}[/math],[math]f(x_t)[/math]即是[math]A x_t[/math]。
为定义EI,设干预空间大小为[math]\displaystyle{ L }[/math],对于单步的映射我们可以得到维度平均有效信息
, the EI for a single step mapping is:
[math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal{J}(A,\Sigma)\equiv \frac{EI(A,\Sigma)}{n}=\frac{1}{n}\ln\displaystyle\frac{|\det(A)|L^n}{(2\pi e)^\frac{n}{2}\displaystyle \det(\Sigma)^\frac{1}{2}}=\ln\displaystyle\frac{|\det(A)|^\frac{1}{n}L}{(2\pi e)^\frac{1}{2}\displaystyle \det(\Sigma)^\frac{1}{2n}}. }[/math]
随机迭代系统的有效信息可以分解确定性和简并性为两项,
[math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal{J}=\mathcal{J}_1-\mathcal{J}_2 }[/math]
其中确定性
[math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal{J}_1\equiv-\left\lt H(p(x_{t+1}|x_t))\right\gt =-\ln\left[(2\pi e)^\frac{n}{2}\det(\Sigma)^\frac{1}{2}\right] }[/math]
描述系统前一时刻状态已知的情况下,后一时刻的随机性,确定性越强,随机性越小,越容易对系统未来趋势进行预测;
简并性:
[math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal{J}_2\equiv-H(\tilde{x}_{t+1}))=-\ln\left(|\det(A)|L^n\right) }[/math]
描述后一时刻已知的情况下,对前一时刻的可追溯性,简并性越弱,越容易推断系统以往的演化路径。其中,[math]\tilde{x}_{t+1}[/math]是保持因果机制不变,经过干预以后得到的新的[math]x_{t+1}[/math]变量。
确定性越强,简并性越弱,有效信息则会越大,因果效应越强。
宏观有效信息与微观有效信息做差之后就可以得到随即迭代系统的因果涌现为:
[math]\displaystyle{ \Delta\mathcal{J}=\ln\frac{|\det(WAW^{\dagger})|^{1/N}}{|\det(A)|^{1/n}}-\ln\frac{|\det(W\Sigma W^T)|^{\frac{1}{2N}}}{|\det(\Sigma)|^{\frac{1}{2n}}} }[/math]
其中,[math]W[/math]为粗粒化矩阵,它的阶数为n*m,m为宏观状态空间的维度,它的作用是把任意的微观态[math]x_t[/math]映射为宏观态[math]y_t[/math]。[math]W^{\dagger}[/math]为W的伪逆运算。式中第一项是由确定性引发的涌现,简称确定性涌现(Determinism Emergence),第二项为简并性引发的涌现,简称简并性涌现。更详细的内容参看随机迭代系统的因果涌现。
The effective information of a random iterative system can be decomposed into two terms: determinism and degeneracy.
- Determinism describes the predictability of the system's future state based on the current state.
- Degeneracy describes the ability to trace back the previous state from the current state.
The stronger the determinism and the weaker the degeneracy, the greater the effective information, leading to stronger causal effects.
前馈神经网络
针对复杂系统自动建模任务,我们往往使用神经网络来建模系统动力学。具体的,对于前馈神经网络来说,张江等人推导出了前馈神经网络有效信息的计算公式[1],其中神经网络的输入是[math]\displaystyle{ x(x_1,...,x_n) }[/math],输出是[math]\displaystyle{ y(y_1,...,y_n) }[/math],并且满足[math]\displaystyle{ y=f(x) }[/math],[math]\displaystyle{ f }[/math]是由神经网络实现的确定性映射。然而,根据公式5,映射中必须包含噪声才能够体现不确定性。
因而,在神经网络中,我们假设神经网络从输入到输出的计算也是不确定性的,即也符合公式5:
[math]\displaystyle{ y=f(x)+\xi, }[/math]
这里,[math]\xi\sim \mathcal{N}(0,\Sigma)[/math]为一高斯噪声,且[math]\Sigma=\mathrm{diag}(\sigma_1,\sigma_2,\cdots,\sigma_n)[/math],这里[math]\sigma_i[/math]为第i个维度的最小平方误差(Mean Square Error,简称MSE误差)。也就是说,我们假设从x到y的神经网络映射实际上满足一个均值为[math]f(x)[/math],协方差为[math]\Sigma[/math]的条件高斯分布,即:
[math]\displaystyle{ Pr(y|x)\sim \mathcal{N}(f(x),\Sigma) }[/math]
由此,套用高维映射一般情况下的结论,我们可以给出神经网络有效信息的一般计算公式:
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{gathered}EI(f)=I(do(x\sim \mathcal{U}([-\frac{L}{2},\frac{L}{2}]^n));y)\approx-\frac{n+n\ln(2\pi)+\sum_{i=1}^n\ln\sigma_i^2}2+n\ln(2L)+\mathbb{E}_{x\sim \mathcal{U}([-\frac{L}{2},\frac{L}{2}]^n)}(\ln|\det(\partial_{x}f(x)))|)\end{gathered} }[/math]
其中[math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal{U}\left(\left[-L/2, L/2\right]^n\right) }[/math]表示范围在[math]\displaystyle{ \left[-L/2 ,L/2\right]^n }[/math]上的[math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math]维均匀分布,[math]\displaystyle{ \det }[/math]表示行列式。维度平均EI为:
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{gathered} \mathcal{J}\equiv \frac{EI(f)}{n}\approx -\frac{\ln(2\pi e)}{2}-\frac{\sum_{i=1}^n\ln\sigma_i}{n}+\ln(2L)+\frac{1}{n}\cdot\mathbb{E}_{x\sim \mathcal{U}([-\frac{L}{2},\frac{L}{2}]^n)}(\ln|\det(\partial_{x}f(x)))|) \end{gathered} }[/math]
如果设微观的动力学可以用神经网络f来拟合,宏观动力学则可以用F来拟合,则因果涌现可以由下式计算:
[math]\displaystyle{
\begin{gathered}
\mathcal{\Delta J}\equiv \frac{EI(F)}{m}-\frac{EI(f)}{n}\approx \frac{\sum_{i=1}^n\ln\sigma_i}{n}-\frac{\sum_{i=1}^m\ln\sigma'_i}{m}+\frac{1}{m}\cdot\mathbb{E}_{X\sim \mathcal{U}([-\frac{L}{2},\frac{L}{2}]^n)}(\ln|\det(\partial_{X}F(X)))|)-\frac{1}{n}\cdot\mathbb{E}_{x\sim \mathcal{U}([-\frac{L}{2},\frac{L}{2}]^m)}(\ln|\det(\partial_{x}f(x)))|)
\end{gathered}
}[/math]
其中,[math]m[/math]为宏观态维度,[math]\sigma'_i[/math]为第i个宏观维度的平均平方误差(MSE),这一误差可以通过反向传播算法计算的宏观态[math]X_i[/math]的梯度计算得出。
注意,上述结论都要求:[math]\displaystyle{ \partial_{x}f(x) }[/math]不为0,而对于所有的[math]\displaystyle{ x }[/math],[math]\displaystyle{ \partial_{x}f(x) }[/math]处处为0时,我们得到: [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{gathered}EI(f)\approx\end{gathered}0 }[/math]。对于更一般的情形,则需要考虑矩阵不满秩的情况,请参考神经网络的有效信息。
连续系统EI的源代码
可逆神经网络下的数值解以及随机迭代系统的解析解都可以给出计算方法。
对于一般的神经网络,它可看做是从输入X到输出Y的一种不确定的函数映射: [math]\displaystyle{ y=f(x)+\xi }[/math]
其中x的维度为input_size,y的维度为output_size,[math]\xi[/math]为一高斯分布,其协方差矩阵为:[math]\Sigma=\mathrm{diag}(\sigma_1,\sigma_2,\cdots,\sigma_n)[/math],这里,[math]\sigma_i[/math]为该神经网络第i个维度的均方误差(MSE)。该矩阵的逆记为sigmas_matrix。映射函数f记为func,则可以用下面的代码计算该神经网络的EI。该算法的基本思想是利用蒙特卡洛方法计算公式6的积分。
- 输入变量:
神经网络的输入维度(input_size)输出维数(output_size)、输出变量视为高斯分布后的协方差矩阵的逆(sigmas_matrix)、映射函数(func)、干预区间大小(L的取值)、以及蒙特卡罗积分的样本数(num_samples)。
- 输出变量:
维度平均EI(d_EI)、EI系数(eff)、EI值(EI)、确定性(term1)、简并性(term2)和[math]\ln L[/math](-np.log(rho))。
def approx_ei(input_size, output_size, sigmas_matrix, func, num_samples, L, easy=True, device=None):
rho=1/(2*L)**input_size #the density of X even distribution
#the first term of EI, the entropy of a gaussian distribution
#sigmas_matrix_np=sigmas_matrix.cpu() if use_cuda else sigmas_matrix
dett=1.0
if easy:
dd = torch.diag(sigmas_matrix)
dett = torch.log(dd).sum()
else:
#dett = np.log(np.linalg.det(sigmas_matrix_np))
dett = torch.log(torch.linalg.det(sigmas_matrix))
term1 = - (output_size + output_size * np.log(2*np.pi) + dett)/2
#sampling x on the space [-L,L]^n, n is the number of samples
xx=L*2*(torch.rand(num_samples, input_size, device=sigmas_matrix.device)-1/2)
dets = 0
logdets = 0
#iterate all samples of x
for i in range(xx.size()[0]):
jac=jacobian(func, xx[i,:]) #use pytorch's jacobian function to obtain jacobian matrix
det=torch.abs(torch.det(jac)) #calculate the determinate of the jacobian matrix
dets += det.item()
if det!=0:
logdets+=torch.log(det).item() #log jacobian
else:
#if det==0 then, it becomes a gaussian integration
logdet = -(output_size+output_size*np.log(2*np.pi)+dett)
logdets+=logdet.item()
int_jacobian = logdets / xx.size()[0] #take average of log jacobian
term2 = -np.log(rho) + int_jacobian # derive the 2nd term
if dets==0:
term2 = - term1
EI = max(term1 + term2, 0)
if torch.is_tensor(EI):
EI = EI.item()
eff = -EI / np.log(rho)
d_EI = EI/output_size
return d_EI, eff, EI, term1, term2, -np.log(rho)
对于随机迭代系统,由于是解析解,相对会简单许多。既可以直接计算,也可以作为上述神经网络计算结果的对照。输入的变量分别为参数矩阵和协方差矩阵。
def EI_calculate_SIS(A,Sigma):
n=A.shape[0]
return math.log(abs(sl.det(A))/(np.sqrt(sl.det(Sigma))*math.pow(2*np.pi*np.e,n/2)))
EI与其它相关主题
EI与整合信息论
有效信息这一指标最早出现在文献Tononi等人(2003)的文章中[2],在这篇文章中,作者们定义了整合信息能力这一指标,并建立了整合信息理论,这一理论后来演化成意识理论的一个重要分支。而整合信息能力这一指标的定义是以有效信息为基础的。
EI与Φ
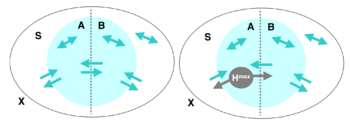
整合信息能力(或者叫整合程度)[math]\displaystyle{ \Phi }[/math],可以被定义为系统的任意一个二划分两部分之间相互影响的有效信息最小值。假如系统是X,S是X的一个子集,它被划分为两个部分,分别是A和B。那么,A、B之间以及它们跟X中其余的部分都存在着相互作用和因果关系。
这时,我们可以度量这些因果关系的强弱。首先,我们来计算从A到B的有效信息。即干预A,使其服从最大熵分布,然后度量A和B之间的互信息:
[math]\displaystyle{ EI(A\rightarrow B) = I(A^{H^{max}}: B) }[/math]
这里[math]\displaystyle{ A^{H^{max}} }[/math]表示A上的最大熵分布,也就是前文中的均匀分布。该式子中没有明确表示,但实际上暗含了一种从A到B的因果机制,即[math]Pr(B|A)[/math]。它在干预中始终保持不变。这样,如果A的不同状态会导致B有很不一样的变化,这个EI值会很高;反之,如果无论A怎么变,B都受到很少的影响,那么EI就会很低。显然,这种度量是有方向的,A对B的EI和B对A的EI可以很不同。我们可以把这两个方向的EI加在一起,得到S在某一个划分下的EI大小。
[math]\displaystyle{ EI(A\leftrightarrow B) = EI(A\rightarrow B) + EI(B\rightarrow A) }[/math]
遍历各种划分,如果存在某一个划分S,使得EI为0,说明这个S可以被看做是两个因果独立的部分,所以整合程度也应该是0。从这种特殊例子中我们可以看出,我们应该关注所有划分中有效信息最小的那个。当然,不同划分会导致A和B的状态空间就不一样,所以应该做一个归一化处理,即除以A和B最大熵值中较小的那一个。于是,我们可以有一个最小信息划分(minimum information bipartition,MIB)。整合程度[math]\displaystyle{ \Phi }[/math]定义如下:
[math]\displaystyle{ \Phi(S) = EI(MIB(S)) }[/math]
这就是整合信息能力与有效信息的关系。
区别
值得注意的是,与马尔科夫链的EI计算不同,这里的EI更多衡量的是系统中两个部分彼此之间的因果联系。而马尔科夫链的EI衡量的是同一个系统在不同两个时刻之间的因果关联强度。
EI与其它因果度量指标
EI是一种度量因果机制中因果变量的因果联系强弱的一种指标。而在EI提出之前,已有多个因果度量指标被提出了。那么,EI和这些因果度量指标之间存在着什么样的联系呢?事实上,正如Comolatti与Hoel在2022年的文章中所指出的,包括EI在内的这些因果度量指标都可以统一表达为两个基本要素的组合[3]。这两个基本要素被称为“因果元语”(Causal Primatives),分别代表了因果关系中的充分性和必要性。
因果元语的定义
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{aligned} \text{充分性:}~~~&suff(e,c) = P(e|c) \\ \text{必要性:}~~~&nec(e,c) = 1 - P(e|C \backslash c) \end{aligned} }[/math]
其中[math]\displaystyle{ c }[/math]和[math]\displaystyle{ e }[/math]分别表示因事件(cause)和果事件(effect),[math]\displaystyle{ C }[/math]表示因事件的全部集合,[math]\displaystyle{ C \backslash c }[/math]则为因事件[math]\displaystyle{ c }[/math]的补集,即[math]\displaystyle{ c }[/math]之外的事件,也可记作[math]\displaystyle{ \lnot c }[/math]。充分性表明当因发生时,果发生的概率,当[math]\displaystyle{ suff = 1 }[/math]时,因发生确定导致果发生;而必要性则衡量当因不发生时,果也不发生的概率;当[math]\displaystyle{ nec = 1 }[/math]时,因不发生则果一定不发生。
有些因果指标中的必要性表现为以下的变型形式,在此也给出定义:
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{aligned} \text{必要性}' \text{:}~~~nec'(e) = 1 - P(e|C) \end{aligned} }[/math]
根据定义,当[math]\displaystyle{ c }[/math]为极小概率事件时,[math]\displaystyle{ nec(e,c) \approx nec'(e) }[/math]。当[math]\displaystyle{ C }[/math]为连续状态空间时,可认为两者等价。
注意:[math]\displaystyle{ nec'(e) }[/math]的定义与文献[3]中定义的[math]\displaystyle{ nec^\dagger(e) = P(e|C) }[/math]不同,两者关系为[math]\displaystyle{ net'(e) = 1 - nec^\dagger(e) }[/math]。
因果元语与确定性和简并性
如前所述,EI可被分解为确定性与简并性两项,这两项分别对应充分性和必要性的因果元语表达:
[math]\displaystyle{ Determinism\quad Coef= \sum_{e \in E, c \in C}{P(e,c)\cdot \left[1 - \frac{\log{\frac{1}{suff(e,c)}}}{\log{N}}\right]} }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ Degeneracy\quad Coef= \sum_{e \in E}{P(e|C)\cdot\left[1 - \frac{\log{\frac{1}{1 - nec'(e)}}}{\log{N}}\right]} }[/math]
可以看到,充分性和确定性之间,以及必要性和简并性之间存在单调映射关系。充分性越高,确定性也越高;必要性越高,简并性则越小。
因果度量指标的因果元语表示
| 因果指标 | 概率定义 | 因果元语定义 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 有效信息EI | [math]\displaystyle{ \log_2{\frac{P(e|c)}{P(e|C)}} }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ \log_2\frac{suff}{1 - nec'} }[/math] | [4] |
| Galton度量 | [math]\displaystyle{ P(c)P(C\backslash c)(P(e|c) - P(e|C\backslash c)) }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ P(c)P(C\backslash c)(suff + nec - 1) }[/math] | [5] |
| Suppes度量 | [math]\displaystyle{ P(e|c) - P(e|C) }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ suff + nec' - 1 }[/math] | [6] |
| Eells度量(等同于Judea Pearl的充要概率PNS) | [math]\displaystyle{ P(e|c) - P(e|C\backslash c) }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ suff + nec - 1 }[/math] | [7][8] |
| Cheng度量(等同于Judea Pearl的充分概率PS) | [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{P(e|c) - P(e|C\backslash c)}{1 - P(e|C\backslash c)} }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{suff + nec - 1}{nec} }[/math] | [7][9] |
| Lewis度量(等同于Judea Pearl的必要概率PN) | [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{P(e|c) - P(e|C\backslash c)}{P(e|c)} }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{suff + nec - 1}{suff} }[/math] | [7][10] |
EI与动力学可逆性
正如示例example中的马尔科夫链所示,当概率转移矩阵呈现为一种排列置换矩阵(Permutation matrix)的时候,EI会更大。
可以证明,排列置换矩阵是唯一一种能同时满足如下两个条件的矩阵:
1、矩阵是可逆的; 2、矩阵满足马尔科夫链的归一化条件,也就是对于任意的[math]i\in[1,N][/math]来说,[math]|P_i|_1=1[/math]
我们将这一性质称为动力学可逆性。因此,从某种程度上说,EI衡量的是马尔科夫链的一种动力学可逆性。
需要注意的是,这里所说的马尔科夫链的动力学可逆性与通常意义下的马尔科夫链的可逆性是不等同的。前者的可逆性体现为马尔科夫概率转移矩阵的可逆性,也就是它针对状态空间中的每一个确定性状态的运算都是可逆的,所以也称其为动力学可逆的。但是,文献中通常意义下的可逆的马尔科夫链并不要求转移矩阵是可逆的,而是要以稳态分布为时间反演对称轴,使得在动力学P作用构成的演化下的正向时间形成的状态分布序列和逆向状态分布序列完全相同。
由于排列置换矩阵过于特殊,我们需要能够衡量一般的马尔科夫概率转移矩阵与排列置换矩阵的靠近程度,以度量其近似动力学可逆性。在文献[11]中,作者们提出了一种用矩阵的类Schatten范数来度量一个马尔科夫概率转移矩阵的近似动力学可逆性的方法,定义为:
[math]\displaystyle{ \Gamma_{\alpha}\equiv \sum_{i=1}^N\sigma_i^{\alpha}=|P|_{\alpha}^{\alpha} }[/math]
这里,[math]|P|_{\alpha}[/math]为矩阵P的Schatten范数,[math]\Gamma_{\alpha}[/math]为近似动力学可逆性指标,[math]\sigma_i[/math]为概率转移矩阵P的奇异值,并且按照从大到小的顺序排列,[math]\alpha\in(0,2)[/math]为一个指定的参数,它起到让[math]\Gamma_{\alpha}[/math]能够更多地反映确定性还是简并性这样一种权重或倾向性。事实上,不难看出,如果让[math]\alpha\rightarrow 0[/math],则[math]\Gamma_{\alpha}[/math]就退化成了矩阵P的秩,即:
[math]\displaystyle{ rank(P)=\sum_{i=1}^N\sigma_i^{0} }[/math]
而矩阵的秩衡量的是矩阵P非退化(也就是可逆)的程度,与Degeneracy有着类似的效果。
而当[math]\alpha\rightarrow 2[/math],则[math]\Gamma_{\alpha}[/math]就退化成了矩阵P的Frobinius范数的平方,即:
[math]\displaystyle{ ||P||_F^2=\sum_{i=1}^N\sigma_i^{2} }[/math] 这一指标衡量的是矩阵P的确定性的程度,这是因为只有当矩阵P中的所有行向量都是独热向量(one-hot)的时候,[math]||P||_F[/math]才会最大,因此它与Determinism有着类似的衡量效果。
所以,当[math]\alpha\in(0,2)[/math]连续变化的时候,[math]\Gamma_{\alpha}[/math]就可以在简并性与确定性二者之间切换了。通常情况下,我们取[math]\alpha=1[/math],这可以让[math]\Gamma_{\alpha}[/math]能够在确定性与简并性之间达到一种平衡。
在文献[11]中,作者们证明了EI与动力学可逆性[math]\Gamma_{\alpha}[/math]之间存在着一种近似的关系:
[math]\displaystyle{ EI\sim \log\Gamma_{\alpha} }[/math]
关于马尔科夫链的近似动力学可逆性的进一步讨论和说明,请参考词条:近似动力学可逆性,以及论文:[11]
EI与JS散度
根据2的表达式,我们知道,EI实际上是一种广义的JS散度,即Jensen-Shannon divergence。
所谓的JS散度是一种度量两个定义在同一个支撑集上的概率分布之间差异的指标。设两个定义在支撑集[math]\mathcal{X}[/math]上的概率分布[math]P[/math]和[math]Q[/math],它们之间的JS散度定义为:
[math]\displaystyle{ JSD(P||Q)\equiv \frac{1}{2}D_{KL}(P||M)+\frac{1}{2}D_{KL}(Q||M) }[/math]
其中,[math]M=\frac{P+Q}{2}=\frac{1}{2}\sum_{x\in\mathcal{X}}\left[P(x)+Q(x)\right][/math]为P和Q的平均分布,[math]D_{KL}[/math]为KL散度。
与KL散度相比,JS散度是一种对称的度量,即[math]JSD(P||Q)=JSD(Q||P)[/math],而KL散度是非对称的。
可以看出,该式与2式的相似之处。不难验证,当P和Q都是2维向量,且构成了一个马尔科夫转移矩阵K的时候,K的EI就是P、Q的JS散度。
-
[math]\displaystyle{ JSD_{\pi}(P_1,P_2,\cdots,P_n)\equiv H(\sum_{i=1}^n\pi_iP_i)-\sum_{i=1}^n\pi_i H(P_i) }[/math]
(GJSD)
其中,[math]P_i,i\in[1,m][/math]为一组概率分布向量,m为它们的维度,而[math]\pi=(\pi_1,\pi_2,\cdots,\pi_n)[/math]为一组权重,并满足:[math]\pi_i\in[0,1],\forall i\in[1,n][/math]和[math]\sum_{i=1}^n\pi_i=1[/math]。
通过与公式tow_terms比较,不难发现,当[math]\pi_i=\frac{1}{n}[/math],则[math]JSD_{\pi}[/math]就退化为EI了。
在文献[13]中,作者们讨论了广义JS散度在分类多样性度量方面的应用。因此,EI也可以理解为是对行向量多样化程度的一种度量。
进一步,如果我们将Shannon熵[math]H(P_i)[/math]看做一个函数,则不难验证,H是一个凹函数,那么公式GJSD实际上是H函数的Jensen差距,即Jensen Gap。关于这一差距的数学性质,包括它的上下界估计,有大量的论文进行讨论[14]。
参考文献
- ↑ Zhang, Jiang; Liu, Kaiwei (2022). "Neural Information Squeezer for Causal Emergence". Entropy. 25 (1): 26.
- ↑ Tononi, G.; Sporns, O. (2003). "Measuring information integration". BMC Neuroscience. 4 (31).
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Comolatti, R., & Hoel, E. (2022). Causal emergence is widespread across measures of causation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2202.01854.
- ↑ Hoel, Erik P.; Albantakis, L.; Tononi, G. (2013). "Quantifying causal emergence shows that macro can beat micro". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 110 (49): 19790–19795.
- ↑ Fitelson, B., & Hitchcock, C. (2011). Probabilistic measures of causal strength (pp. 600-627). na.
- ↑ Suppes, P. (1973). A probabilistic theory of causality. British Journal for the Philosophy of Science, 24(4).
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Judea Pearl; 刘礼; 杨矫云; 廖军; 李廉 (4 2022). 因果论——模型、推理和推断. 机械工业出版社.
- ↑ Eells, E. (1991). Probabilistic causality (Vol. 1). Cambridge University Press.
- ↑ Cheng, P. W., & Novick, L. R. (1991). Causes versus enabling conditions. Cognition, 40(1-2), 83-120.
- ↑ Lewis, D. (1973). Causation. The journal of philosophy, 70(17), 556-567.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 Jiang Zhang; Ruyi Tao; Keng Hou Leong; Mingzhe Yang; Bing Yuan (2024). "Dynamical reversibility and a new theory of causal emergence". arXiv.
- ↑ Jianhua Lin (1991). "Divergence Measures Based on the Shannon Entropy". IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY. 37 (1): 145-151.
- ↑ Erik Englesson; Hossein Azizpour (2021). Generalized Jensen-Shannon Divergence Loss for Learning with Noisy Labels. 35th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2021).
- ↑ Gao, Xiang; Sitharam, Meera; Roitberg, Adrian (2019). "Bounds on the Jensen Gap, and Implications for Mean-Concentrated Distributions" (PDF). The Australian Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications. 16 (2). arXiv:1712.05267.
编者推荐
下面是一些链接能够帮助读者更好的了解因果涌现的相关信息:
因果涌现读书会
文章推荐
- Zhang, J.; Liu, K. Neural Information Squeezer for Causal Emergence. Entropy 2023, 25, 26.
- Yuan, B.; Zhang, J. et al. Emergence and Causality in Complex Systems: A Survey of Causal Emergence and Related Quantitative Studies. Entropy 2024, 26, 108.
路径推荐
- 张江老师根据因果涌现读书会第一季梳理的关于因果涌现的学习路径:https://pattern.swarma.org/article/153
- 张江老师根据因果涌现前五季读书会整理的因果涌现入门路径:https://pattern.swarma.org/article/296
此词条由张江编写,张江、袁冰、刘凯威、杨明哲和王志鹏整理和审校。
本词条内容源自wikipedia及公开资料,遵守 CC3.0协议。